肝硬化患者肌少症的发生机制及诊疗进展
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.09.025
-
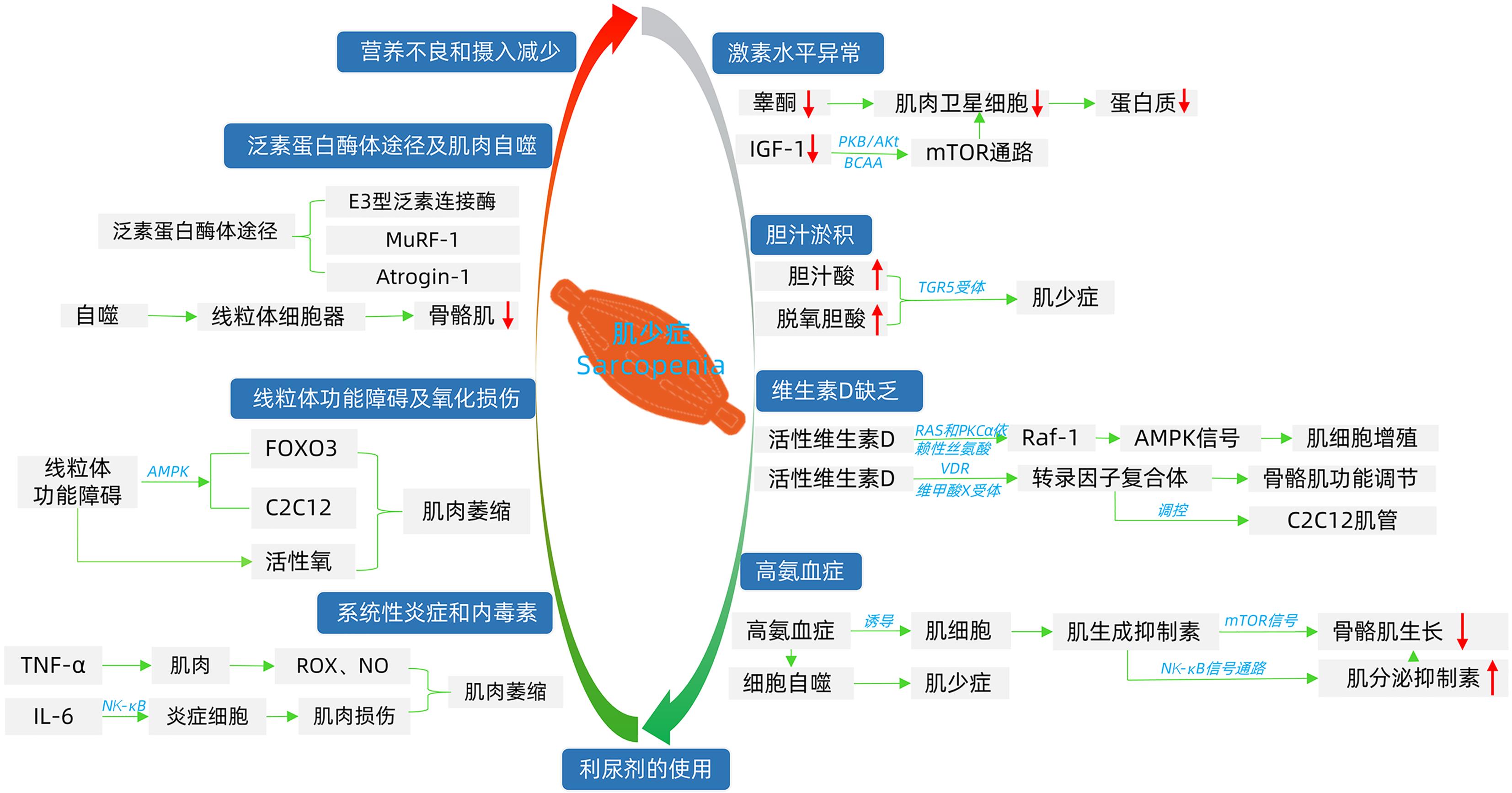
摘要: 肌少症是一种因年龄增长导致肌肉进行性、广泛性下降的疾病。随着研究的深入,发现其与多种慢性病有关,其中在肝硬化患者中因蛋白质摄入减少、分解代谢失衡、自身合成不足等原因,发病率极高,与患者治疗效果、远期生存呈负相关,是肝硬化患者预后不良的独立危险因素。因此,积极干预肌少症对肝硬化患者具有重要的临床价值。本文从定义、诊断、发病机制、临床影响、治疗等方面综述肝硬化与肌少症之间的关系。Abstract: Sarcopenia is a progressive and generalized muscle loss due to aging. With the deepening of research, it is found to be related to many chronic diseases. In patients with liver cirrhosis, owing to reduced protein intake, catabolism imbalance, insufficient self synthesis, and other reasons, the incidence of sarcopenia is extremely high, which negatively affects the treatment outcome and long-term survival, so it is an independent risk factor for poor prognosis in patients with liver cirrhosis. Therefore, it has important clinical value to manage sarcopenia in patients with liver cirrhosis. This review will explain the relationship between liver cirrhosis and sarcopenia from the aspects of definition, diagnosis, pathogenesis, clinical impact, and treatment.
-
Key words:
- Liver Cirrhosis /
- Sarcopenia /
- Diagnosis
-
表 1 肌少症诊断标准的区别
Table 1. Diagnostic difference of sarcopenia
诊断类型 AWGS(2019) EWGSOP2(2019) 肌少症(前期)的诊断 低肌力或低体能 低肌力 肌少症的诊断 低肌量+低肌力或低体能 低肌量+低肌力 严重肌少症的诊断 低肌量+低肌力+低体能 低肌量+低肌力+低体能 表 2 AWGS(2019)和EWGSOP2(2019)肌少症的常用工具诊断标准
Table 2. Common diagnostic criteria of AWGS (2019) and EWGSOP2 (2019) for sarcopenia
检测内容 检测工具 AWGS(2019) EWGSOP2(2019) 男 女 男 女 肌量测定 CT <36.5 cm2/m2[3] <30.2 cm2/m2[3] <52.4 cm2/m2[4] <38.5 cm2/m2[4] BIA <7.0 kg/m2[5] <5.7 kg/m2[5] <7.0 kg/m2[6] <5.5 kg/m2[6] DEXA <7.0 kg/m2[5] <5.4 kg/m2[5] <7.0 kg/m2[6] <5.5 kg/m2[6] 肌力测定 握力器 <28 kg[5] <18 kg[5] <27 kg[6] <16 kg[6] 5次椅立测试 ≥12 s[5] ≥15 s[6] 身体活动功能 步速测试 ≤1 m/s[5] ≤0.8 m/s[6] SPPB ≤9分[5] ≤8分[6] 注:亚洲标准采用6 m步速测定实验,欧洲标准采用4 m步速测定实验。 -
[1] BUNCHORNTAVAKUL C, REDDY KR. Review article: malnutrition/sarcopenia and frailty in patients with cirrhosis[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2020, 51( 1): 64- 77. DOI: 10.1111/apt.15571. [2] PONZIANI FR, GASBARRINI A. Sarcopenia in patients with advanced liver disease[J]. Curr Protein Pept Sci, 2018, 19( 7): 681- 691. DOI: 10.2174/1389203718666170428121647. [3] ANAND A, MOHTA S, AGARWAL S, et al. European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People(EWGSOP2) criteria with population-based skeletal muscle index best predicts mortality in Asians with cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Exp Hepatol, 2022, 12( 1): 52- 60. DOI: 10.1016/j.jceh.2021.03.015. [4] PRADO CM, LIEFFERS JR, MCCARGAR LJ, et al. Prevalence and clinical implications of sarcopenic obesity in patients with solid tumours of the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts: a population-based study[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2008, 9( 7): 629- 635. DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70153-0. [5] CHEN LK, WOO J, ASSANTACHAI P, et al. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 consensus update on sarcopenia diagnosis and treatment[J]. J Am Med Dir Assoc, 2020, 21( 3): 300- 307. DOI: 10.1016/j.jamda.2019.12.012 [6] CRUZ-JENTOFT AJ, BAHAT G, BAUER J, et al. Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis[J]. Age Ageing, 2019, 48( 1): 16- 31. DOI: 10.1093/ageing/afy169. [7] YIN Y, QI XS, YANG YP. Assessment and management of nutritional status in patients with liver cirrhosis[J]. Med J Chin PLA, 2023, 48( 1): 13- 17. DOI: 10.11855/j.issn.0577-7402.2023.01.0013.殷悦, 祁兴顺, 杨永平. 肝硬化患者营养状态的评估及管理[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2023, 48( 1): 13- 17. DOI: 10.11855/j.issn.0577-7402.2023.01.0013. [8] LIN N, KONG M. Pathogenesis of sarcopenia in liver diseases[J]. J Practical Hepatol, 2022, 25( 2): 301- 304. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2022.02.038.蔺宁, 孔明. 肝病肌肉减少症发病机制研究进展[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2022, 25( 2): 301- 304. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2022.02.038. [9] QIU J, THAPALIYA S, RUNKANA A, et al. Hyperammonemia in cirrhosis induces transcriptional regulation of myostatin by an NF-κB-mediated mechanism[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2013, 110( 45): 18162- 18167. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1317049110. [10] DENG W, CHEN Q, GONG ZJ. Research progress on the pathogenesis of sarcopenia in end-stage liver disease[J]. Chin J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 31( 8): 942- 946. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5709.2022.08.020.邓威, 陈倩, 龚作炯. 终末期肝病肌少症发生机制的研究进展[J]. 胃肠病学和肝病学杂志, 2022, 31( 8): 942- 946. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5709.2022.08.020. [11] SINCLAIR M, GROSSMANN M, HOERMANN R, et al. Testosterone therapy increases muscle mass in men with cirrhosis and low testosterone: A randomised controlled trial[J]. J Hepatol, 2016, 65( 5): 906- 913. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.06.007. [12] MOCTEZUMA-VELÁZQUEZ C, LOW G, MOURTZAKIS M, et al. Association between low testosterone levels and sarcopenia in cirrhosis: A cross-sectional study[J]. Ann Hepatol, 2018, 17( 4): 615- 623. DOI: 10.5604/01.3001.0012.0930. [13] SINCLAIR M, GOW PJ, GROSSMANN M, et al. Review article: sarcopenia in cirrhosis——aetiology, implications and potential therapeutic interventions[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2016, 43( 7): 765- 777. DOI: 10.1111/apt.13549. [14] MARZETTI E, CALVANI R, CESARI M, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction and sarcopenia of aging: from signaling pathways to clinical trials[J]. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2013, 45( 10): 2288- 2301. DOI: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.06.024. [15] ROMANELLO V, GUADAGNIN E, GOMES L, et al. Mitochondrial fission and remodelling contributes to muscle atrophy[J]. EMBO J, 2010, 29( 10): 1774- 1785. DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2010.60. [16] EBADI M, BHANJI RA, MAZURAK VC, et al. Sarcopenia in cirrhosis: from pathogenesis to interventions[J]. J Gastroenterol, 2019, 54( 10): 845- 859. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-019-01605-6. [17] TUTTLE C, THANG L, MAIER AB. Markers of inflammation and their association with muscle strength and mass: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Ageing Res Rev, 2020, 64: 101185. DOI: 10.1016/j.arr.2020.101185. [18] PAN L, XIE W, FU X, et al. Inflammation and sarcopenia: A focus on circulating inflammatory cytokines[J]. Exp Gerontol, 2021, 154( 15): 111544. DOI: 10.1016/j.exger.2021.111544 [19] BANO G, TREVISAN C, CARRARO S, et al. Inflammation and sarcopenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Maturitas, 2017, 96: 10- 15. DOI: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2016.11.006. [20] ABRIGO J, GONZALEZ F, AGUIRRE F, et al. Cholic acid and deoxycholic acid induce skeletal muscle atrophy through a mechanism dependent on TGR5 receptor[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2021, 236( 1): 260- 272. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.29839. [21] O’BRIEN A, CHINA L, MASSEY KA, et al. Bile duct-ligated mice exhibit multiple phenotypic similarities to acute decompensation patients despite histological differences[J]. Liver Int, 2016, 36( 6): 837- 846. DOI: 10.1111/liv.12876. [22] BHANJI RA, MOCTEZUMA-VELAZQUEZ C, DUARTE-ROJO A, et al. Myosteatosis and sarcopenia are associated with hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis[J]. Hepatol Int, 2018, 12( 4): 377- 386. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-018-9875-9. [23] MEYER F, BANNERT K, WIESE M, et al. Molecular mechanism contributing to malnutrition and sarcopenia in patients with liver cirrhosis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21( 15): 5357. DOI: 10.3390/ijms21155357 [24] FAN J, KOU X, JIA S, et al. Autophagy as a potential target for sarcopenia[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2016, 231( 7): 1450- 1459. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.25260. [25] LI LX, ZHU YK. Progress in understanding of relationship between sarcopenia and vitamin D[J]. Chin J Clin, 2021, 15( 1): 61- 64. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1674-0785.2021.01.012.李林雪, 朱亦堃. 肌肉减少症与维生素D关系的研究进展[J]. 中华临床医师杂志, 2021, 15( 1): 61- 64. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1674-0785.2021.01.012. [26] BHAT M, KALAM R, QADRI SS, et al. Vitamin D deficiency-induced muscle wasting occurs through the ubiquitin proteasome pathway and is partially corrected by calcium in male rats[J]. Endocrinology, 2013, 154( 11): 4018- 4029. DOI: 10.1210/en.2013-1369. [27] GIRGIS CM, CHA KM, HOUWELING PJ, et al. Vitamin D receptor ablation and vitamin D deficiency result in reduced grip strength, altered muscle fibers, and increased myostatin in mice[J]. Calcif Tissue Int, 2015, 97( 6): 602- 610. DOI: 10.1007/s00223-015-0054-x. [28] HANAI T, SHIRAKI M, MIWA T, et al. Effect of loop diuretics on skeletal muscle depletion in patients with liver cirrhosis[J]. Hepatol Res, 2019, 49( 1): 82- 95. DOI: 10.1111/hepr.13244. [29] MANDAI S, FURUKAWA S, KODAKA M, et al. Loop diuretics affect skeletal myoblast differentiation and exercise-induced muscle hypertrophy[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7( 1): 1- 9. DOI: 10.1038/srep46369. [30] NAKANO I, TSUDA M, KINUGAWA S, et al. Loop diuretic use is associated with skeletal muscle wasting in patients with heart failure[J]. J Cardiol, 2020, 76( 1): 109- 114. DOI: 10.1016/j.jjcc.2020.01.003. [31] ISHIKAWA S, NAITO S, IIMORI S, et al. Loop diuretics are associated with greater risk of sarcopenia in patients with non-dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13( 2): e0192990. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192990. [32] LIU XL, HUANG JM, LIU JH, et al. Clinical value of the third lumbar skeletal muscle index in patients with cirrhosis and sarcopenia[J] Jiangxi Med J, 2021, 56( 12): 2183- 2184, 2190. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2238.2021.12.024.刘晓龙, 黄家明, 刘景鸿, 等. 第三腰椎骨骼肌指数对肝硬化并肌肉减少症患者临床价值[J]. 江西医药, 2021, 56( 12): 2183- 2184, 2190. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2238.2021.12.024. [33] KANG SH, JEONG WK, BAIK SK, et al. Impact of sarcopenia on prognostic value of cirrhosis: going beyond the hepatic venous pressure gradient and MELD score[J]. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle, 2018, 9( 5): 860- 870. DOI: 10.1002/jcsm.12333. [34] KIM G, KANG SH, KIM MY, et al. Prognostic value of sarcopenia in patients with liver cirrhosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12( 10): e0186990. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186990. [35] LI X, FU YM, SUN Y, et al. Research progress in correlation between vitamin D and sarcopenia in the elderly[J]. Med Recapitulate, 2021, 27( 3): 436- 441. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2021.03.004.李想, 傅伊铭, 孙悦, 等. 维生素D与老年肌肉减少症关系的研究进展[J]. 医学综述, 2021, 27( 3): 436- 441. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2021.03.004. [36] UCHITOMI R, OYABU M, KAMEI Y. Vitamin D and sarcopenia: Potential of vitamin D supplementation in sarcopenia prevention and treatment[J]. Nutrients, 2020, 12( 10): 3189. DOI: 10.3390/nu12103189 [37] KUMAR A, DAVULURI G, SILVA R, et al. Ammonia lowering reverses sarcopenia of cirrhosis by restoring skeletal muscle proteostasis[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 65( 6): 2045- 2058. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29107. [38] LIU YY, CHEN DF, YAN QX. Current status of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of sarcopenia in patients with liver cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 1): 191- 195. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.01.033.刘钰懿, 陈东风, 颜綦先. 肝硬化肌少症的发病机制与诊疗现状[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38( 1): 191- 195. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.01.033. [39] MOHTA S, ANAND A, SHARMA S, et al. Randomised clinical trial: effect of adding branched chain amino acids to exercise and standard-of-care on muscle mass in cirrhotic patients with sarcopenia[J]. Hepatol Int, 2022, 16( 3): 680- 690. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-022-10334-7. [40] AAMANN L, DAM G, BORRE M, et al. Resistance training increases muscle strength and muscle size in patients with liver cirrhosis[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 18( 5): 1179- 1187. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.07.058 [41] THOMPSON JL, BUTTERFIELD GE, GYLFADOTTIR UK, et al. Effects of human growth hormone, insulin-like growth factor I, and diet and exercise on body composition of obese postmenopausal women[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 1998, 83( 5): 1477- 1484. DOI: 10.1210/jcem.83.5.4826. [42] Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Medical Association. Clinical guidelines on nutrition in end-stage liver disease[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 6): 1222- 1230. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.06.010.中华医学会肝病学分会, 中华医学会消化病学分会. 终末期肝病临床营养指南[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35( 6): 1222- 1230. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.06.010. [43] HEY P, GOW P, TESTRO AG, et al. Nutraceuticals for the treatment of sarcopenia in chronic liver disease[J]. Clin Nutr ESPEN, 2021, 41: 13- 22. DOI: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2020.11.015. [44] BURTON LA, MCMURDO ME, STRUTHERS AD. Mineralocorticoid antagonism: a novel way to treat sarcopenia and physical impairment in older people?[J]. Clin Endocrinol(Oxf), 2011, 75( 6): 725- 729. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2011.04148.x. [45] NAMBA M, HIRAMATSU A, AIKATA H, et al. Management of refractory ascites attenuates muscle mass reduction and improves survival in patients with decompensated cirrhosis[J]. J Gastroenterol, 2020, 55( 2): 217- 226. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-019-01623-4. -



 PDF下载 ( 1935 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1935 KB)

 下载:
下载:


