GPD1基因新发突变p.K327N致高甘油三酯血症性急性胰腺炎反复发作1例报告
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240222
伦理学声明:本例报告已获得患者知情同意。
利益冲突声明:本文不存在任何利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:李孝尧、王大成负责课题设计,患者随访,撰写论文;段剑锋负责数据收集分析,采集血样;陈显成、张北源参与临床诊疗,修改论文;虞文魁负责指导论文撰写并最后定稿。
Recurrent hypertriglyceridemic acute pancreatitis in an adult patient caused by the de novo mutation of p.K327N in the GPD1 gene: A case report
-
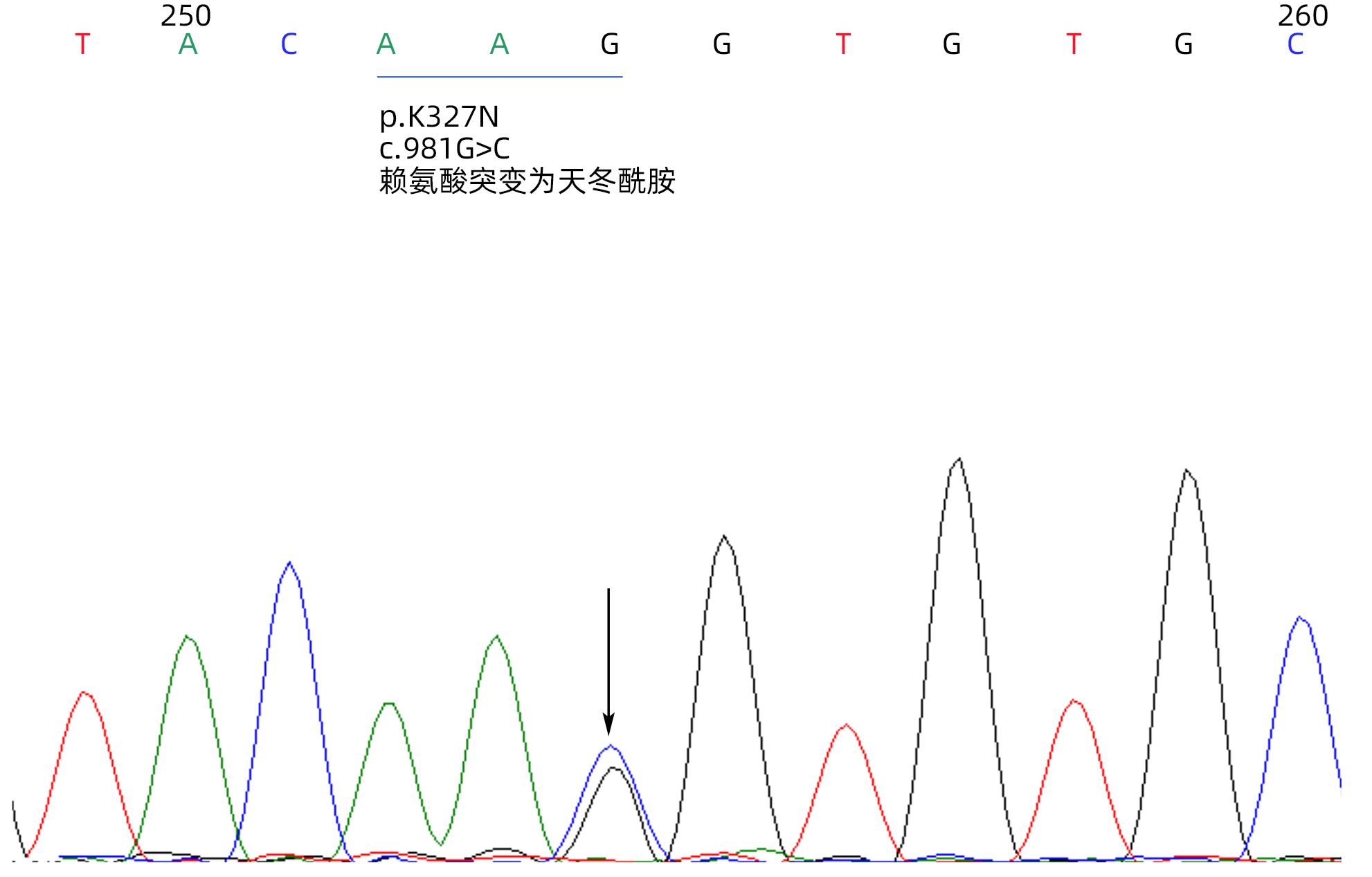
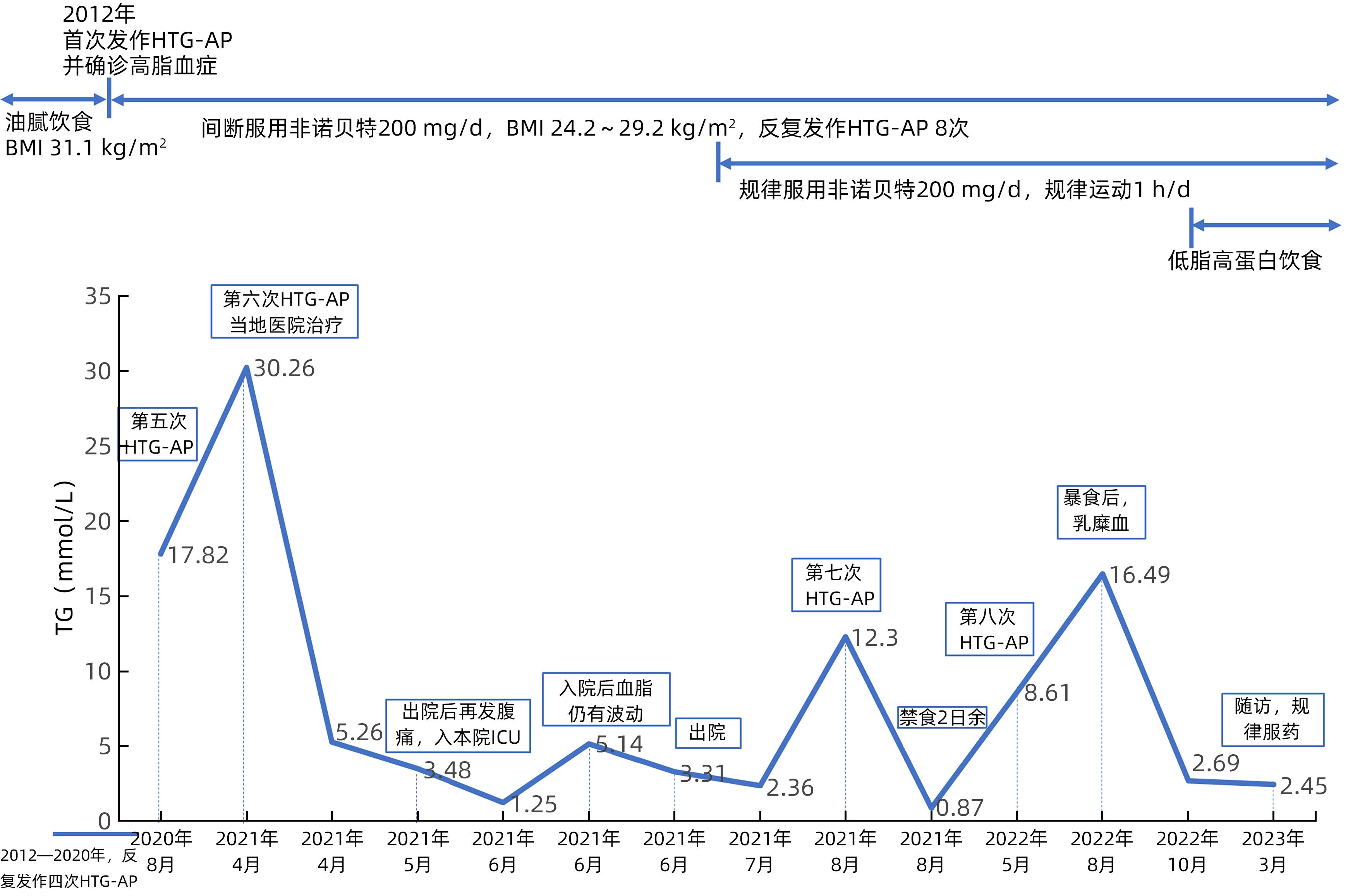
摘要: 高甘油三酯血症为我国急性胰腺炎的第二大病因,可以由原发性因素即基因突变引起,所导致的高甘油三酯血症性急性胰腺炎(HTG-AP)易反复发作,且甘油三酯水平难以有效控制。本文报道了1例罹患8次HTG-AP的中国成年男性患者,发现其携带GPD1新发杂合突变p.K327N,可能导致甘油三酯水平持续较高及HTG-AP反复发作。Abstract: Hypertriglyceridemia (HTG) is the second leading cause of acute pancreatitis in China and can be caused by primary factors, namely gene mutations, which may lead to recurrent hypertriglyceridemic acute pancreatitis (HTG-AP) and difficulties in effective control of triglyceride. This article reports an adult Chinese male patient who experienced eight attacks of HTG-AP and was found to carry a de novo heterozygous mutation, p.K327N, of the GPD1 gene, which may cause the persistent high level of triglyceride and recurrent attacks of HTG-AP.
-
Key words:
- Hypertriglyceridemia /
- Pancreatitis /
- Glycerolphosphate Dehydrogenase /
- Mutation
-
[1] DRON JS, WANG J, MCINTYRE AD, et al. The polygenic nature of mild-to-moderate hypertriglyceridemia[J]. J Clin Lipidol, 2020, 14( 1): 28- 34. DOI: 10.1016/j.jacl.2020.01.003. [2] MEDEROS MA, REBER HA, GIRGIS MD. Acute pancreatitis: A review[J]. JAMA, 2021, 325( 4): 382- 390. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2020.20317. [3] FORTSON MR, FREEDMAN SN, WEBSTER PD 3rd. Clinical assessment of hyperlipidemic pancreatitis[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 1995, 90( 12): 2134- 2139. [4] CARR RA, REJOWSKI BJ, COTE GA, et al. Systematic review of hypertriglyceridemia-induced acute pancreatitis: A more virulent etiology?[J]. Pancreatology, 2016, 16( 4): 469- 476. DOI: 10.1016/j.pan.2016.02.011. [5] ZHENG Y, ZHOU Z, LI H, et al. A multicenter study on etiology of acute pancreatitis in Beijing during 5 years[J]. Pancreas, 2015, 44( 3): 409- 414. DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000273. [6] JIN M, BAI X, CHEN X, et al. A 16-year trend of etiology in acute pancreatitis: The increasing proportion of hypertriglyceridemia-associated acute pancreatitis and its adverse effect on prognosis[J]. J Clin Lipidol, 2019, 13( 6): 947- 953. DOI: 10.1016/j.jacl.2019.09.005. [7] LI XY, KE L, DONG J, et al. Significantly different clinical features between hypertriglyceridemia and biliary acute pancreatitis: A retrospective study of 730 patients from a tertiary center[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2018, 18( 1): 89. DOI: 10.1186/s12876-018-0821-z. [8] WU YQ, ZHAO JC. Predictive value of Ranson score in the classification of moderate to severe hyperlipidemia acute pancreatitis[J]. J Clin Exp Med, 2022, 21( 2): 222- 225. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2022.02.029.吴永强, 赵景成. Ranson评分在高脂血症性急性胰腺炎病情严重程度评估中的应用价值[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志, 2022, 21( 2): 222- 225. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2022.02.029. [9] SU W, GUO F. Triglyceride-controlling during acute phase of hypertriglyceridemia induced pancreatitis[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2023, 22( 1): 89- 93. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20221220-00755.苏伟, 郭丰. 高甘油三酯血症性胰腺炎急性期的血脂控制[J]. 中华消化外科杂志, 2023, 22( 1): 89- 93. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20221220-00755. [10] FAN JY, YAO Y, FENG L, et al. Relationship of serum creatinine, PLT and HCT with the severity and prognosis of hyperlipidemic acute pancreatitis[J]. J Clin Exp Med, 2023, 22( 10): 1049- 1052. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2023.10.011.樊景云, 姚勇, 奉镭, 等. 高甘油三酯血症性急性胰腺炎患者血清肌酐、PLT和HCT水平与病情严重程度和预后的关系[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志, 2023, 22( 10): 1049- 1052. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2023.10.011. [11] LI XY, YANG Q, SHI XL, et al. Compound but non-linked heterozygous p.W14X and p.L279 V LPL gene mutations in a Chinese patient with long-term severe hypertriglyceridemia and recurrent acute pancreatitis[J]. Lipids Health Dis, 2018, 17( 1): 144. DOI: 10.1186/s12944-018-0789-2. [12] BASEL-VANAGAITE L, ZEVIT N, ZAHAV AH, et al. Transient infantile hypertriglyceridemia, fatty liver, and hepatic fibrosis caused by mutated GPD1, encoding glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1[J]. Am J Hum Genet, 2012, 90( 1): 49- 60. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.11.028. [13] OU XJ, JI CN, HAN XQ, et al. Crystal structures of human glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1(GPD1)[J]. J Mol Biol, 2006, 357( 3): 858- 869. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2005.12.074. [14] POLCHAR L, VALLABHANENI P. Case of GPD1 deficiency causing hypertriglyceridaemia and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. BMJ Case Rep, 2022, 15( 4): e246369. DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2021-246369. [15] LI JQ, XIE XB, FENG JY, et al. A novel homozygous mutation in the glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1 gene in a Chinese patient with transient infantile hypertriglyceridemia: A case report[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2018, 18( 1): 96. DOI: 10.1186/s12876-018-0827-6. [16] DIONISI-VICI C, SHTEYER E, NICETA M, et al. Expanding the molecular diversity and phenotypic spectrum of glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1 deficiency[J]. J Inherit Metab Dis, 2016, 39( 5): 689- 695. DOI: 10.1007/s10545-016-9956-7. [17] JOSHI M, EAGAN J, DESAI NK, et al. A compound heterozygous mutation in GPD1 causes hepatomegaly, steatohepatitis, and hypertriglyceridemia[J]. Eur J Hum Genet, 2014, 22( 10): 1229- 1232. DOI: 10.1038/ejhg.2014.8. [18] LI N, CHANG GY, XU YF, et al. Biallelic mutations in GPD1 gene in a Chinese boy mainly presented with obesity, insulin resistance, fatty liver, and short stature[J]. Am J Med Genet A, 2017, 173( 12): 3189- 3194. DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.a.38473. [19] LIN HH, FANG YH, HAN L, et al. Case report: Identification of a novel homozygous mutation in GPD1 gene of a Chinese child with transient infantile hypertriglyceridemia[J]. Front Genet, 2021, 12: 726116. DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2021.726116. [20] MATARAZZO L, RAGNONI V, MALAVENTURA C, et al. Successful fenofibrate therapy for severe and persistent hypertriglyceridemia in a boy with cirrhosis and glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1 deficiency[J]. JIMD Rep, 2020, 54( 1): 25- 31. DOI: 10.1002/jmd2.12125. [21] WANG J, SUN F, XU PF, et al. Transient infantile hypertriglyceridemia with jaundice: A case report[J]. Medicine, 2021, 100( 17): e25697. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000025697. [22] KUMAR P, SHARMA S. Transient infantile hypertriglyceridemia and hepatic steatosis in an infant with GPD1 mutation[J]. Indian J Pediatr, 2021, 88( 5): 495- 496. DOI: 10.1007/s12098-021-03663-2. [23] TESAROVA M, STRANECKY V, KONECNA P, et al. GPD1 deficiency-underdiagnosed cause of liver disease[J]. Indian J Pediatr, 2021, 88( 1): 80- 81. DOI: 10.1007/s12098-020-03385-x. [24] XIE XB, LI MP, WANG JS. Transient infantile hypertriglyceridemia caused by GPD1 deficiency: report of two cases and literature review[J]. Chin J Pediatr, 2020, 58( 11): 923- 927. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112140-20200411-00375.谢新宝, 李梦萍, 王建设. GDP1基因缺陷导致婴儿暂时性高甘油三酯血症二例并文献复习[J]. 中华儿科杂志, 2020, 58( 11): 923- 927. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112140-20200411-00375. [25] MA PF, LI WQ, CHEN L, et al. A case of transient infantile hypertriglyceridemia caused by mutations in the glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1 gene[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2021, 29( 10): 1014- 1016. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20210122-00040.马鹏飞, 李王强, 陈莲, 等. 3-磷酸甘油脱氢酶1基因突变致婴儿期短暂性高甘油三酯血症1例[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2021, 29( 10): 1014- 1016. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20210122-00040. -



 PDF下载 ( 813 KB)
PDF下载 ( 813 KB)

 下载:
下载: