早期血清前S1抗原(PreS1)对干扰素α治疗的HBeAg阳性慢性乙型肝炎儿童HBsAg阴转的预测价值
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.08.010
Value of serum PreS1 in early prediction of HBsAg clearance after IFN-α treatment in children with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B
-
摘要:
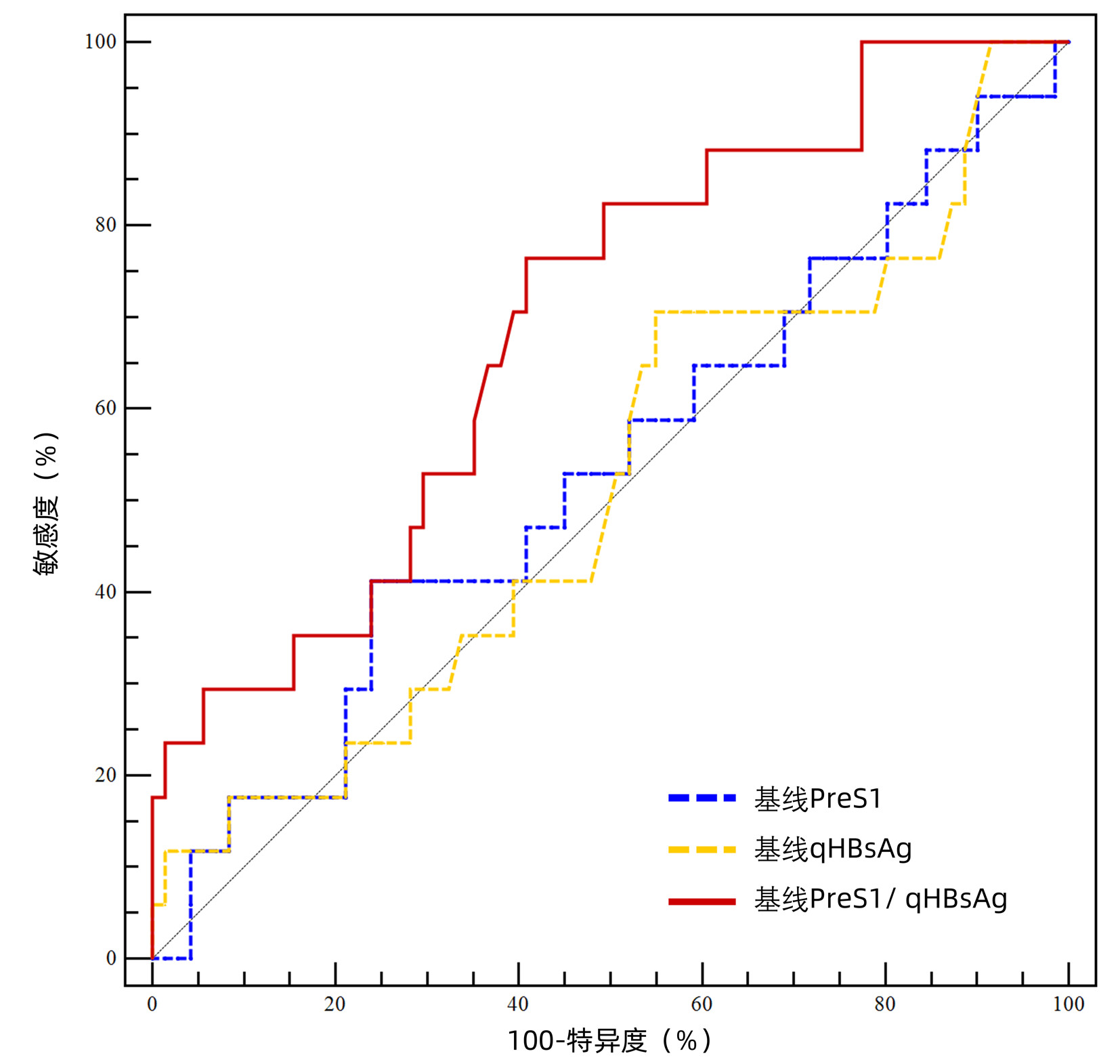
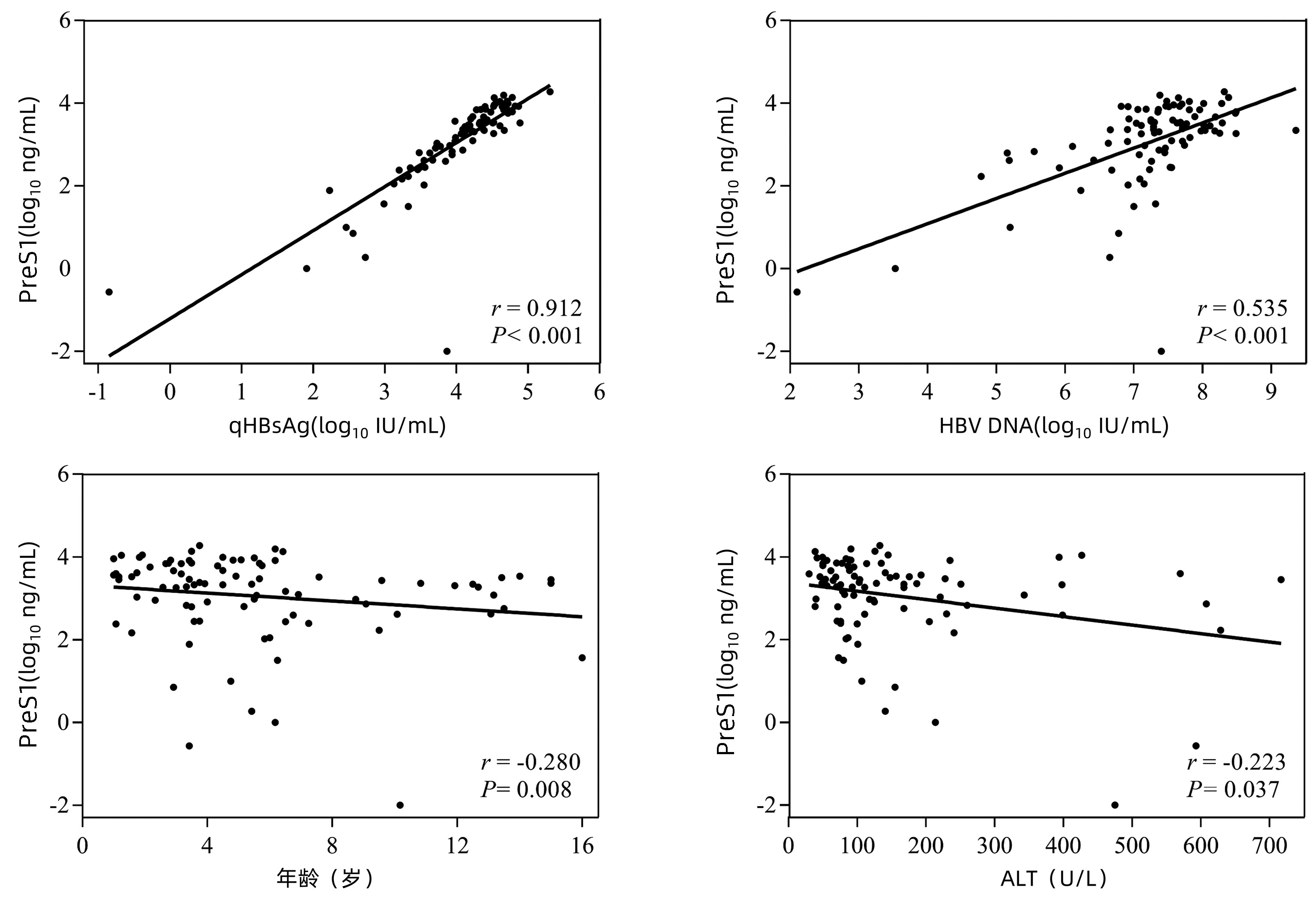
目的 探讨血清前S1抗原(PreS1)水平作为预测干扰素α(IFN-α)治疗48周的HBeAg阳性慢性乙型肝炎(CHB)儿童HBsAg转阴指标的价值。 方法 纳入2016年6月—2020年1月接受IFN-α治疗48周的88例1~16岁HBeAg阳性CHB患儿,每3个月评估患儿的HBsAg定量(qHBsAg)、HBV DNA定量、ALT等,并采用磁微粒化学发光免疫分析法(双抗体夹心法)检测PreS1水平。根据IFN-α治疗48周终点时HBsAg是否转阴分为转阴组(n=17)和未转阴组(n=71)。计量资料的两组间比较采用Mann-Whitney U检验,计数资料的两组间比较采用χ2检验或Fisher精确检验。用Spearman秩相关检验评估PreS1水平和其他生物标志物之间的关系。用受试者工作特征曲线下面积(AUC)评估不同标志物对IFN-α治疗48周终点HBsAg转阴的预测价值。 结果 PreS1水平与血清qHBsAg、HBV DNA水平呈正相关(r值分别为0.912、0.535,P值均<0.05)。基线时,PreS1/qHBsAg比值(AUC=0.694)较PreS1水平(AUC=0.530)和qHBsAg水平(AUC=0.514)具有较好的48周HBsAg转阴预测价值。治疗12周的PreS1水平(AUC=0.867,P<0.001)和PreS1/qHBsAg比值下降量(AUC=0.800,P=0.002)均对48周终点时HBsAg转阴有很好的预测作用。治疗24周的PreS1水平、qHBsAg水平和HBV DNA均可有效预测第48周的HBsAg转阴,AUC分别为0.917、0.949和0.762(P值均<0.001)。 结论 治疗12周时血清PreS1水平和PreS1/qHBsAg比值下降量是预测IFN-α治疗期间CHB患儿HBsAg转阴的候选标志物。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the value of PreS1 level in predicting HBsAg clearance in children with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B (CHB) after 48 weeks of IFN-α treatment. Methods A total of 88 children with HBeAg-positive CHB, aged 1-16 years, who received 48 weeks of IFN-α treatment from June 2016 to January 2020 were enrolled. HBsAg quantification (qHBsAg), HBV DNA quantification, and alanine aminotransferase were measured every three months, and magnetic particle chemiluminescence immunoassay (double-antibody sandwich) was used to measure the level of PreS1. According to whether HBsAg clearance was achieved at the end of IFN-α treatment for 48 weeks, the 88 children were divided into HBsAg clearance group with 17 children and non-HBsAg clearance group with 71 children. The Mann-Whitney U test was used for comparison of quantitative data between the two groups, and the chi-square test or the Fisher's exact test was used for comparison of qualitative data between the two groups. The Spearman rank correlation test was used to evaluate the correlation of PreS1 level with other biomarkers, and the area under the ROC curve (AUC) was used to investigate the value of different markers in predicting HBsAg clearance at the end of 48-week IFN-α treatment. Results PreS1 level was positively correlated with the serum levels of qHBsAg and HBV DNA (r=0.912 and 0.535, both P < 0.05), and baseline PreS1/qHBsAg ratio (AUC=0.694) had a better value than PreS1 level (AUC=0.530) and qHBsAg level (AUC=0.514) in predicting HBsAg clearance at week 48. PreS1 level (AUC=0.867, P < 0.001) and the reduction in PreS1/qHBsAg ratio (AUC=0.800, P=0.002) at week 12 of treatment had a good value in predicting HBsAg clearance at week 48. PreS1 level, qHBsAg level, and HBV DNA at week 24 of treatment could effectively predict HBsAg clearance at week 48, with AUCs of 0.917, 0.949, and 0.762, respectively (all P < 0.001). Conclusion Serum PreS1 level and the reduction in PreS1/qHBsAg ratio at week 12 of treatment can be used as candidate markers for predicting HBsAg clearance in children with CHB during IFN-α treatment. -
Key words:
- PreS1 /
- Biomarkers /
- Hepatitis B, Chronic /
- Child /
- Interferon-alpha
-
表 1 HBeAg阳性CHB患儿的基线特征
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of the pediatric patients with HBeAg-positive CHB
指标 总体(n=88) 转阴组(n=17) 未转阴组(n=71) 统计值 P值 年龄(岁) 4.62(3.13~6.56) 3.42(2.67~3.75) 5.42(3.38~8.16) Z=-2.759 0.006 PreS1(log10 ng/mL) 3.35(2.78~3.76) 3.38(2.83~3.84) 3.34(2.77~3.64) Z=-0.386 0.700 qHBsAg(log10 IU/mL) 4.19(3.73~4.52) 4.19(3.78~4.53) 4.19(3.72~4.51) Z=-0.185 0.849 HBV DNA(log10 IU/mL) 7.37(6.98~7.75) 7.53(6.68~7.81) 7.36 (7.02~7.72) Z=-0.011 0.992 ALT(U/L) 103.50(75.25~178.75) 100.00(71.00~124.00) 111.00(76.00~199.00) Z=-1.020 0.308 性别[例(%)] χ2=0.547 0.459 男 56(63.6) 9(52.9) 47(66.2) 女 32(36.4) 8(47.1) 24(33.8) HBV基因型[例(%)] χ2=1.610 0.447 B 14(15.9) 2(11.8) 12(16.9) C 69(78.4) 13(76.4) 56(78.9) 未检测 5(5.7) 2(11.8) 3(4.2) 炎症活动度[例(%)] 0.081 G1 20(23.5) 7(41.2) 13(19.1) G2 57(67.1) 10(58.8) 47(69.1) G3 8(9.4) 0 8(11.8) 纤维化程度[例(%)] χ2=0.926 0.629 S1 48(56.4) 8(47.0) 40(58.8) S2 27(31.8) 7(41.2) 20(29.4) S3 10(11.8) 2(11.8) 8(11.8) -
[1] BRAKENHOFF SM, de KNEGT RJ, OLIVEIRA J, et al. Levels of antibodies to hepatitis B core antigen are associated with liver inflammation and response to peginterferon in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Infect Dis, 2022, 227(1): 113-122. DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiac210. [2] LIU YH, LI H, YAN XH, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of peginterferon in the treatment of children with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2019, 26(Suppl 1): 69-76. DOI: 10.1111/jvh.13154. [3] FAN HM, LIN LP, JIA SJ, et al. Interferon alpha treatment leads to a high rate of hepatitis B surface antigen seroconversion in Chinese children with chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2019, 26(Suppl 1): 77-84. DOI: 10.1111/jvh.13165. [4] PAN J, WANG HY, YAO TT, et al. Clinical predictors of functional cure in children 1-6 years-old with chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Clin Transl Hepatol, 2022, 10(3): 405-411. DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2021.00142. [5] ZHU SS, DONG Y, XU ZQ, et al. A retrospective study on HBsAg clearance rate after antiviral therapy in children with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B aged 1-7 years[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2016, 24(10): 738-743. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2016.10.005.朱世殊, 董漪, 徐志强, 等. 1~7岁慢性乙型肝炎HBeAg阳性儿童经抗病毒治疗HBsAg清除率的回顾性研究[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2016, 24(10): 738-743. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2016.10.005. [6] WANG LM, ZHAO JF, LIU JY, et al. Long-term benefits of interferon-α therapy in children with HBeAg-positive immune-active chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2021, 28(11): 1554-1562. DOI: 10.1111/jvh.13598. [7] REN Y, BIAN DD, LIANG C, et al. Predictive value of serum sphingolipids combined with HBsAg quantification in HBsAg clearance of chronic hepatitis B patients treated with nucleos(t)ide analog add-on pegylated interferon α[J]. Translat Med J, 2023, 12(1): 15-21. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-3097.2023.01.004.任艳, 卞丹丹, 梁晨, 等. 血清鞘脂联合定量HBsAg对核苷(酸)类似物经治慢性乙型肝炎患者加用聚乙二醇干扰素α后HBsAg阴转的预测价值[J]. 转化医学杂志, 2023, 12(1): 15-21. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-3097.2023.01.004. [8] ZHONG YW, SHI YM, CHU F, et al. Prediction for HBsAg seroconversion in children with chronic hepatitis B[J]. BMC Infect Dis, 2021, 21(1): 1211. DOI: 10.1186/s12879-021-06883-1. [9] WANG WX, JIA R, GAO YY, et al. Quantitative anti-HBc combined with quantitative HBsAg can predict HBsAg clearance in sequential combination therapy with PEG-IFN-α in NA-suppressed chronic hepatitis B patients[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 894410. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.894410. [10] WU WK, YUAN XJ, ZHANG WL, et al. Clinical significance of novel biomarkers to predict the natural course of hepatitis B infection[J]. Front Public Health, 2022, 10: 1037508. DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1037508. [11] RINKER F, BREMER CM, SCHRÖDER K, et al. Quantitation of large, middle and small hepatitis B surface proteins in HBeAg-positive patients treated with peginterferon Alfa-2a[J]. Liver Int, 2020, 40(2): 324-332. DOI: 10.1111/liv.14298. [12] ZHU XJ, GONG QM, YU DM, et al. Early serum hepatitis B virus large surface protein level: A stronger predictor of virological response to peginterferon Alfa-2a than that to entecavir in HBeAg-positive patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Clin Virol, 2013, 57(4): 318-322. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcv.2013.04.003. [13] WANG NY, ZHANG D, ZHAO W, et al. Hepatitis B virus large surface protein in serum as a candidate biomarker for evaluating hepatitis B virus infection[J]. Clin Biochem, 2011, 44(14-15): 1199-1204. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2011.07.002. [14] LIU C, WU WN, SHANG HY, et al. Prediction value of serum HBV large surface protein in different phases of HBV infection and virological response of chronic hepatitis B patients[J]. Clin Chimica Acta, 2018, 481: 12-19. DOI: 10.1016/j.cca.2018.02.015. [15] PFEFFERKORN M, SCHOTT T, BÖHM S, et al. Composition of HBsAg is predictive of HBsAg loss during treatment in patients with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Hepatol, 2021, 74(2): 283-292. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.08.039. [16] PFEFFERKORN M, BÖHM S, SCHOTT T, et al. Quantification of large and middle proteins of hepatitis B virus surface antigen (HBsAg) as a novel tool for the identification of inactive HBV carriers[J]. Gut, 2018, 67(11): 2045-2053. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2017-313811. [17] Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B (version 2019)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(12): 2648-2669. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.007.中华医学会感染病学分会, 中华医学会肝病学分会. 慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2019年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(12): 2648-2669. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.007. [18] SCHEUER PJ. Classification of chronic viral hepatitis: A need for reassessment[J]. J Hepatol, 1991, 13(3): 372-374. DOI: 10.1016/0168-8278(91)90084-0. [19] CUI AX, DOU XG, DING Y. Antiviral therapy for pregnant women and children with chronic HBV infection[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38(11): 2448-2451. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.11.003.崔傲雪, 窦晓光, 丁洋. 慢性HBV感染孕妇和儿童的抗病毒治疗药物选择及疗效评价[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38(11): 2448-2451. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.11.003. [20] CLEMENTE MG, ANTONUCCI R, SOTGIU G, et al. Present and future management of viral hepatitis B and C in children[J]. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol, 2020, 44(6): 801-809. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinre.2020.02.010. [21] YAN H, ZHONG GC, XU GW, et al. Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide is a functional receptor for human hepatitis B and D virus[J]. eLife, 2012, 1: e00049. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.00049. [22] BIAN YJ, ZHANG Z, SUN ZC, et al. Vaccines targeting preS1 domain overcome immune tolerance in hepatitis B virus carrier mice[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 66(4): 1067-1082. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29239. [23] ZHUANG H. Clinical significance of determining the serum levels of large, middle, and small hepatitis B virus surface proteins[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38(3): 528-531. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.03.007.庄辉. 血清HBV大、中、小表面蛋白检测的临床意义[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38(3): 528-531. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.03.007. [24] NISHIDA Y, IMAMURA M, TERAOKA Y, et al. Serum PreS1 and HBsAg ratio reflects liver fibrosis and predicts the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B patients[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2021, 28(9): 1304-1311. DOI: 10.1111/jvh.13557. [25] ZHANG M, LI J, WANG FS. Antiviral therapy and clinical cure for chronic hepatitis B in children: Progress and challenges[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2021, 29(12): 1218-1223. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20210628-00303.张敏, 李静, 王福生. 儿童慢性乙型肝炎抗病毒治疗与临床治愈: 进展与挑战[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2021, 29(12): 1218-1223. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20210628-00303. -



 PDF下载 ( 2264 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2264 KB)

 下载:
下载: