Chinese expert consensus on clinical management of hepatopathy-related thrombocytopenia
-
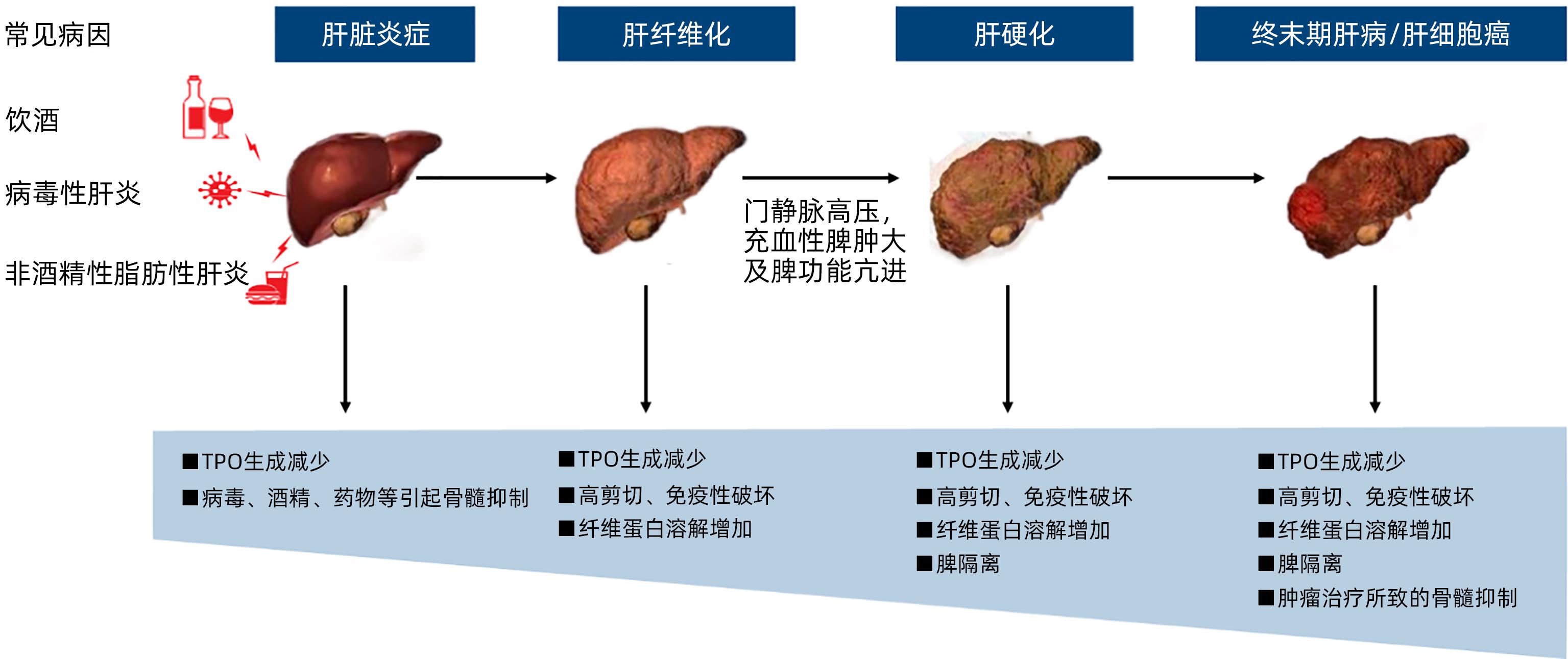
摘要: 肝病相关血小板减少症指肝病或肝病治疗所致的血小板减少症,发生率与肝病病程及严重程度相关。血小板减少症对肝病患者临床结局的直接影响是出血风险增加,间接影响涉及因潜在出血风险导致的治疗延迟或终止。肝病相关血小板减少症的病理生理机制涉及血小板生成减少、分布异常、破坏或消耗增加等。目前,针对不同机制的治疗策略包括促血小板生成药物、手术、免疫抑制药物及输注血小板等,但临床应用有待进一步规范。为提升我国肝病相关血小板减少症在诊断、分型及治疗方案合理选择等方面的临床管理水平,国家感染性疾病临床医学研究中心组织专家,参考领域最新循证医学证据,讨论制定了本共识。Abstract: Hepatopathy-related thrombocytopenia refers to a decrease in platelet count caused by liver disease or its treatment, and the incidence rate of this disease is associated with the course and severity of liver disease. The direct effect of thrombocytopenia on the clinical outcome of patients with liver disease is an increased risk of bleeding, and its indirect effect involves delay or discontinuation of treatment due to the potential risk of bleeding. The pathophysiological mechanisms of hepatopathy-related thrombocytopenia involve reduced platelet production, abnormal platelet distribution, and increased destruction or consumption. Current treatment strategies aiming at different mechanisms include thrombopoietic agents, surgery, immunosuppressants, and platelet transfusion, but their clinical application needs further standardization. In order to improve the clinical management of hepatopathy-related thrombocytopenia in China in terms of diagnosis, typing, and rational selection of treatment regimens, National Clinical Research Center for Infectious Diseases organized experts to discuss and develop these consensus statements with reference to the latest evidence of evidence-based medicine in this field.
-
Key words:
- Liver Diseases /
- Thrombocytopenia /
- Consensus
-
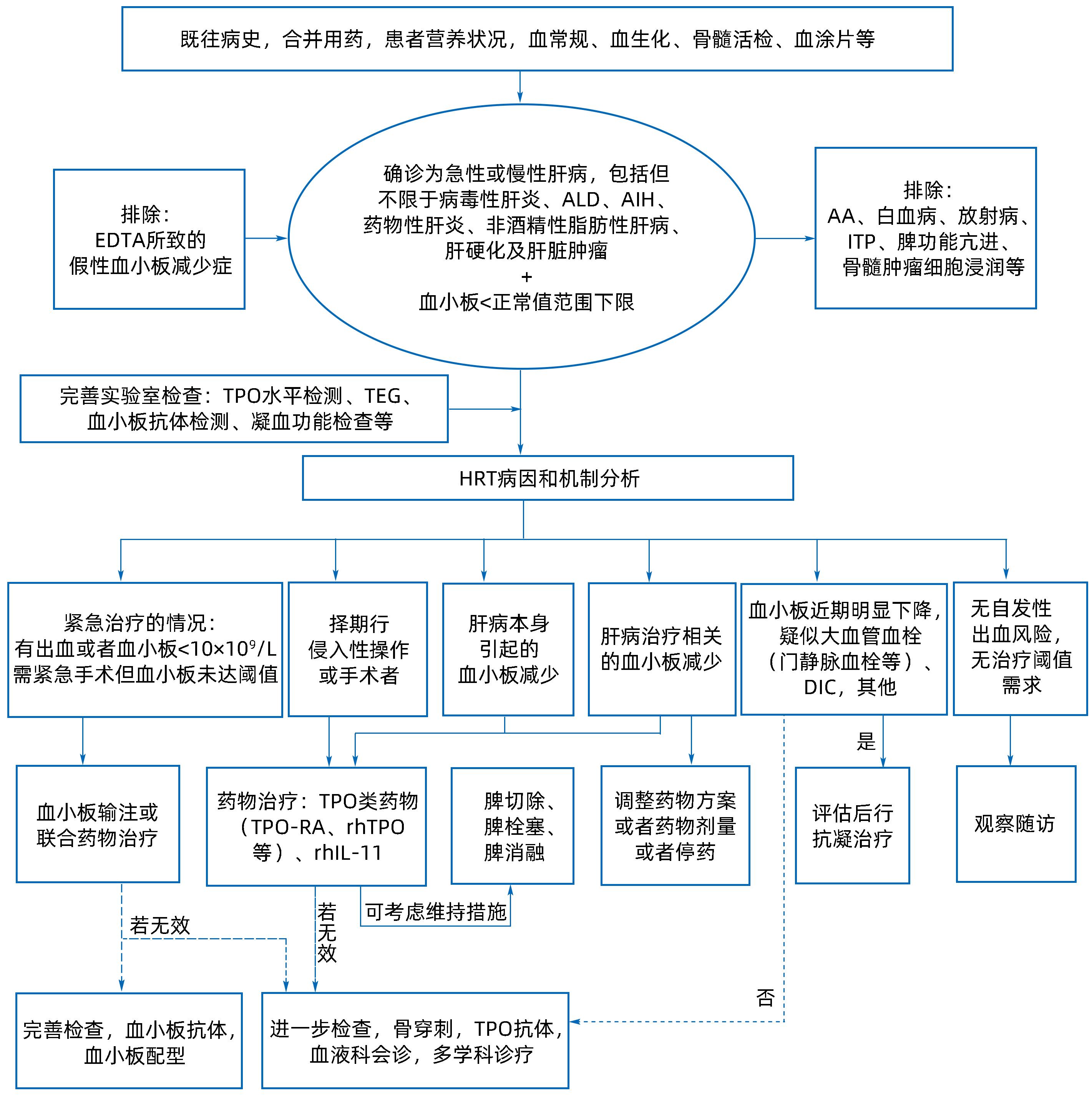
表 1 推荐级别及定义
Table 1. Recommendation grades and definitions
推荐级别 代表意义 1类 基于高级别临床证据,专家意见高度一致 2A类 基于低级别临床证据,专家意见高度一致;或基于高级别证据,专家意见基本一致 2B类 基于低级别临床证据,专家意见基本一致 3类 不论基于何种级别临床证据,专家意见明显分歧 表 2 血小板功能相关检测
Table 2. Platelet function related tests
指标 检测设备 标本 正常值 临床意义 TPO水平检测 离心机、37 ℃恒温水浴箱、酶标仪、移液器、洗板机等 血清样本或血浆(EDTA或柠檬酸钠或肝素抗凝)样本均可 最广泛使用的ELISA法测定的正常值为(64±41)pg/mL(范围27~188 pg/mL) 根据《成人原发免疫性血小板减少症诊断与治疗中国指南(2020年版)》,血清TPO水平测定的意义:(1)鉴别不典型再生障碍性贫血(AA)、低增生骨髓增生异常综合征;(2)用于常规治疗无效患者及脾切除前疾病重新评估 TEG TEG仪(检测方法按仪器说明书进行操作) 动脉血或静脉血均可 参考医院提供的实验室检查正常值范围标准 凝血因子定性分析、纤维蛋白原的定性分析、血小板数量与质量的定性分析、检测血液中是否有肝素的影响、测定纤溶活性、诊断高凝状态、判断血栓风险、鉴别术后渗血和出血、准确判断原因、诊断弥散性血管内凝血(DIC)、监测体外循环和心脏介入治疗等的抗凝情况、监测肝移植手术的出血及凝血状态,以及监测抗血小板药物治疗效果和并发症等 血小板抗体检查 离心机、恒温水浴箱、酶标仪、移液器、振荡器等 血清样本或血浆(EDTA或枸橼酸钠抗凝)样本均可 结果判定:阴性 用途:(1)人类血小板抗原(HPA)抗体检测;(2)HPA型。 根据《成人原发免疫性血小板减少症诊断与治疗中国指南(2020年版)》,血小板糖蛋白特异性自身抗体检查的意义:(1)鉴别非免疫性血小板减少;(2)常规治疗无效患者及脾切除前疾病重新评估;(3)指导静脉注射人免疫球蛋白治疗 注:EDTA,乙二胺四乙酸。 表 3 HRT鉴别诊断
Table 3. Differential diagnosis of HRT
病因 疾病 临床特征 实验室/影像检查 血小板生成减少 AA[16] 全血细胞减少,网织红细胞计数减少,淋巴细胞比例增高;多部位骨髓增生减低或重度减低;小粒空虚,非造血细胞比例增高;巨核细胞明显减少或缺如;红系、粒系细胞均明显减少;骨髓活检全切片增生减低,造血组织减少,非造血细胞增多,网硬蛋白不增加,无异常细胞 血常规、骨髓穿刺、骨髓活检、TPO水平检测、血小板抗体检测、TEG 肿瘤骨髓转移[17] 临床症状为骨痛、脊髓压迫、病理性骨折、出血;血液系统改变多见于血细胞减少,包括一系或二系血细胞减少,最常见的是贫血,其次是TP 骨髓涂片、骨髓活检、TPO水平检测、PET-CT、免疫细胞化学、流式细胞仪、分子测定和荧光原位杂交 营养不良 由于摄入的造血物质不足,长期营养不良很有可能会引起巨幼细胞性贫血等症状 维生素B12、叶酸、TPO水平检测 药物诱导的非免疫性TP 发病前应有确切的应用引起血小板减少的药物(化疗、肿瘤靶向、免疫治疗等药物)停药后血小板减少所致症状与体征逐渐减轻或血小板计数恢复正常;再次使用同样抗肿瘤药物后,TP再次出现 血常规、TPO水平检测 血小板破坏增加 感染[18] 因感染性疾病就诊,出血症状较轻或不明显;实验室检查:外周血象WBC水平升高,Hb轻度降低,血小板轻度或中度减少,严重时可降至10×109/L~20×109/L。纤维蛋白原偏高 血常规、骨髓穿刺、血小板抗体检查、C反应蛋白、降钙素原、病原学诊断、TPO水平检测 免疫性TP[12] 至少连续2次血常规检查示血小板计数减少,外周血涂片镜检血细胞形态无明显异常;脾脏一般不增大;巨核细胞增多或正常,伴成熟障碍,幼稚或颗粒型巨核细胞比例明显增多,产血小板型巨核细胞减少或缺如 血常规、血涂片、骨髓活检、血小板抗体检测、影像学检查、TPO浓度检测、TEG 风湿免疫系统疾病[19]:系统性红斑狼疮、干燥综合征、类风湿关节炎、成人斯蒂尔病等 部分患者并发血小板减少,且疾病不同可伴有不同程度出血现象,包括皮肤、黏膜、消化道出血等症状。骨髓绝大多数无异常,巨核细胞成熟无障碍,产板无减少 血常规、抗核抗体、类风湿因子、TPO水平检测、血小板抗体检测 妊娠期血小板减少[20] 妊娠前及既往无血小板减少病史,多见于妊娠中晚期,期间无其他相关临床表现及出血史;患者虽有血小板下降,但MPV、PDW并无变化 血清铁蛋白、叶酸、维生素B12水平、TEG 血小板分布异常 脾功能亢进 存在脾肿大和全血细胞减少,骨髓巨核细胞功能未受损,形态无异常改变 血常规、B超、MRI等辅助检查、TPO水平检测 血小板消耗增加 药源性血小板减少症(DITP) 用药(抗生素、肝素等)后出现血小板减少,停药后血小板计数恢复;重新用药后血小板再次减少 血常规、抗核抗体、HIT抗体检测、TEG、TPO水平检测 溶血性贫血[21]、阵发性睡眠血红蛋白尿 慢性溶血多表现贫血、黄疸和脾肿大三大特征,可并发胆石症和肝功能损害。急性溶血发病急骤,短期大量溶血引起寒战、发热、头痛、呕吐、四肢腰背疼痛及腹痛,继之出现血红蛋白尿,严重者可发生急性肾衰竭、周围循环衰竭或休克,其后出现黄疸、面色苍白和其他严重贫血的症状和体征 血常规、骨髓涂片、抗人球蛋白试验、蔗糖溶血试验、流式细胞术检测、酸化血清溶血试验等进行溶血筛查 弥漫性血管内凝血[22] 有多部位的出血倾向,皮肤瘀斑、紫癜、咯血、消化道出血等症状 凝血酶原时间、部分活化凝血酶原时间、凝血酶时间、纤维蛋白原、D-二聚体、纤维蛋白降解产物、TPO水平检测、血小板抗体检测 其他 EDTA相关假性TP[23] 患者并无血小板减少,减少的表象是因为血小板与抗凝剂在体外反应而聚集于抗凝管中;通过新鲜样本或检查外周血涂片重复血小板计数检查 血常规、荧光染色法(P-LT-O法)复检 表 4 TP分级标准
Table 4. Criteria for grading thrombocytopenia
级别 血小板计数(×109/L) 1级 ≥75~<100 2级 ≥50~<75 3级 ≥25~<50 4级 <25 表 5 HRT患者诊疗相关操作血小板计数参考阈值推荐
Table 5. Recommendation of reference threshold for platelet count in diagnosis and treatment related procedures of patients with HRT
诊疗类型 血小板计数参考阈值 操作或手术 胸穿、腹穿;内镜检查;中心静脉置管[25] ≥20×109/L 拔牙[26] ≥40×109/L 腰椎穿刺[25];内镜下活检、食管胃底静脉曲张镜下治疗、大息肉切除,内镜下治疗出血,内镜下逆行胰胆管造影括约肌切开术,或内镜下超声细针穿刺[25];经皮肝穿[27];TACE[28];消融[29];HAIC[30];TIPS[31];PTCD;非神经手术[25];人工肝血液净化治疗[32] ≥50×109/L 神经或血管手术[26] ≥100×109/L 系统治疗 免疫治疗(PD-1/PD-L1)[33] ≥50×109/L 靶向治疗(酪氨酸激酶抑制剂)[34] ≥60×109/L 化疗[35] ≥75×109/L 其他 钇-90(90Y)微球选择性内放射治疗[36] ≥80×109/L 注:PTCD,经皮肝内胆道引流术;TIPS,经颈静脉肝内门体分流术。 表 6 中国(NMPA)获批上市的促血小板生成类药物[50-51]
Table 6. Thrombopoietic agents approved for market in China (NMPA)
项目 rhIL-11 rhTPO 罗普司亭 艾曲泊帕 阿伐曲泊帕 芦曲泊帕 海曲泊帕 TPO受体结合 NA 胞外 胞外 跨膜,胞外 跨膜 跨膜 跨膜 给药途径 注射 注射 注射 口服 口服 口服 口服 半衰期 (6.9±1.7) h (40.2±9.4) h 1~34 d(中位3.5 d) 21~32 h 约为19 h 约为27 h 11.9~40.1 h 饮食影响 NA NA NA 是 是 否 是 与阳离子相互作用 无 无 无 ++ 无 无 ++ 肝功能不全者需降低剂量 否 否 否 是 否 否 是 需增加肝功能监测 否 否 否 是 否 否 是 可用于肾衰竭 需减量 是 是 可能可以 可能可以 可能可以 无数据 国内获批适应证 CIT CIT、ITP二线 ITP二线 ITP二线 择期行诊断性操作或者手术的慢性HRT的成年患者 计划接受手术(含诊断性操作)的慢性肝病伴TP的成年患者 ITP二线、SAA二线 注:CIT,肿瘤化疗相关血小板减少症。 表 7 促血小板生成类药物用于HRT用法用量推荐
Table 7. Recommended usage and dosage of thrombopoietic agents for HRT
促血小板生成药物 临床研究数据 备注 本共识推荐用法 研究类型 患者人群及病例数 用法用量 阿伐曲泊帕[37] Ⅲ期 择期行侵入性操作的慢性HRT(血小板<50×109/L)患者(n=277) 血小板<40×109/L,口服阿伐曲泊帕60 mg/d,连续5 d; 血小板40~<50×109/L口服阿伐曲泊帕40 mg/d,连续5 d 血小板<40×109/L,口服阿伐曲泊帕60 mg/d,连续5 d; 血小板40~<50×109/L口服阿伐曲泊帕40 mg/d,连续5 d 芦曲泊帕[41] Ⅲ期 计划接受手术(含诊断性操作)的慢性肝病伴TP(血小板<50×109/L)的成年患者(n=96) 口服芦曲泊帕3 mg/d,连续7 d 口服芦曲泊帕3 mg/d,连续7 d 艾曲泊帕[44] Ⅲ期 择期行侵入性操作的慢性HRT(血小板<50×109/L)患者(n=143) 口服艾曲泊帕75 mg/d,连续14 d Ⅲ期研究因发生6例门静脉血栓导致研究提前终止 因国外血栓风险而暂停Ⅲ期研究,所以待积累国内临床用药经验后再补充 罗普司亭[46] 单中心、单臂、开放标签 择期手术的HCV感染继发血小板减少(血小板<50×109/L)患者(n=35) 注射罗普司亭2 μg/kg,1次/周,最长给药1个月,目标血小板为70×109/L 2 μg/kg皮下注射,1次/周,1~2周 停药标准:连续两次血小板≥70×109/L rhTPO[47-48] 多中心、真实世界研究 乙型肝炎肝硬化合并TP(血小板<30×109/L)(单药组,n=29) rhTPO 15 000U皮下注射,1次/d,治疗中位时间4周 15 000U皮下注射,1次/d,7 d 停药标准:当血小板计数升高至≥50×109/L且较基线升高≥10×109/L 单中心、单臂、回顾性分析 择期行侵入性操作肝病合并TP(血小板<50×109/L)患者(n=100) rhTPO 15 000U皮下注射,1次/d,平均用药12 d rhIL-11[49] 单中心、非随机对照研究 肝硬化脾功能亢进所致TP(血小板<75×109/L)患者(n=42) 皮下注射rhIL-11 3 mg/次,1次/d,平均治疗时间(6.82±3.51)d 说明书提到水钠潴留副作用 皮下注射,3 mg/次,1次/d,连续7~14 d 表 8 糖皮质激素用法用量参考
Table 8. Usage and dosage of glucocorticoid for reference
激素用量(mg/d) 减量方法 60 血小板≥30×109/L后减量 30~40 持续1周 20 持续1周 10 持续1周 5 维持 注:依据病情酌情调整。 英文缩写 中文全称 英文缩写 中文全称 AA 再生障碍性贫血 PICC 经外周静脉穿刺中心静脉置管 AIH 自身免疫性肝炎 PLT 血小板 ALD 酒精性肝病 P-LT-O法 荧光染色法 APTT 活化部分凝血酶原时间 PROVEE 国际静脉血栓栓塞医学预防登记处 CIT 肿瘤化疗相关性血小板减少症 PSE 部分脾动脉栓塞 CTCAE 不良事件术语标准 PT 凝血酶原时间 D-D D-二聚体 PTA 凝血酶原活动度 DIC 弥散性血管内凝血 PTCD 经皮肝内胆道引流术 DITP 药源性血小板减少症 PTR 血小板输注无效 DOAC 口服抗凝剂 PVT 门静脉血栓 EDTA 乙二胺四乙酸 RFA 射频消融 FIB 纤维蛋白原 rhIL-11 重组人白介素11 HAIC 肝动脉灌注化疗 rhTPO 重组人血小板生成素 Hb 血红蛋白 SAA 重型再生障碍性贫血 HBV 乙型肝炎病毒 SIRT 选择性体内放射疗法 HCC 肝细胞癌 TACE 经肝动脉化疗栓塞术 HIT 肝素诱导的血小板减少症 TEG 血栓弹力图 HPA 血小板抗原 TIPS 经颈静脉肝内门体分流术 HRT 肝病相关血小板减少症 TP 血小板减少症 ITP 原发免疫性血小板减少症 TPO 血小板生成素 MDT 多学科会诊 TPO-RA 血小板生成素受体激动剂 MPV 平均血小板体积 TT 凝血酶时间 MRI 核磁共振成像 VKAs 维生素K拮抗剂 OS 总生存期 vWF 血管性血友病因子 PDW 血小板分布宽度 WBC 白细胞 PET-CT 正电子发射断层显像 90Y 钇-90 -
[1] GANGIREDDY VGR, KANNEGANTI PC, SRIDHAR S, et al. Management of thrombocytopenia in advanced liver disease[J]. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2014, 28( 10): 558- 564. DOI: 10.1155/2014/532191. [2] HUANG CH, CHANG JJ, WU YY, et al. Different impacts of common risk factors associated with thrombocytopenia in patients with hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infection[J]. Biomed J, 2022, 45( 5): 788- 797. DOI: 10.1016/j.bj.2021.09.001. [3] LI QJ, HE MK, CHEN HW, et al. Hepatic arterial infusion of oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin versus transarterial chemoembolization for large hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomized phase III trial[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2022, 40( 2): 150- 160. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.21.00608. [4] KUDO M, UESHIMA K, YOKOSUKA O, et al. Sorafenib plus low-dose cisplatin and fluorouracil hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy versus sorafenib alone in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma(SILIUS): A randomised, open label, phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 3( 6): 424- 432. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(18)30078-5. [5] PECK-RADOSAVLJEVIC M. Thrombocytopenia in chronic liver disease[J]. Liver Int, 2017, 37( 6): 778- 793. DOI: 10.1111/liv.13317. [6] GALLO P, TERRACCIANI F, DI PASQUALE G, et al. Thrombocytopenia in chronic liver disease: Physiopathology and new therapeutic strategies before invasive procedures[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2022, 28( 30): 4061- 4074. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i30.4061. [7] ADINOLFI LE, GIORDANO MG, ANDREANA A, et al. Hepatic fibrosis plays a central role in the pathogenesis of thrombocytopenia in patients with chronic viral hepatitis[J]. Br J Haematol, 2001, 113( 3): 590- 595. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.2001.02824.x. [8] PEREIRA J, ACCATINO L, ALFARO J, et al. Platelet autoantibodies in patients with chronic liver disease[J]. Am J Hematol, 1995, 50( 3): 173- 178. DOI: 10.1002/ajh.2830500305. [9] XIAO H, WANG L. Mechanisms of throm bocytopenia in liver cirrhosis[J]. J Pract Hepatol, 2019, 22( 4): 462- 465. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2019.04.003.肖函, 王利. 肝硬化血小板减少的病理生理发生机制[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2019, 22( 4): 462- 465. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2019.04.003. [10] MITCHELL O, FELDMAN DM, DIAKOW M, et al. The pathophysiology of thrombocytopenia in chronic liver disease[J]. Hepat Med, 2016, 8: 39- 50. DOI: 10.2147/HMER.S74612. [11] KANEKO J, SUGAWARA Y, MATSUI Y, et al. Normal splenic volume in adults by computed tomography[J]. Hepato-gastroenterology, 2002, 49( 48): 1726- 1727. [12] Thrombosis and Hemostasis Group, Society of Hematology, Chinese Medical Association. Chinese guideline on the diagnosis and management of adult primary immune thrombocytopenia(version 2020)[J]. Chin J Hematol, 2020, 41( 8): 617- 623. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-2727.2020.08.001中华医学会血液学分会血栓与止血学组, 成人原发免疫性血小板减少症诊断与治疗中国指南(2020年版)[J]. 中华血液学杂志, 2020, 41( 8): 617- 623. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-2727.2020.08.001 [13] Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of autoimmune hepatitis(2021)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 1): 42- 49. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112138-20211112-00796.中华医学会肝病学分会. 自身免疫性肝炎诊断和治疗指南(2021)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38( 1): 42- 49. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112138-20211112-00796. [14] General Office of National Health Commission. Standard for diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer(2022 edition)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 2): 288- 303. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.02.009.国家卫生健康委办公厅. 原发性肝癌诊疗指南(2022年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38( 2): 288- 303. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.02.009. [15] AL-SAMKARI H, SOFF GA. Clinical challenges and promising therapies for chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia[J]. Expert Rev Hematol, 2021, 14( 5): 437- 448. DOI: 10.1080/17474086.2021.1924053. [16] Red Cell Diseases(Anemia) Group, Society of Hematology, Chinese Medical Association. Diagnosis and treatment of aplastic anemia China guide(2022 edition)[J]. Chin J Hematol, 2022( 11): 881- 888.中华医学会血液学分会红细胞疾病(贫血)学组, 再生障碍性贫血诊断与治疗中国指南(2022年版)[J]. 中华血液学杂志, 2022( 11): 881- 888. [17] POCKETT RD, CASTELLANO D, MCEWAN P, et al. The hospital burden of disease associated with bone metastases and skeletal-related events in patients with breast cancer, lung cancer, or prostate cancer in Spain[J]. Eur J Cancer Care, 2010, 19( 6): 755- 760. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2354.2009.01135.x. [18] FRANCHINI M, VENERI D, LIPPI G. Thrombocytopenia and infections[J]. Expert Rev Hematol, 2017, 10( 1): 99- 106. DOI: 10.1080/17474086.2017.1271319. [19] KLEIN A, MOLAD Y. Hematological manifestations among patients with rheumatic diseases[J]. Acta Haematol, 2021, 144( 4): 403- 412. DOI: 10.1159/000511759. [20] LI LP, YING H. Etiology and differential diagnosis of thrombocytopenia in pregnancy[J]. Chin J Pract Gynecol Obstet, 2022, 38( 12): 1166- 1170.李莉平, 应豪. 妊娠期血小板减少的原因与鉴别诊断[J]. 中国实用妇科与产科杂志, 2022, 38( 12): 1166- 1170. [21] HE YY. Application value of systematic analysis of hemolytic etiology in diagnosis and differentiation of hereditary hemolytic anemia[J]. Mod Med J China, 2018, 20( 4): 55- 57.何永艳. 溶血病因系统分析在遗传性溶血性贫血诊断和鉴别中的应用价值[J]. 中国现代医药杂志, 2018, 20( 4): 55- 57. [22] IKEZOE T. Advances in the diagnosis and treatment of disseminated intravascular coagulation in haematological malignancies[J]. Int J Hematol, 2021, 113( 1): 34- 44. DOI: 10.1007/s12185-020-02992-w. [23] SALAMA A. Autoimmune thrombocytopenia complicated by EDTA-and/or citrate-dependent pseudothrombocytopenia[J]. Transfus Med Hemother, 2015, 42( 5): 345- 348. DOI: 10.1159/000437220. [24] LI Q, CHEN L, YU XH. Differentiation of bone marrow cell morphology of thrombocytopenia in chronic liver disease and primary immune thrombocytopenia[J]. Chin J Pract Med, 2022, 49( 8): 10- 12. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115689-20220122-00349.李清, 陈雷, 余晓红. 慢性肝病血小板减少症与原发免疫性血小板减少症的骨髓细胞形态的鉴别[J]. 中国实用医刊, 2022, 49( 8): 10- 12. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115689-20220122-00349. [25] BIOLATO M, VITALE F, GALASSO T, et al. Minimum platelet count threshold before invasive procedures in cirrhosis: Evolution of the guidelines[J]. World J Gastrointest Surg, 2023, 15( 2): 127- 141. DOI: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i2.127. [26] ALVARO D, CAPORASO N, GIANNINI EG, et al. Procedure-related bleeding risk in patients with cirrhosis and severe thrombocytopenia[J]. Eur J Clin Invest, 2021, 51( 6): e13508. DOI: 10.1111/eci.13508. [27] Writing Group of The Xiangya Expert Consensus on Liver Needle Biopsy. Writing group of the xiangya expert consensus on liver needle biopsy[J]. Chin J Gen Surg, 2021, 30( 1): 1- 8. DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.2021.01.001.肝脏穿刺活检湘雅专家共识编写组. 肝脏穿刺活检湘雅专家共识[J]. 中国普通外科杂志, 2021, 30( 1): 1- 8. DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.2021.01.001. [28] Clinical Guidelines Committee of Chinese Interventionalists College. Chinese clinical practice guidelines for transarterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Chin J Intern Med, 2021, 60( 7): 599- 614. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20210425-00991.中国医师协会介入医师分会临床诊疗指南专委会. 中国肝细胞癌经动脉化疗栓塞(TACE)治疗临床实践指南(2021年版)[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2021, 60( 7): 599- 614. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20210425-00991. [29] WANG GZ, HE XH, WANG Y, et al. Clinical practice guideline for image-guided multimode tumour ablation therapy in hepatic malignant tumours[J]. Curr Oncol, 2019, 26( 5): e658-e664. DOI: 10.3747/co.26.5423. [30] Chinese Society of Liver Cancer, China Anti-Cancer Association. Chinese expert consensus on hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma(2021 edition)[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2021, 20( 7): 754- 759. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20210618-00288.中国抗癌协会肝癌专业委员会. 肝动脉灌注化疗治疗肝细胞癌中国专家共识(2021版)[J]. 中华消化外科杂志, 2021, 20( 7): 754- 759. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20210618-00288. [31] TRIPATHI D, STANLEY AJ, HAYES PC, et al. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent-shunt in the management of portal hypertension[J]. Gut, 2020, 69( 7): 1173- 1192. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-320221. [32] Liver Failure and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association; Severe Liver Disease and Artificial Liver Group, et al. Guideline for diagnosis and treatment of liver failure(2018)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 1): 38- 44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.01.007.中华医学会感染病学分会肝衰竭与人工肝学组, 中华医学会肝病学分会重型肝病与人工肝学组. 肝衰竭诊治指南(2018年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35( 1): 38- 44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.01.007. [33] Chinese Chapter of The International Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Association; Group of Liver Surgery, Surgical Society of Chinese Medical Association; Expert Committee on Liver Cancer, Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology. Chinese multidisciplinary expert consensus on combined immunotherapy based on immune checkpoint inhibitors for hepatocellular carcinoma(2021 version)[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2021, 29( 7): 636- 647. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20210604-00261.国际肝胆胰协会中国分会, 中华医学会外科学分会肝脏外科学组, 中国临床肿瘤学会(CSCO)肝癌专家委员会. 基于免疫节点抑制剂的肝细胞癌免疫联合治疗多学科中国专家共识(2021版)[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2021, 29( 7): 636- 647. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20210604-00261. [34] Liver Cancer Committee of Chinese Medical Doctor Association. China expert consensus on clinical application of molecular targeted drugs for hepatocellular carcinoma(2020 edition)[J]. Natl Med J China, 2021, 101( 28): 2185- 2194. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20210329-00760.中国医师协会肝癌专业委员会. 肝细胞癌分子靶向药物临床应用中国专家共识(2020版)[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2021, 101( 28): 2185- 2194. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20210329-00760. [35] Cuidelines Working Committee of Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology. Chinese society of clinical oncology(CSCO). Guidelines of Chinese society of clinical oncology(CSCO) cancer therapy induced thrombocytopenia[M]. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House, 2022.中国临床肿瘤学会指南工作委员会组织. 中国临床肿瘤学会(CSCO)肿瘤治疗所致血小板减少症诊疗指南-2022[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2022. [36] Nuclear Medicine Committee, Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology; Beijing Nuclear Medicine Quality Control and Improvement Center. Chinese expert consensus on selective internal radiation therapy with yttrium-90 for primary and metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2021, 29( 7): 648- 658. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20210302-00103.中国临床肿瘤学会核医学专家委员会, 北京市核医学质量控制和改进中心. 钇-90( 90Y)微球选择性内放射治疗原发性和转移性肝癌的中国专家共识[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2021, 29( 7): 648- 658. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20210302-00103. [37] TERRAULT N, CHEN YC, IZUMI N, et al. Avatrombopag before procedures reduces need for platelet transfusion in patients with chronic liver disease and thrombocytopenia[J]. Gastroenterology, 2018, 155( 3): 705- 718. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.05.025. [38] HUANG A, CHEN JF, WU JZ, et al. Effectiveness and safety of avatrombopag in liver cancer patients with severe thrombocytopenia: Real-world data and challenges[J]. J Oncol, 2022, 2022: 9138195. DOI: 10.1155/2022/9138195. [39] LI RX, YANG H, SONG YH, et al. Avatrombopag combined with intensive immune inhibition in the treatment of severe hepatitis-associated aplastic anemia: Report of two cases[J]. Chin J Pract Intern Med, 2021, 41( 12): 1086- 1088. DOI: 10.19538/j.nk2021120120.李瑞鑫, 杨慧, 宋玉华, 等. 阿伐曲泊帕联合强化免疫抑制治疗重型肝炎相关性再生障碍性贫血2例报告[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2021, 41( 12): 1086- 1088. DOI: 10.19538/j.nk2021120120. [40] LI RX, LIU ZY, ZHOU JT, et al. Avatrombopag in treatment of lenvatinib-related severe aplastic anemia: Report of one case and review of literature[J]. J Leuk Lymphoma, 2021, 30( 10): 618- 620. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115356-20210409-00078.李瑞鑫, 刘正媛, 周炯涛, 等. 阿伐曲泊帕治疗仑伐替尼相关重型再生障碍性贫血一例并文献复习[J]. 白血病·淋巴瘤, 2021, 30( 10): 618- 620. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115356-20210409-00078. [41] HIDAKA H, KUROSAKI M, TANAKA H, et al. Lusutrombopag reduces need for platelet transfusion in patients with thrombocytopenia undergoing invasive procedures[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 17( 6): 1192- 1200. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.11.047. [42] DING ZB, WU H, ZENG YY, et al. Lusutrombopag for thrombocytopenia in Chinese patients with chronic liver disease undergoing invasive procedures[J]. Hepatol Int, 2023, 17( 1): 180- 189. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-022-10421-9. [43] KATSUBE T, WAJIMA T, FUKUHARA T, et al. Effects of food and calcium carbonate on the pharmacokinetics of lusutrombopag, a novel thrombopoietin receptor agonist[J]. Clin Ther, 2019, 41( 9): 1747- 1754.e 2. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2019.06.004. [44] AFDHAL NH, GIANNINI EG, TAYYAB G, et al. Eltrombopag before procedures in patients with cirrhosis and thrombocytopenia[J]. N Engl J Med, 2012, 367( 8): 716- 724. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1110709. [45] HERMANN E, FERDJALLAH A. Eltrombopag-induced metabolic acidosis and hepatic encephalopathy in pediatric ITP[J]. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol, 2022, 44( 2): e453-e455. DOI: 10.1097/MPH.0000000000002300. [46] MOUSSA MM, MOWAFY N. Preoperative use of romiplostim in thrombocytopenic patients with chronic hepatitis C and liver cirrhosis[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2013, 28( 2): 335- 341. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2012.07246.x. [47] FENG R, LIU Y, ZHU XL, et al. Recombinant human thrombopoietin increases platelet count in severe thrombocytopenic patients with hepatitis B-related cirrhosis: Multicentre real-world observational study[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2022, 29( 5): 306- 316. DOI: 10.1111/jvh.13655. [48] DING JN, FENG TT, SUN W, et al. Recombinant human thrombopoietin treatment in patients with chronic liver disease-related thrombocytopenia undergoing invasive procedures: A retrospective study[J]. World J Gastrointest Surg, 2022, 14( 11): 1260- 1271. DOI: 10.4240/wjgs.v14.i11.1260. [49] LIU BW, XIANG HL, LIANG J, et al. Comparison of efficacy of recombinant human interleukin-11 and recombinant human thrombopoietin in treating thrombocytopenia with hypersplenism in cirrhotic patients[J]. World Chin J Dig, 2016, 24( 34): 4608- 4614. DOI: 10.11569/wcjd.v24.i34.4608.刘保文, 向慧玲, 梁静, 等. 重组人白介素-11及重组人血小板生成素在治疗肝硬化脾功能亢进所致血小板减少的疗效对比[J]. 世界华人消化杂志, 2016, 24( 34): 4608- 4614. DOI: 10.11569/wcjd.v24.i34.4608. [50] KUTER DJ. Treatment of chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia in patients with non-hematologic malignancies[J]. Haematologica, 2022, 107( 6): 1243- 1263. DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2021.279512. [51] Anti-Lymphoma Alliance in CSCO, Anti-Leukemia Alliance in CSCO, ASMC Group in CSCO, et al. China expert consensus on clinical application of recombinant human interleukin-11 in prevention and treatment of thrombocytopenia(2021 edition)[J]. Chin Clin Oncol, 2020, 25( 12): 1129- 1137. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0460.2020.12.014.中国临床肿瘤学会抗淋巴瘤联盟, 中国临床肿瘤学会抗白血病联盟, 中国临床肿瘤学会抗肿瘤药物安全管理专家委员会, 等. 重组人白介素-11防治血小板减少症临床应用中国专家共识(2021年版)[J]. 临床肿瘤学杂志, 2020, 25( 12): 1129- 1137. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0460.2020.12.014. [52] LIU L, LIU Y, GAO FY, et al. Clinical features of chronic liver disease with autoimmune blood diseases and the clinical effect of glucocorticoid[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37( 8): 1878- 1882. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.08.025.刘龙, 刘遥, 高方媛, 等. 慢性肝病合并自身免疫性血液系统疾病的临床特征及应用糖皮质激素治疗效果分析[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2021, 37( 8): 1878- 1882. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.08.025. [53] WU YY, LI HY, ZHANG TS, et al. Splanchnic vein thrombosis in liver cirrhosis after splenectomy or splenic artery embolization: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Adv Ther, 2021, 38( 4): 1904- 1930. DOI: 10.1007/s12325-021-01652-7. [54] ZHAO P, LI T, XIE JL, et al. Value of early anticoagulant intervention in cirrhotic patients with portal hypertension after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent shunt combined with PSE[J]. J Pract Hepatol, 2020, 23( 1): 82- 85. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2020.01.023.赵平, 黎涛, 谢吉良, 等. 早期抗凝干预用于经颈静脉肝内门体静脉支架分流术联合PSE治疗肝硬化患者价值探讨[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2020, 23( 1): 82- 85. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2020.01.023. [55] FENG K, MA K, LIU Q, et al. Randomized clinical trial of splenic radiofrequency ablation versus splenectomy for severe hypersplenism[J]. Br J Surg, 2011, 98( 3): 354- 361. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.7367. [56] OGATA T, OKUDA K, SATO T, et al. Long-term outcome of splenectomy in advanced cirrhotic patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and thrombocytopenia[J]. Kurume Med J, 2013, 60( 2): 37- 45. DOI: 10.2739/kurumemedj.ms62010. [57] SHI XB, FENG JK, WANG JH, et al. Does splenectomy significantly improve the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma patients with hypersplenism? A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2021, 9( 8): 641. DOI: 10.21037/atm-20-6748. [58] CHU HB, HAN W, WANG L, et al. Long-term efficacy of subtotal splenectomy due to portal hypertension in cirrhotic patients[J]. BMC Surg, 2015, 15: 89. DOI: 10.1186/s12893-015-0077-2. [59] LIU X, QI XS, LI HY, et al. Prevalence of portal or splenic vein thrombosis in cirrhotic patients after splenectomy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies[J]. Int J Clin Exp Med, 2016, 9( 4): 7534- 7547. [60] TRIPODI A, PRIMIGNANI M, CHANTARANGKUL V, et al. Global hemostasis tests in patients with cirrhosis before and after prophylactic platelet transfusion[J]. Liver Int, 2013, 33( 3): 362- 367. DOI: 10.1111/liv.12038. [61] WANG SY, ZHOU WH, LI XY, et al. Analysis of platelet transfusion in liver disease patient[J]. J Clin Transfus Lab Med, 2017, 19( 4): 328- 331. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2587.2017.04.005.王淑英, 周文辉, 李新颖, 等. 肝病患者血小板输注情况调查分析[J]. 临床输血与检验, 2017, 19( 4): 328- 331. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2587.2017.04.005. [62] FURUICHI Y, TAKEUCHI H, YOSHIMASU Y, et al. Thrombopoietin receptor agonist is more effective than platelet transfusion for chronic liver disease with thrombocytopenia, shown by propensity score matching[J]. Hepatol Res, 2020, 50( 9): 1062- 1070. DOI: 10.1111/hepr.13530. [63] WEN LL, YU ZL, LIANG HL, et al. The main recommendation and enlightenment of application guidelines for platelet transfusion from British Society for Haematology[J]. Chin J Blood Transfus, 2018, 31( 4): 440- 444. DOI: 10.13303/j.cjbt.issn.1004-549x.2018.04.032.温丽玲, 余卓丽, 梁惠兰, 等. 英国血小板输注应用指南主要推荐及其启示[J]. 中国输血杂志, 2018, 31( 4): 440- 444. DOI: 10.13303/j.cjbt.issn.1004-549x.2018.04.032. [64] ZHU H, WANG SY, ZHU JH, et al. Efficacy and safety of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization combined with ginsenosides in hepatocellular carcinoma treatment[J]. Phytomedicine, 2021, 91: 153700. DOI: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153700. [65] NORONHA FERREIRA C, MARINHO RT, CORTEZ-PINTO H, et al. Incidence, predictive factors and clinical significance of development of portal vein thrombosis in cirrhosis: A prospective study[J]. Liver Int, 2019, 39( 8): 1459- 1467. DOI: 10.1111/liv.14121. [66] QI XS, DE STEFANO V, LI HY, et al. Anticoagulation for the treatment of portal vein thrombosis in liver cirrhosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies[J]. Eur J Intern Med, 2015, 26( 1): 23- 29. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejim.2014.12.002. [67] LOFFREDO L, PASTORI D, FARCOMENI A, et al. Effects of anticoagulants in patients with cirrhosis and portal vein thrombosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2017, 153( 2): 480- 487.e 1. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.04.042. [68] ZHOU T, SUN X, ZHOU T, et al. Efficacy and safety of nadroparin calcium-warfarin sequential anticoagulation in portal vein thrombosis in cirrhotic patients: A randomized controlled trial[J]. Clin Transl Gastroenterol, 2020, 11( 9): e00228. DOI: 10.14309/ctg.0000000000000228. [69] Hepatobiliary Disease Study Group, Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Medical Association. Consensus for management of portal vein thrombosis in liver cirrhosis(2020,Shanghai)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36( 12): 2667- 2674. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.12.007.中华医学会消化病学分会肝胆疾病学组. 肝硬化门静脉血栓管理专家共识(2020年, 上海)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2020, 36( 12): 2667- 2674. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.12.007. [70] DECOUSUS H, TAPSON VF, BERGMANN JF, et al. Factors at admission associated with bleeding risk in medical patients: Findings from the IMPROVE investigators[J]. Chest, 2011, 139( 1): 69- 79. DOI: 10.1378/chest.09-3081. [71] KHANAL N, BOCIEK RG, CHEN BJ, et al. Venous thromboembolism in patients with hematologic malignancy and thrombocytopenia[J]. Am J Hematol, 2016, 91( 11): E468-E472. DOI: 10.1002/ajh.24526. [72] FALANGA A, LEADER A, AMBAGLIO C, et al. EHA guidelines on management of antithrombotic treatments in thrombocytopenic patients with cancer[J]. HemaSphere, 2022, 6( 8): e750. DOI: 10.1097/HS9.0000000000000750. -



 PDF下载 ( 1405 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1405 KB)

 下载:
下载: