生物型人工肝支持系统种子细胞的来源与应用
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240205
利益冲突声明:本文不存在任何利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:朱雪晶、黄伟健负责文献资料搜集和分析,撰写论文;鄢和新负责拟定写作思路,指导撰写文章并最后定稿。
-
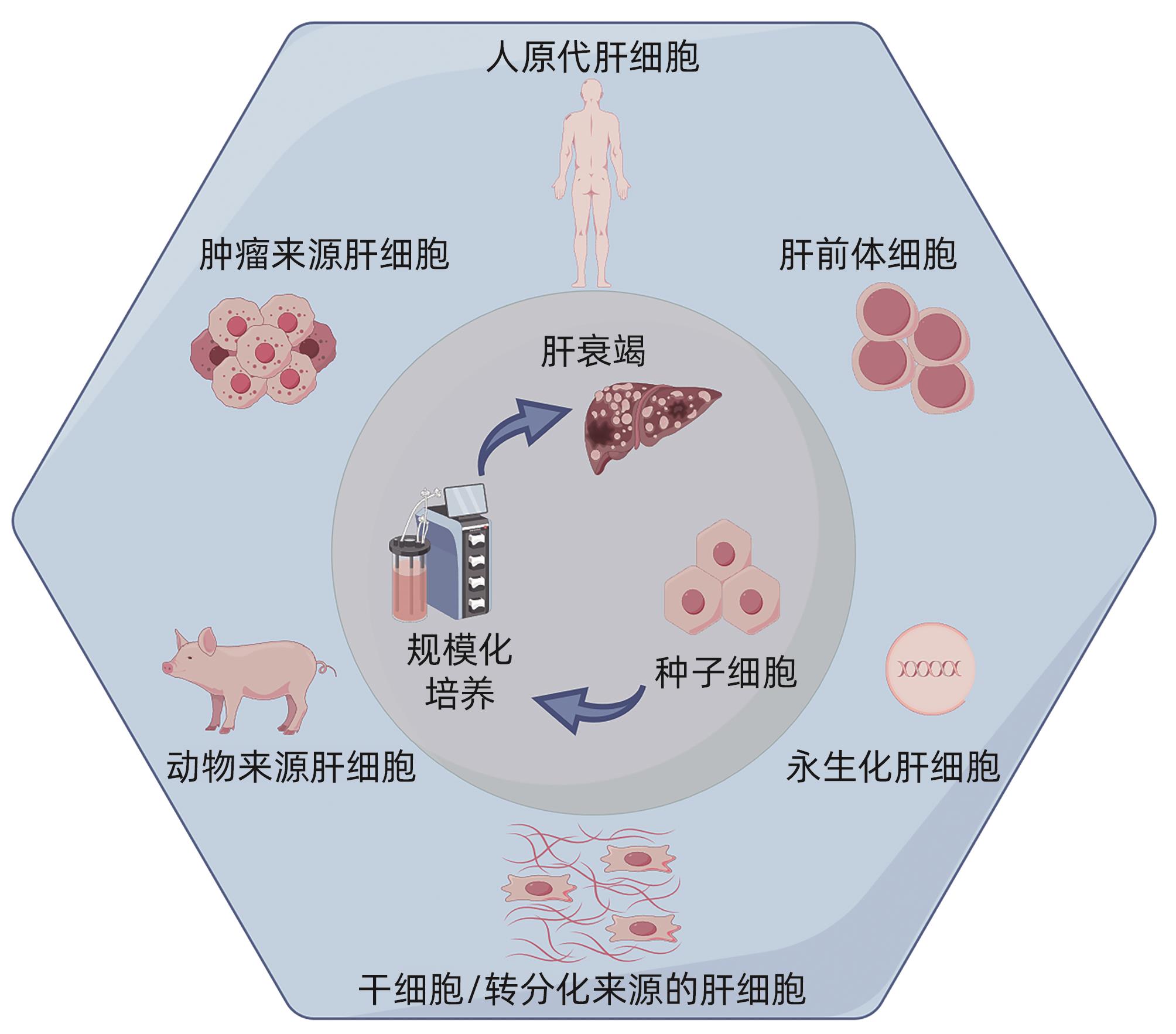
摘要: 迄今为止,重症肝炎、肝衰竭尚无特效治疗方法,病死率高达70%,是国内外危重症中的治疗难点。肝移植术是目前终末期肝病最有效的治疗方法,然而仅有1%~2%的患者能够获得器官移植机会。生物型人工肝支持系统通过体外机械、理化以及生物装置,清除患者体内蓄积的各种有害物质,代偿肝脏代谢功能,补充必需物质,改善内环境,帮助患者恢复肝功能,度过危险期,亦为患者肝移植争取宝贵时间,因此被认为是治疗终末期肝病的重要方法之一。生物型人工肝的核心要素是肝细胞,本综述总结了当前生物型人工肝主要的肝种子细胞来源、3D培养方法以及相应的生物反应器培养系统,期望逐步实现肝细胞体外规模化制备,从而获得足够数量和质量的肝细胞这一临床应用亟待解决的核心问题。Abstract: So far, there are still no specific treatment methods for severe hepatitis and liver failure, resulting in a mortality rate of over 70%, and they are the difficulties in the treatment of critical illness in China and globally. Liver transplantation is currently the most effective treatment method for end-stage liver disease, but only 1% — 2% of patients can receive the opportunity for organ transplantation. The bioartificial liver support system utilizes external mechanical, physical, and biological devices to remove various harmful substances accumulated in the patient’s body, compensate for the metabolic functions of the liver, supplement necessary substances, improve internal environment, promote the recovery of liver function, help patients get through the critical period, and save time for liver transplantation, and therefore, it is considered one of the important methods for the treatment of end-stage liver disease. Since hepatocytes are the core element of bioartificial liver, this article summarizes the sources of liver seed cells, 3D culture methods, and corresponding bioreactor culture systems and hopes to gradually solve the core issue of large-scale in vitro preparation of hepatocytes to obtain hepatocytes with adequate quantity and quality, which urgently needs to be addressed in clinical application.
-
Key words:
- Liver, Artificial /
- Cell Sources /
- Culture Techniques
-
[1] PAN XP, LI LJ. Advances in cell sources of hepatocytes for bioartificial liver[J]. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int, 2012, 11( 6): 594- 605. DOI: 10.1016/s1499-3872(12)60230-6. [2] DUAN ZP. Artificial liver technology and its progress[C]∥ Proceedings of the 10th National Military Infectious Disease Academic Symposium. 2007: 82- 84.段钟平. 人工肝技术及其进展[C]∥ 全军第十次传染病学学术研讨会论文集. 2007: 82- 84. [3] GAO YM, SUN LL, HUI LJ. Advances in research of bioartificial liver[J]. Chin Bull Life Sci, 2016, 28( 8): 915- 920. DOI: 10.13376/j.cbls/2016123.高义萌, 孙露露, 惠利健. 生物人工肝研究进展[J]. 生命科学, 2016, 28( 8): 915- 920. DOI: 10.13376/j.cbls/2016123. [4] TUERXUN K, HE JY, IBRAHIM I, et al. Bioartificial livers: A review of their design and manufacture[J]. Biofabrication, 2022, 14( 3): 032003. DOI: 10.1088/1758-5090/ac6e86. [5] ROZGA J, UMEHARA Y, TROFIMENKO A, et al. A novel plasma filtration therapy for hepatic failure: Preclinical studies[J]. Ther Apher Dial, 2006, 10( 2): 138- 144. DOI: 10.1111/j.1744-9987.2006.00355.x. [6] DETHLOFF T, TOFTENG F, FREDERIKSEN HJ, et al. Effect of Prometheus liver assist system on systemic hemodynamics in patients with cirrhosis: A randomized controlled study[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2008, 14( 13): 2065- 2071. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.14.2065. [7] MATSUMURA KN, GUEVARA GR, HUSTON H, et al. Hybrid bioartificial liver in hepatic failure: Preliminary clinical report[J]. Surgery, 1987, 101( 1): 99- 103. [8] GARCÍA MARTÍNEZ JJ, BENDJELID K. Artificial liver support systems: What is new over the last decade?[J]. Ann Intensive Care, 2018, 8( 1): 109. DOI: 10.1186/s13613-018-0453-z. [9] Liver Failure and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association; Severe Liver Disease and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guideline for diagnosis and treatment of liver failure(2018)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 1): 38- 44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.01.007.中华医学会感染病学分会肝衰竭与人工肝学组, 中华医学会肝病学分会重型肝病与人工肝学组. 肝衰竭诊治指南(2018年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35( 1): 38- 44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.01.007. [10] XIANG C, DU Y, MENG G, et al. Long-term functional maintenance of primary human hepatocytes in vitro[J]. Science, 2019, 364( 6438): 399- 402. DOI: 10.1126/science.aau7307. [11] KATSUDA T, KAWAMATA M, INOUE A, et al. Long-term maintenance of functional primary human hepatocytes using small molecules[J]. FEBS Lett, 2020, 594( 1): 114- 125. DOI: 10.1002/1873-3468.13582. [12] LIU MY, YANG JC, HU WJ, et al. Superior performance of co-cultured mesenchymal stem cells and hepatocytes in poly(lactic acid-glycolic acid) scaffolds for the treatment of acute liver failure[J]. Biomed Mater, 2016, 11( 1): 015008. DOI: 10.1088/1748-6041/11/1/015008. [13] HARPER AM, ROSENDALE JD, MCBRIDE MA, et al. The UNOS OPTN waiting list and donor registry[J]. Clin Transpl, 1998: 73- 90. [14] FACCIOLI LAP, KOCAS-KILICARSLAN ZN, DIAZ-ARAGON R, et al. Human hepatocytes isolated from explanted livers: A powerful tool to understand end-stage liver disease and drug screening[J]. Organogenesis, 2021, 17( 3-4): 117- 125. DOI: 10.1080/15476278.2021.1992216. [15] MIYAJIMA A, TANAKA M, ITOH T. Stem/progenitor cells in liver development, homeostasis, regeneration, and reprogramming[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2014, 14( 5): 561- 574. DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2014.04.010. [16] TARLOW BD, PELZ C, NAUGLER WE, et al. Bipotential adult liver progenitors are derived from chronically injured mature hepatocytes[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2014, 15( 5): 605- 618. DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2014.09.008. [17] FU GB, HUANG WJ, ZENG M, et al. Expansion and differentiation of human hepatocyte-derived liver progenitor-like cells and their use for the study of hepatotropic pathogens[J]. Cell Res, 2019, 29( 1): 8- 22. DOI: 10.1038/s41422-018-0103-x. [18] CHEN Y, TANG D, WU HP, et al. Assessment of long-term functional maintenance of primary human hepatocytes to predict drug-induced hepatoxicity in vitro[J]. Arch Toxicol, 2021, 95( 7): 2431- 2442. DOI: 10.1007/s00204-021-03050-y. [19] ZHANG K, ZHANG LD, LIU WM, et al. In vitro expansion of primary human hepatocytes with efficient liver repopulation capacity[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2018, 23( 6): 806- 819. DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2018.10.018. [20] HU HL, GEHART H, ARTEGIANI B, et al. Long-term expansion of functional mouse and human hepatocytes as 3D organoids[J]. Cell, 2018, 175( 6): 1591- 1606. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.11.013. [21] FANG Q, GAO FY, XU M, et al. Treatment of acute liver failure in mice by immortalized human hepatocytes[J]. Chin Med Biotechnol, 2010, 5( 4): 252- 256. DOI: 10.3969/cmba.j.issn.1673-713X.2010.04.003.房青, 高福云, 徐梅, 等. 永生化人肝细胞治疗小鼠急性肝衰竭的实验研究[J]. 中国医药生物技术, 2010, 5( 4): 252- 256. DOI: 10.3969/cmba.j.issn.1673-713X.2010.04.003. [22] ZHANG YF, SHI J, LIU SY. Establishment and characterization of a telomerase-immortalized sheep trophoblast cell line[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2016, 2016: 5808575. DOI: 10.1155/2016/5808575. [23] LU YZ, LI S, JIANG H, et al. Pre-clinical acute toxicity of an immortalized human hepatocyte cell line HepZJ[J]. Chin J Tissue Engineer Res, 2019, 23( 13): 2067- 2074. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1659.卢扬洲, 黎少, 姜华, 等. 永生化人肝细胞HepZJ的临床前急性毒性评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2019, 23( 13): 2067- 2074. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1659. [24] LI WJ, ZHU XJ, YUAN TJ, et al. An extracorporeal bioartificial liver embedded with 3D-layered human liver progenitor-like cells relieves acute liver failure in pigs[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2020, 12( 551): eaba5146. DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aba5146. [25] YANGER K, ZONG YW, MAGGS LR, et al. Robust cellular reprogramming occurs spontaneously during liver regeneration[J]. Genes Dev, 2013, 27( 7): 719- 724. DOI: 10.1101/gad.207803.112. [26] DUAN YY, CATANA A, MENG Y, et al. Differentiation and enrichment of hepatocyte-like cells from human embryonic stem cells in vitro and in vivo[J]. Stem Cells Dayt Ohio, 2007, 25( 12): 3058- 3068. DOI: 10.1634/stemcells.2007-0291. [27] WANG YF, ZHENG Q, SUN Z, et al. Reversal of liver failure using a bioartificial liver device implanted with clinical-grade human-induced hepatocytes[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2023, 30( 5): 617- 631. DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2023.03.013. [28] TANG W, GUO R, SHEN SJ, et al. Chemical cocktails enable hepatic reprogramming of human urine-derived cells with a single transcription factor[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2019, 40( 5): 620- 629. DOI: 10.1038/s41401-018-0170-z. [29] CHAMULEAU RAFM, DEURHOLT T, HOEKSTRA R. Which are the right cells to be used in a bioartificial liver?[J]. Metab Brain Dis, 2005, 20( 4): 327- 335. DOI: 10.1007/s11011-005-7914-4. [30] COLTMAN NJ, COKE BA, CHATZI K, et al. Application of HepG2/C3A liver spheroids as a model system for genotoxicity studies[J]. Toxicol Lett, 2021, 345: 34- 45. DOI: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2021.04.004. [31] ELLIS AJ, HUGHES RD, WENDON JA, et al. Pilot-controlled trial of the extracorporeal liver assist device in acute liver failure[J]. Hepatology, 1996, 24( 6): 1446- 1451. DOI: 10.1002/hep.510240625. [32] THOMPSON J, JONES N, AL-KHAFAJI A, et al. Extracorporeal cellular therapy(ELAD) in severe alcoholic hepatitis: A multinational, prospective, controlled, randomized trial[J]. Liver Transpl, 2018, 24( 3): 380- 393. DOI: 10.1002/lt.24986. [33] NAGAKI M, NAITO T, OHNISHI H, et al. Effects of plasma from patients with fulminant hepatic failure on function of primary rat hepatocytes in three-dimensional culture[J]. Liver Int, 2005, 25( 5): 1010- 1017. DOI: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2005.01127.x. [34] NIBOURG GAA, CHAMULEAU RAFM, VAN DER HOEVEN TV, et al. Liver progenitor cell line HepaRG differentiated in a bioartificial liver effectively supplies liver support to rats with acute liver failure[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7( 6): e38778. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038778. [35] GLORIOSO JM, MAO SA, RODYSILL B, et al. Pivotal preclinical trial of the spheroid reservoir bioartificial liver[J]. J Hepatol, 2015, 63( 2): 388- 398. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.03.021. [36] CHEN HS, JOO DJ, SHAHEEN M, et al. Randomized trial of spheroid reservoir bioartificial liver in porcine model of posthepatectomy liver failure[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 69( 1): 329- 342. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30184. [37] HE YT, QI YN, ZHANG BQ, et al. Bioartificial liver support systems for acute liver failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the clinical and preclinical literature[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2019, 25( 27): 3634- 3648. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i27.3634. [38] LI Y, WU Q, WANG YJ, et al. Novel spheroid reservoir bioartificial liver improves survival of nonhuman primates in a toxin-induced model of acute liver failure[J]. Theranostics, 2018, 8( 20): 5562- 5574. DOI: 10.7150/thno.26540. [39] MAZARIEGOS GV, KRAMER DJ, LOPEZ RC, et al. Safety observations in phase I clinical evaluation of the excorp medical bioartificial liver support system after the first four patients[J]. ASAIO J, 2001, 47( 5): 471- 475. DOI: 10.1097/00002480-200109000-00015. [40] MULLON C, PITKIN Z. The HepatAssist bioartificial liver support system: Clinical study and pig hepatocyte process[J]. Expert Opin Investig Drugs, 1999, 8( 3): 229- 235. DOI: 10.1517/13543784.8.3.229. [41] DEMETRIOU AA, BROWN RS JR, BUSUTTIL RW, et al. Prospective, randomized, multicenter, controlled trial of a bioartificial liver in treating acute liver failure[J]. Ann Surg, 2004, 239( 5): 660-667; discussion 667-670. DOI: 10.1097/01.sla.0000124298.74199.e5. [42] MARTIN U, WINKLER ME, ID M, et al. Productive infection of primary human endothelial cells by pig endogenous retrovirus(PERV)[J]. Xenotransplantation, 2000, 7( 2): 138- 142. DOI: 10.1034/j.1399-3089.2000.00052.x. [43] FENG L, WANG Y, FU Y, et al. A simple and efficient strategy for cell-based and cell-free-based therapies in acute liver failure: hUCMSCs bioartificial liver[J]. Bioeng Transl Med, 2023, 8( 5): e10552. DOI: 10.1002/btm2.10552. [44] KNAZEK RA, GULLINO PM, KOHLER PO, et al. Cell culture on artificial capillaries: An approach to tissue growth in vitro[J]. Science, 1972, 178( 4056): 65- 67. DOI: 10.1126/science.178.4056.65. [45] CASTILLO AB, JACOBS CR. Mesenchymal stem cell mechanobiology[J]. Curr Osteoporos Rep, 2010, 8( 2): 98- 104. DOI: 10.1007/s11914-010-0015-2. [46] WANG Y, LI H, LI X, et al. Hypoxic preconditioning of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells is an effective strategy for treating acute lung injury[J]. Stem Cells Dev, 2021, 30( 3): 128- 134. DOI: 10.1089/scd.2020.0174. [47] CHEN ST, WANG JL, REN HZ, et al. Hepatic spheroids derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells in bio-artificial liver rescue porcine acute liver failure[J]. Cell Res, 2020, 30( 1): 95- 97. DOI: 10.1038/s41422-019-0261-5. [48] LU ZY, PRIYA RAJAN SA, SONG QQ, et al. 3D scaffold-free microlivers with drug metabolic function generated by lineage-reprogrammed hepatocytes from human fibroblasts[J]. Biomaterials, 2021, 269: 120668. DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.120668. [49] LIU WM, ZHOU X, CHEN CY, et al. Establishment of functional liver spheroids from human hepatocyte-derived liver progenitor-like cells for cell therapy[J]. Front Bioeng Biotechnol, 2021, 9: 738081. DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.738081. [50] LI K, ZHANG GH, ZHANG C, et al. Assessment of in vitro 3D large-scale hepatocyte proliferation culture system and automated and intelligent bioreactor systems[J]. Chin J Tissue Engineer Res, 2022, 26( 19): 3100- 3107.李柯, 张广浩, 张丞, 等. 体外3D规模化扩增肝细胞的培养体系及自动化、智能化生物反应器的评估[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26( 19): 3100- 3107. [51] TEIXEIRA AP, OLIVEIRA R, ALVES PM, et al. Advances in on-line monitoring and control of mammalian cell cultures: Supporting the PAT initiative[J]. Biotechnol Adv, 2009, 27( 6): 726- 732. DOI: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2009.05.003. [52] DEMUTH C, VARONIER J, JOSSEN V, et al. Novel probes for pH and dissolved oxygen measurements in cultivations from millilitre to benchtop scale[J]. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 2016, 100( 9): 3853- 3863. DOI: 10.1007/s00253-016-7412-0. [53] RENNEBERG R, TROTT-KRIEGESKORTE G, LIETZ M, et al. Enzyme sensor-FIA-system for on-line monitoring of glucose, lactate and glutamine in animal cell cultures[J]. J Biotechnol, 1991, 21( 1-2): 173- 185. DOI: 10.1016/0168-1656(91)90269-2. -



 PDF下载 ( 877 KB)
PDF下载 ( 877 KB)

 下载:
下载:


