MELD 3.0、MELD和MELD-Na评分对慢加急性肝衰竭患者短期预后的评估价值
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.11.018
Value of MELD 3.0, MELD, and MELD-Na scores in assessing the short-term prognosis of patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure: A comparative study
-
摘要:
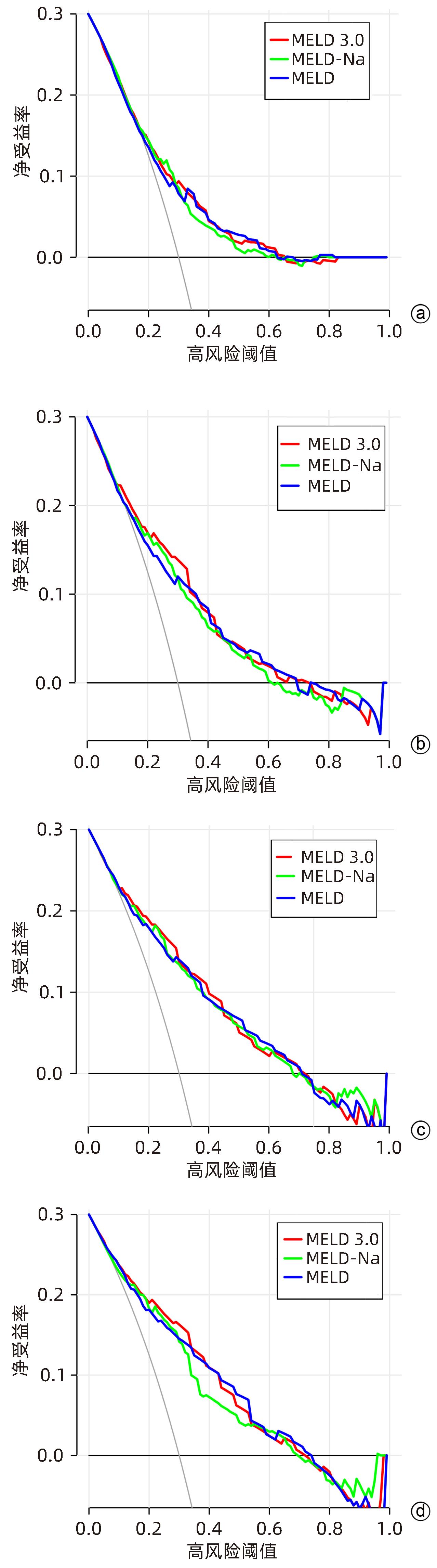
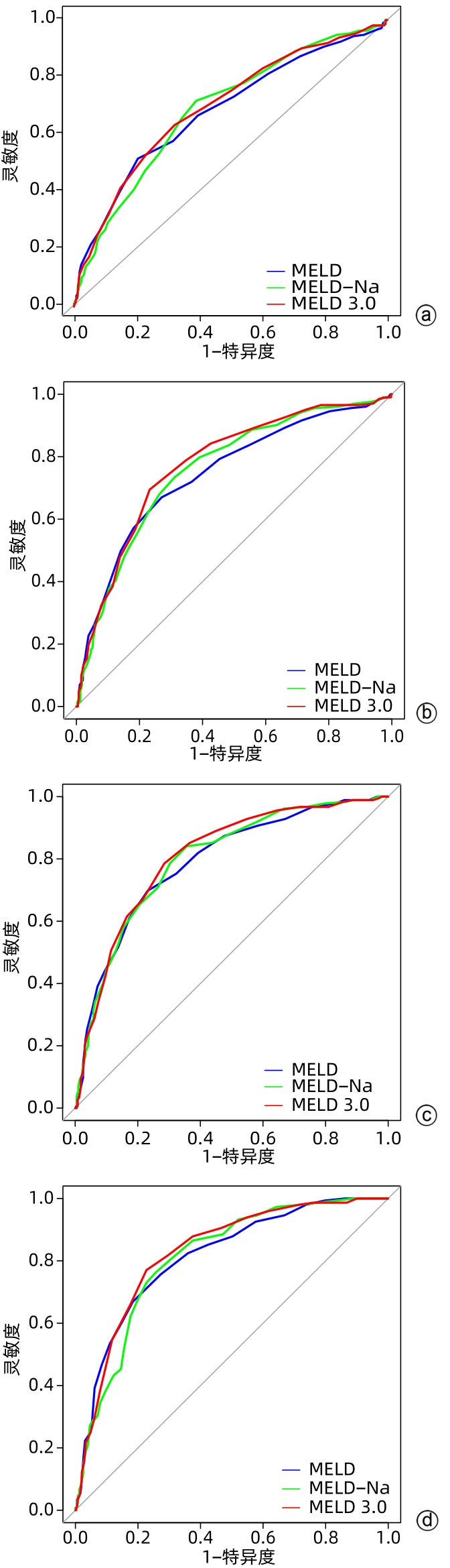
目的 比较MELD 3.0、MELD和MELD-Na评分对慢加急性肝衰竭(ACLF)患者90 d生存预后的评估价值。 方法 回顾性分析2012年11月—2019年6月天津市第三中心医院、解放军总医院第五医学中心和北京佑安医院共605例ACLF患者的临床资料,根据入院后90 d随访结果将其分为生存组(n=392)和死亡组(n=213),应用受试者工作特征曲线(ROC曲线)以及曲线下面积(AUC)、净重分类改善度(NRI)、综合区分改善度(IDI)和决策曲线(DCA曲线)研究基线、3 d、1周和2周时MELD 3.0、MELD和MELD-Na评分对疾病预后的预测价值。 结果 在3 d和1周时,MELD 3.0评分的AUC分别为0.775、0.808,优于MELD评分(P值均<0.05);在3 d、1周和2周时,MELD 3.0相较于MELD预测ACLF患者预后的NRI分别为0.125、0.100、0.081,相较于MELD-Na预测ACLF患者预后的NRI分别为0.093、0.140、0.204;在基线、3 d、1周和2周时,MELD 3.0相较于MELD预测ACLF患者预后的IDI分别为0.011、0.025、0.017、0.013;在3 d和2周时,MELD 3.0相较于MELD-Na预测ACLF患者预后的IDI分别为0.027、0.038;以上NRI和IDI均>0,为正向改善(P值均<0.05);DCA曲线发现MELD 3.0在3 d时优于MELD,MELD 3.0在2周时明显优于MELD-Na;3种评分对不同分型ACLF患者预后预测能力无明显差异(P值均>0.05);3种评分对病因为HBV感染、酒精、HBV感染合并酒精ACLF患者预后预测能力无明显差异(P值均>0.05),但是对于其他病因的患者,MELD 3.0优于MELD评分(P<0.05)。 结论 MELD 3.0评分对ACLF患者90 d生存情况的预测能力优于MELD和MELD-Na评分,但优势有限。 -
关键词:
- 慢加急性肝功能衰竭 /
- MELD-Na评分 /
- MELD 3.0评分 /
- MELD评分 /
- 预后
Abstract:Objective To investigate the value of MELD 3.0, MELD, and MELD-Na scores in assessing the 90-day prognosis of patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) through a comparative study. Methods A retrospective analysis was performed for the clinical data of 605 patients with ACLF who were treated in Tianjin Third Central Hospital, The Fifth Medical Center of Chinese PLA General Hospital, and Beijing YouAn Hospital from November 2012 to June 2019, and according to the 90-day follow-up results after admission, they were divided into survival group with 392 patients and death group with 213 patients. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, the area under the ROC curve (AUC), net reclassification improvement (NRI), integrated discrimination improvement (IDI), and decision curve analysis (DCA) curve were used to investigate the value of MELD 3.0, MELD, and MELD-Na scores at baseline, day 3, week 1, and week 2 in predicting the prognosis of the disease. Results At day 3 and week 1, MELD 3.0 score had an AUC of 0.775 and 0.808, respectively, with a better AUC than MELD score (P<0.05). At day 3, week 1, and week 2, MELD 3.0 score showed an NRI of 0.125, 0.100, and 0.081, respectively, compared with MELD in predicting the prognosis of ACLF patients, as well as an NRI of 0.093, 0.140, and 0.204, respectively, compared with MELD-Na score in predicting prognosis. At baseline, day 3, week 1, and week 2, MELD 3.0 showed an IDI of 0.011, 0.025, 0.017, and 0.013, respectively, compared with MELD in predicting the prognosis of ACLF patients. At day 3 and week 2, MELD 3.0 showed an IDI of 0.027 and 0.038, respectively, compared with MELD-Na in predicting the prognosis of ACLF patients. All the above NRIs and IDIs were >0, indicating a positive improvement (all P<0.05). DCA curves showed that MELD 3.0 was superior to MELD at day 3 and was significantly superior to MELD-Na at week 2. There was no significant difference in the ability of the three scores in predicting the prognosis of ACLF patients with different types, and there was also no significant difference in the ability of the three scores in predicting the prognosis of ACLF patients with the etiology of HBV infection, alcohol, or HBV infection combined with alcohol, while MELD 3.0 was superior to MELD for ACLF patients with other etiologies (P<0.05). Conclusion MELD 3.0 score is better than MELD and MELD-Na scores in predicting the 90-day survival of patients with ACLF, but with limited superiority. -
Key words:
- Acute-On-Chronic Liver Failure /
- MELD-Na Score /
- MELD 3.0 Score /
- MELD Score /
- Prognosis
-
表 1 605例ACLF患者基线临床特征
Table 1. Baseline clinical characteristics of 605 patients of ACLF
指标 生存组(n=392) 死亡组(n=213) 统计值 P值 男/女(例) 311/81 165/48 χ 2=0.288 0.591 年龄(岁) 48.1±11.7 52.2±11.1 t=4.131 <0.001 ABC分型[例(%)] χ 2=14.780 0.001 A型 120(30.6) 42(19.7) B型 113(28.8) 51(23.9) C型 159(40.6) 120(56.3) 病因[例(%)] χ 2=8.276 0.041 HBV感染 230(58.7) 130(61.0) 酒精 87(22.2) 30(14.1) HBV感染合并酒精 24(6.1) 22(10.3) 其他 51(13.0) 31(14.6) ALT(U/L) 156.6(50.0~506.0) 131.5(58.5~385.0) Z=-0.811 0.418 AST(U/L) 179.5(96.9~473.5) 163.0(94.2~424.0) Z=-0.871 0.384 ALP(U/L) 142.0(114.5~183.0) 142.0(105.8~179.0) Z=-0.732 0.464 GGT(U/L) 99.0(57.0~165.3) 71.0(48.9~129.0) Z=-3.494 <0.001 TBil(mg/dL) 13.8(8.7~20.1) 17.6(11.8~25.3) Z=-4.727 <0.001 Cr(mg/dL) Na(mmol/L) 0.8(0.6~1.0) 136.0(132.4~138.0) 1.0(0.7~1.2) 133.6(129.7~136.6) Z=-4.981 Z=-5.323 <0.001 <0.001 INR 2.0(1.7~2.4) 2.2(1.8~2.8) Z=-3.746 <0.001 Alb(g/dL) 2.9±0.5 2.8±0.5 t=-2.379 0.018 PTA(%) 36.8(29.2~45.0) 32.0(24.4~40.0) Z=-5.090 <0.001 WBC(×109/L) 6.5(4.6~9.1) 7.4(5.2~10.3) Z=-2.250 0.024 NEUT%(%) 67.0(54.5~76.4) 73.9(52.9~81.0) Z=-2.599 0.009 LYMPH%(%) 14.7(5.9~24.5) 9.5(2.3~15.0) Z=-5.131 <0.001 PLT(×109/L) 94.5(64.8~135.0) 84.0(55.0~121.5) Z=-2.504 0.012 MELD评分 25.0(22.0~27.0) 28.0(24.0~31.0) Z=-7.405 <0.001 MELD-Na评分 26.0(23.0~31.0) 31.0(27.0~38.0) Z=-7.664 <0.001 MELD 3.0评分 27.0(24.0~29.0) 30.0(27.0~33.0) Z=-8.023 <0.001 表 2 ROC曲线分析3种 MELD 评分对 ACLF 患者 90 d预后的预测效能
Table 2. Predictive efficacy of the three MELD scores by ROC curves analysis on the 90-day prognosis of patients with ACLF
时间 例数 变量 AUC 95%CI 截断点 灵敏度 特异度 Z值 P值1) 基线 605 MELD 0.682 0.636~0.727 27.50 79.59 51.64 1.695 0.090 MELD-Na 0.688 0.644~0.732 27.50 60.97 71.83 0.633 0.527 MELD 3.0 0.697 0.652~0.741 28.50 67.86 63.38 3 d 595 MELD 0.746 0.703~0.788 26.50 72.96 67.00 3.175 0.002 MELD-Na 0.759 0.718~0.800 27.50 68.88 73.40 1.547 0.122 MELD 3.0 0.775 0.735~0.815 28.50 76.79 69.46 1周 575 MELD 0.791 0.752~0.831 26.50 76.84 69.78 2.268 0.023 MELD-Na 0.799 0.761~0.837 26.50 64.38 84.07 0.951 0.342 MELD 3.0 0.808 0.771~0.846 27.50 71.50 78.57 2周 540 MELD 0.813 0.773~0.852 25.50 71.63 66.89 1.698 0.089 MELD-Na 0.811 0.773~0.849 26.50 74.23 76.35 1.524 0.127 MELD 3.0 0.827 0.789~0.863 27.50 77.30 77.03 注:1),与MELD 3.0比较。 表 3 NRI和IDI分析3种 MELD 评分对 ACLF 患者 90 d预后的预测效能
Table 3. Predictive efficacy of the three MELD scores by NRI and IDI analysis on the 90-day prognosis of patients with ACLF
时间 例数 变量 NRI 95%CI P值1) IDI 95%CI P值1) 基线 605 MELD 0.039 -0.014~0.092 0.152 0.011 0.003~0.019 0.009 MELD-Na -0.024 -0.084~0.036 0.427 0.010 -0.008~0.027 0.285 MELD 3.0 3 d 595 MELD 0.125 0.067~0.184 <0.001 0.025 0.015~0.035 <0.001 MELD-Na 0.093 0.020~0.167 0.013 0.027 0.006~0.048 0.011 MELD 3.0 1周 575 MELD 0.100 0.041~0.158 0.001 0.017 0.007~0.027 0.001 MELD-Na 0.140 0.058~0.223 0.001 0.014 -0.009~0.037 0.229 MELD 3.0 2周 540 MELD 0.081 0.009~0.153 0.028 0.013 0.001~0.025 0.029 MELD-Na 0.204 0.109~0.299 <0.001 0.038 0.013~0.064 0.004 MELD 3.0 注:1),与MELD 3.0比较。 表 4 3种MELD评分对不同分型ACLF患者90 d预后的预测效能
Table 4. Predictive efficacy of the three MELD scores for 90-day prognosis of patients with ACLF of different types
ABC分型 例数 变量 AUC Z值 P值1) A型 162 MELD 0.719 0.700 0.484 MELD-Na 0.726 0.201 0.840 MELD 3.0 0.731 B型 164 MELD 0.681 1.010 0.313 MELD-Na 0.668 1.294 0.196 MELD 3.0 0.698 C型 279 MELD 0.686 0.593 0.170 MELD-Na 0.659 0.714 0.967 MELD 3.0 0.674 注:1),与MELD 3.0比较。 表 5 3种MELD评分对不同病因ACLF患者90 d预后的预测效能
Table 5. Predictive efficacy of the three MELD scores for 90-day prognosis of patients with ACLF of different etiologies
病因 例数 变量 AUC Z值 P值1) HBV感染 360 MELD 0.686 1.371 0.170 MELD-Na 0.703 -0.042 0.967 MELD 3.0 0.703 酒精 117 MELD 0.658 -0.612 0.541 MELD-Na 0.623 0.762 0.446 MELD 3.0 0.649 HBV感染合并酒精 46 MELD 0.703 0.526 0.599 MELD-Na 0.764 -0.737 0.461 MELD 3.0 0.718 其他 82 MELD 0.653 2.053 0.040 MELD-Na 0.693 0.318 0.750 MELD 3.0 0.702 注:1),与MELD 3.0比较。 -
[1] Liver Failure and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association; Severe Liver Disease and Artificial Liver Group. Guideline for diagnosis and treatment of liver failure(2018)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 1): 38- 44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.01.007.中华医学会感染病学分会肝衰竭与人工肝学组, 中华医学会肝病学分会重型肝病与人工肝学组. 肝衰竭诊治指南(2018年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35( 1): 38- 44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.01.007. [2] ARROYO V, MOREAU R, JALAN R. Acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. N Engl J Med, 2020, 382( 22): 2137- 2145. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra1914900. [3] HERNAEZ R, SOLÀ E, MOREAU R, et al. Acute-on-chronic liver failure: An update[J]. Gut, 2017, 66( 3): 541- 553. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-312670. [4] FAN Q, LI Z. Liver transplantation for acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Organ Transplant, 2022, 13( 3): 333- 337. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7445.2022.03.008.范祺, 李照. 慢加急性肝衰竭的肝移植治疗[J]. 器官移植, 2022, 13( 3): 333- 337. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7445.2022.03.008. [5] BI ZH, WANG LX, LIAN JQ. Definition, prognostic assessment, and advances in the diagnosis and treatment of acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 7): 1671- 1676. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.07.041.毕占虎, 王临旭, 连建奇. 慢加急性肝衰竭的定义、预后评估及诊治进展[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38( 7): 1671- 1676. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.07.041. [6] ZACCHERINI G, WEISS E, MOREAU R. Acute-on-chronic liver failure: Definitions, pathophysiology and principles of treatment[J]. JHEP Rep, 2020, 3( 1): 100176. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2020.100176. [7] KARVELLAS CJ, FRANCOZ C, WEISS E. Liver transplantation in acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Transplantation, 2021, 105( 7): 1471- 1481. DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000003550. [8] KIM WR, MANNALITHARA A, HEIMBACH JK, et al. MELD 3.0: The model for end-stage liver disease updated for the modern era[J]. Gastroenterology, 2021, 161( 6): 1887- 1895. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.08.050. [9] KAMATH PS, KIM WR. The model for end-stage liver disease(MELD)[J]. Hepatology, 2007, 45( 3): 797- 805. DOI: 10.1002/hep.21563. [10] KAMATH PS, WIESNER RH, MALINCHOC M, et al. A model to predict survival in patients with end-stage liver disease[J]. Hepatology, 2001, 33( 2): 464- 470. DOI: 10.1053/jhep.2001.22172. [11] BIGGINS SW, KIM WR, TERRAULT NA, et al. Evidence-based incorporation of serum sodium concentration into MELD[J]. Gastroenterology, 2006, 130( 6): 1652- 1660. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.02.010. [12] MALINCHOC M, KAMATH PS, GORDON FD, et al. A model to predict poor survival in patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts[J]. Hepatology, 2000, 31( 4): 864- 871. DOI: 10.1053/he.2000.5852. [13] ABDALLAH MA, KUO YF, ASRANI S, et al. Validating a novel score based on interaction between ACLF grade and MELD score to predict waitlist mortality[J]. J Hepatol, 2021, 74( 6): 1355- 1361. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.12.003. [14] MEZZANO G, JUANOLA A, CARDENAS A, et al. Global burden of disease: Acute-on-chronic liver failure, a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Gut, 2022, 71( 1): 148- 155. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322161. [15] GOUDSMIT BFJ, BRAAT AE, TUSHUIZEN ME, et al. Development and validation of a dynamic survival prediction model for patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. JHEP Rep, 2021, 3( 6): 100369. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2021.100369. [16] HA JM, SOHN W, CHO JY, et al. Static and dynamic prognostic factors for hepatitis-B-related acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Clin Mol Hepatol, 2015, 21( 3): 232- 241. DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2015.21.3.232. [17] CHEN MJ, LI X, TANG SH. Progress of multidimensional evaluation of liver function in prognosis of patients with liver failure[J]. Clin J Med Offic, 2023, 51( 9): 901- 903, 907. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2023.09.05.陈美娟, 李雪, 汤善宏. 多维度评估肝功能在肝衰竭患者预后中研究进展[J]. 临床军医杂志, 2023, 51( 9): 901- 903, 907. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2023.09.05. [18] GUSTOT T, FERNANDEZ J, GARCIA E, et al. Clinical Course of acute-on-chronic liver failure syndrome and effects on prognosis[J]. Hepatology, 2015, 62( 1): 243- 252. DOI: 10.1002/hep.27849. [19] YU ZJ, ZHANG Y, CAO YY, et al. A dynamic prediction model for prognosis of acute-on-chronic liver failure based on the trend of clinical indicators[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11( 1): 1810. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-81431-0. [20] LIU WS, SHEN LJ, TIAN H, et al. ABC prognostic classification and MELD 3.0 and COSSH-ACLF II prognostic evaluation in acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2022, 30( 9): 976- 980. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20220308-00103.刘婉姝, 申力军, 田华, 等. 慢加急性肝衰竭ABC分型的预后及MELD 3.0和COSSH-ACLFII对预后评估[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2022, 30( 9): 976- 980. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20220308-00103. -



 PDF下载 ( 824 KB)
PDF下载 ( 824 KB)

 下载:
下载: