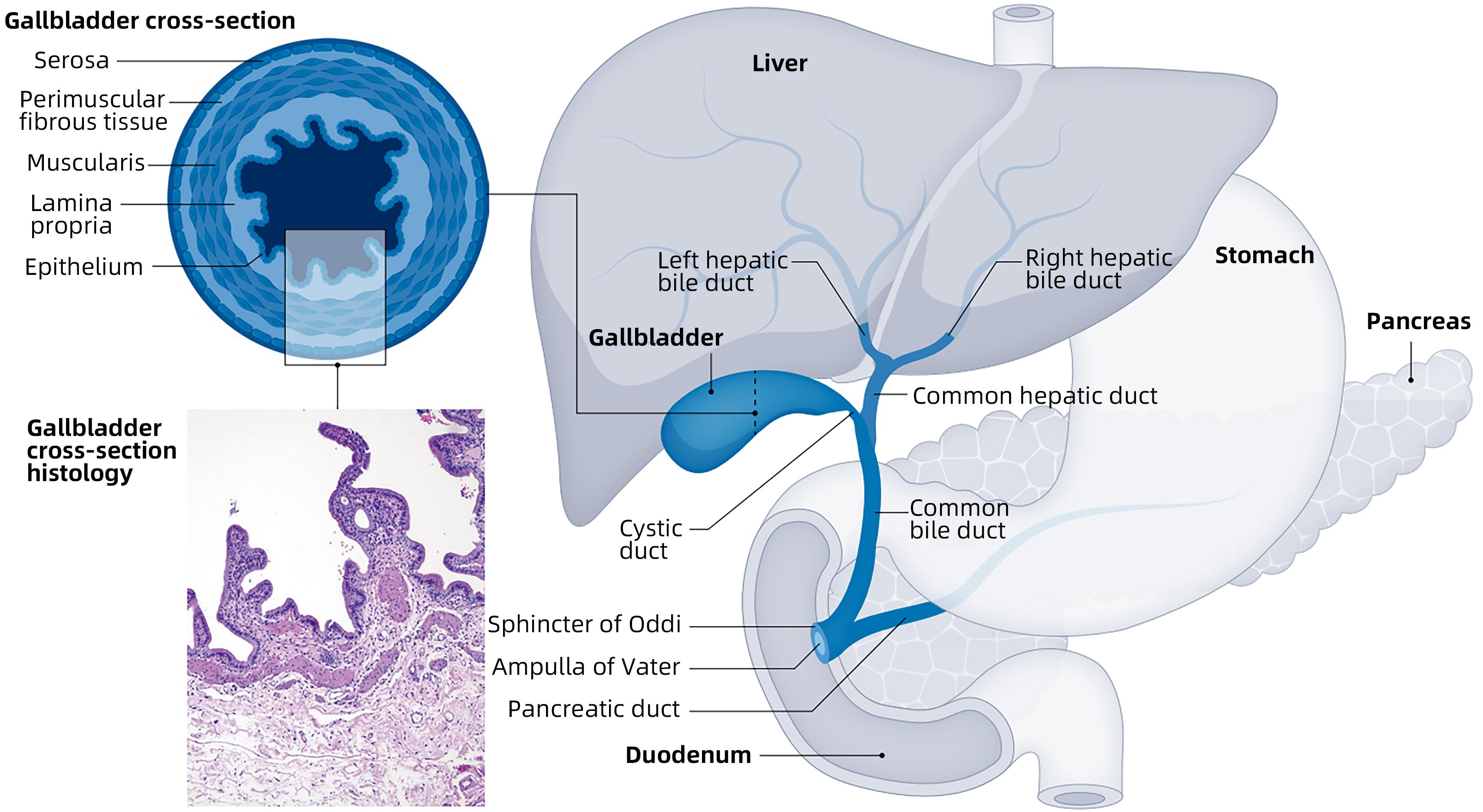
胆囊癌的诊断与治疗进展
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.11.032
-
摘要: 胆囊癌是胆道系统常见的恶性肿瘤,早期症状特异性差,恶性程度极高,进展迅速,难以早期诊断。胆囊结石、胆囊息肉等被认为是最常见的危险因素。超声检查是其首选检查,CT、MRI、PET等也各具优势。胆囊癌缺乏根治性治疗手段,外科手术仍是胆囊癌首选的治疗方式,但其进展迅速,很多患者确诊时已难以行手术治疗,放化疗、靶向治疗、免疫治疗等多种治疗方式联合,在一定程度上改善了患者预后,但其远期治疗效果仍不理想,因此,预防为主、治疗为辅,早发现、早治疗显得尤为重要。Abstract: Gallbladder carcinoma is a common malignant tumor of the biliary system characterized by poor specificity of early symptoms, a high degree of malignancy, and rapid progression, and it is difficult to make an early diagnosis. Gallstones and gallbladder polyps are considered the most common risk factors for gallbladder carcinoma. Ultrasound is the preferred examination, while CT, MRI, and PET also have their own advantages. There is a lack of radical treatment methods for gallbladder carcinoma, and surgical operation remains the preferred treatment method for gallbladder carcinoma; however, due to the rapid progression of this disease, most patients have lost the opportunity for surgery at the time of diagnosis. A combination of various treatment modalities, such as radiochemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy, has improved the prognosis of patients to a certain extent, but with an unsatisfactory long-term therapeutic effect. Therefore, it is of particular importance to give priority to prevention rather than treatment and emphasize early identification and treatment.
-
Key words:
- Gallbladder Neoplasms /
- Risk Factors /
- Diagnosis /
- Therapeutics
-
表 1 GBC危险因素
Table 1. Risk factors of GBC
主要独立病因 依赖性病因 年龄 吸烟史 性别,身体质量指数 芥末油、鱼腥草酮油和黄油黄 家族史 早年怀孕 胆囊结石 使用口服避孕药 慢性胆囊炎 红辣椒 由沙门菌、副伤寒沙门菌或 伤寒沙门菌引起的慢性感染 职业暴露,苯 次级胆汁酸含量 幽门螺杆菌 黄色肉芽肿性胆囊炎 胰胆管汇流异常、先天肝外 胆管囊肿 重金属 胆囊息肉 遗传因素 瓷化胆囊 肥胖 自由基氧化产物 表 2 胆囊癌分期与手术方式
Table 2. Staging and surgical methods of GBC
TNM分期 临床分期 术式 原发性肿瘤(T) Tis:原位癌 0期:Tis、N0、M0 单纯胆囊切除 T1a:侵及固有层 1期:T1、N0、M0 T1b:侵及肌层 2A期:T2a、N0、M0 单纯胆囊切除术+肝十二指韧带淋巴结清扫 T2a:侵及腹膜面的肌周结缔组织,但 未穿透浆膜 2B期:T2b、N0、M0 胆囊癌根治术+胆囊床肝组织切除+胆囊三角清扫+肝十二指肠韧带、肝总动脉旁、十二指肠周围、胰头后方、肠系膜上动脉周围淋巴结清扫 T2b:或侵及肝脏面的肌周结缔组织, 但未进入肝脏 3A期:T3、N0、M0 T3:穿透浆膜和/或直接侵入肝脏和/ 或一个邻近器官或结构,如胃、十二 指肠、结肠、胰腺、网膜或肝外胆管 3B期:T1~3、N1、M0 扩大胆囊癌根治术+受浸润肝段/半肝切除+淋巴结扩大清扫 T4:侵及门静脉,或肝动脉,或两个或 更多肝外器官或结构 4A期:T4、N0~1、M0 区域淋巴结转移情况(N) 4B期:任何T、N2、M0,或任何T、 任何N、M1 远处脏器、淋巴结转移,无法R0切除,应避免手术,保守治疗 N0:无区域淋巴结转移 N1:1~3枚区域淋巴结转移 N2:4枚以上区域淋巴结转移 远处转移(M) M0:无远处转移 M1:有远处 -
[1] SHARMA A, SHARMA KL, GUPTA A, et al. Gallbladder cancer epidemiology, pathogenesis and molecular genetics: Recent update[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2017, 23( 22): 3978- 3998. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i22.3978. [2] ROA JC, GARCÍA P, KAPOOR VK, et al. Gallbladder cancer[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2022, 8( 1): 69. DOI: 10.1038/s41572-022-00398-y. [3] NAGTEGAAL ID, ODZE RD, KLIMSTRA D, et al. The 2019 WHO classification of tumours of the digestive system[J]. Histopathology, 2020, 76( 2): 182- 188. DOI: 10.1111/his.13975. [4] LI WC, HUANG PZ, LEI PR, et al. Risk factors for the recurrence of stones after endoscopic minimally invasive cholecystolithotomy in China: A meta-analysis[J]. Surg Endosc, 2019, 33( 6): 1802- 1810. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-018-6455-y. [5] ZHU Z, LUO K, ZHANG B, WANG G, et al. Risk factor analysis and construction of prediction models of gallbladder carcinoma in patients with gallstones[J]. Front Oncol, 2023, 13: 1037194. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1037194. [6] MCCAIN RS, DIAMOND A, JONES C, et al. Current practices and future prospects for the management of gallbladder polyps: A topical review[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2018, 24( 26): 2844- 2852. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i26.2844. [7] MISHRA SK, KUMARI N, KRISHNANI N. Molecular pathogenesis of gallbladder cancer: An update[J]. Mutat Res, 2019, 816-818: 111674. DOI: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2019.111674. [8] MUHAMMAD JS, KHAN MR, GHIAS K. DNA methylation as an epigenetic regulator of gallbladder cancer: An overview[J]. Int J Surg, 2018, 53: 178- 183. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2018.03.053. [9] BRÄGELMANN J, PONCE CB, MARCELAIN K, et al. Epigenome-wide analysis of methylation changes in the sequence of gallstone disease, dysplasia, and gallbladder cancer[J]. Hepatology, 2021, 73( 6): 2293- 2310. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31585. [10] LU YY, ZHAO HT, CHENG JM, et al. Consensus for clinical application of molecular diagnosis on hepatobiliary carcinoma[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36( 7): 1482- 1488. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.07.008.陆荫英, 赵海涛, 程家敏, 等. 肝胆肿瘤分子诊断临床应用专家共识[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2020, 36( 7): 1482- 1488. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.07.008. [11] ZHANG Y, ZUO C, LIU L, et al. Single-cell RNA-sequencing atlas reveals an MDK-dependent immunosuppressive environment in ErbB pathway-mutated gallbladder cancer[J]. J Hepatol, 2021, 75( 5): 1128- 1141. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.06.023. [12] TIWARI PK. Epigenetic biomarkers in gallbladder cancer[J]. Trends Cancer, 2020, 6( 7): 540- 543. DOI: 10.1016/j.trecan.2020.03.003. [13] TEKCHAM DS, POOJARY SS, BHUNIA S, et al. Epigenetic regulation of APC in the molecular pathogenesis of gallbladder cancer[J]. Indian J Med Res, 2016, 143( Supplement): S82- S90. DOI: 10.4103/0971-5916.191792. [14] WANG YF, FENG FL, ZHAO XH, et al. Combined detection tumor markers for diagnosis and prognosis of gallbladder cancer[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20( 14): 4085- 4092. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i14.4085. [15] KONG WH, ZHANG L, AN R, et al. Diagnostic value of serum D-dimer for detection of gallbladder carcinoma[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2021, 13: 2549- 2556. DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S272116. [16] CHEN XF, WANG DQ, LIU J, et al. Genomic alterations in biliary tract cancer predict prognosis and immunotherapy outcomes[J]. J Immunother Cancer, 2021, 9( 11): e003214. DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2021-003214. [17] XUE XY, LIU YX, WANG C, et al. Identification of exosomal miRNAs as diagnostic biomarkers for cholangiocarcinoma and gallbladder carcinoma[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2020, 5( 1): 77. DOI: 10.1038/s41392-020-0162-6. [18] ZHANG XZ, LI L, ZHANG M, et al. Intelligent recognition of CTCs from gallbladder cancer by ultrasensitive electrochemical cytosensor and diagnosis of chemotherapeutic resistance[J]. Biosens Bioelectron, 2023, 228: 115183. DOI: 10.1016/j.bios.2023.115183. [19] YANG ZY, LIU SL, CAI C, et al. Interpretation of the Gallbladder reporting and data system(GB‑RADS) for risk stratification of gallbladder wall thickening on ultrasonography: an international expert consensus[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2022, 21( 7): 852- 857. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20220505-00252.杨自逸, 刘诗蕾, 蔡晨, 等.《胆囊壁增厚超声检查评估分级系统国际专家共识》解读[J]. 中华消化外科杂志, 2022, 21( 7): 852- 857. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20220505-00252. [20] BO XB, CHEN EB, WANG J, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of imaging modalities in differentiating xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis from gallbladder cancer[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2019, 7( 22): 627. DOI: 10.21037/atm.2019.11.35. [21] BASU SM, GUPTA M, RANA P, et al. RadFormer: Transformers with global-local attention for interpretable and accurate Gallbladder Cancer detection[J]. Med Image Anal, 2023, 83: 102676. DOI: 10.1016/j.media.2022.102676. [22] CHOI SY, KIM JH, PARK HJ, et al. Preoperative CT findings for prediction of resectability in patients with gallbladder cancer[J]. Eur Radiol, 2019, 29( 12): 6458- 6468. DOI: 10.1007/s00330-019-06323-4. [23] TAN CH, LIM KS. MRI of gallbladder cancer[J]. Diagn Interv Radiol, 2013, 19( 4): 312- 319. DOI: 10.5152/dir.2013.044. [24] SASAKI F, NAKAMOTO R, TOKUNAGA K, et al. 18F-FDG PET/CT findings of G-CSF-producing gallbladder cancer[J]. Clin Nucl Med, 2022, 47( 4): e368- e369. DOI: 10.1097/RLU.0000000000004054. [25] JIA X, LI XR, JIA B, et al. The role of[99mTc]Tc-HFAPi SPECT/CT in patients with malignancies of digestive system: First clinical experience[J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2023, 50( 4): 1228- 1239. DOI: 10.1007/s00259-022-06068-1. [26] SHINDOH J, DE ARETXABALA X, ALOIA TA, et al. Tumor location is a strong predictor of tumor progression and survival in T2 gallbladder cancer: An international multicenter study[J]. Ann Surg, 2015, 261( 4): 733- 739. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000000728. [27] GHOLAMI S, COLBY S, HOROWITZ DP, et al. Adjuvant chemoradiation in patients with lymph node-positive biliary tract cancers: Secondary analysis of a single-arm clinical trial(SWOG 0809)[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2023, 30( 3): 1354- 1363. DOI: 10.1245/s10434-022-12863-9. [28] JULKA PK, PURI TR, RATH GK. A phase Ⅱ study of gemcitabine and carboplatin combination chemotherapy in gallbladder carcinoma[J]. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int, 2006, 5( 1): 110- 114. [29] BRIDGEWATER J, FLETCHER P, PALMER DH, et al. Long-term outcomes and exploratory analyses of the randomized phase Ⅲ BILCAP study[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2022, 40( 18): 2048- 2057. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.21.02568. [30] PRIMROSE JN, FOX RP, PALMER DH, et al. Capecitabine compared with observation in resected biliary tract cancer(BILCAP): A randomised, controlled, multicentre, phase 3 study[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2019, 20( 5): 663- 673. DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30915-X. [31] VALLE J, WASAN H, PALMER DH, et al. Cisplatin plus gemcitabine versus gemcitabine for biliary tract cancer[J]. N Engl J Med, 2010, 362( 14): 1273- 1281. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa0908721. [32] MORIZANE C, OKUSAKA T, MIZUSAWA J, et al. Combination gemcitabine plus S-1 versus gemcitabine plus cisplatin for advanced/recurrent biliary tract cancer: The FUGA-BT(JCOG1113) randomized phase Ⅲ clinical trial[J]. Ann Oncol, 2019, 30( 12): 1950- 1958. DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdz402. [33] SHROFF RT, JAVLE MM, XIAO LC, et al. Gemcitabine, cisplatin, and nab-paclitaxel for the treatment of advanced biliary tract cancers: A phase 2 clinical trial[J]. JAMA Oncol, 2019, 5( 6): 824- 830. DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.0270. [34] CUI XY, LI XC, CUI JJ, et al. Modified FOLFIRINOX for unresectable locally advanced or metastatic gallbladder cancer, a comparison with GEMOX regimen[J]. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr, 2021, 10( 4): 498- 506. DOI: 10.21037/hbsn-20-846. [35] IOKA T, KANAI M, KOBAYASHI S, et al. Randomized phase Ⅲ study of gemcitabine, cisplatin plus S-1 versus gemcitabine, cisplatin for advanced biliary tract cancer(KHBO1401-MITSUBA)[J]. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci, 2023, 30( 1): 102- 110. DOI: 10.1002/jhbp.1219. [36] ZHANG YJ, ZUO CM, LIU LG, et al. Single-cell RNA-sequencing atlas reveals an MDK-dependent immunosuppressive environment in ErbB pathway-mutated gallbladder cancer[J]. J Hepatol, 2021, 75( 5): 1128- 1141. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.06.023. [37] JAVLE M, CHURI C, KANG HC, et al. HER2/neu-directed therapy for biliary tract cancer[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2015, 8: 58. DOI: 10.1186/s13045-015-0155-z. [38] JAVLE M, BORAD MJ, AZAD NS, et al. Pertuzumab and trastuzumab for HER2-positive, metastatic biliary tract cancer(MyPathway): A multicentre, open-label, phase 2a, multiple basket study[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2021, 22( 9): 1290- 1300. DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00336-3. [39] LIN JZ, LONG JY, WAN XS, et al. Classification of gallbladder cancer by assessment of CD8+ TIL and PD-L1 expression[J]. BMC Cancer, 2018, 18( 1): 766. DOI: 10.1186/s12885-018-4651-8. [40] OTT PA, BANG YJ, PIHA-PAUL SA, et al. T-cell-inflamed gene-expression profile, programmed death ligand 1 expression, and tumor mutational burden predict efficacy in patients treated with pembrolizumab across 20 cancers: KEYNOTE-028[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2019, 37( 4): 318- 327. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2018.78.2276. [41] KASSAB J, SABA L, GEBRAEL G, et al. Update on immunotherapy in the management of gallbladder cancer[J]. Immunotherapy, 2023, 15( 1): 35- 42. DOI: 10.2217/imt-2022-0191. [42] FENG KC, LIU Y, GUO YL, et al. Phase I study of chimeric antigen receptor modified T cells in treating HER2-positive advanced biliary tract cancers and pancreatic cancers[J]. Protein Cell, 2018, 9( 10): 838- 847. DOI: 10.1007/s13238-017-0440-4. [43] FENG KC, GUO YL, LIU Y, et al. Cocktail treatment with EGFR-specific and CD133-specific chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells in a patient with advanced cholangiocarcinoma[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2017, 10( 1): 4. DOI: 10.1186/s13045-016-0378-7. [44] HACK SP, VERRET W, MULLA S, et al. IMbrave 151: A randomized phase II trial of atezolizumab combined with bevacizumab and chemotherapy in patients with advanced biliary tract cancer[J]. Ther Adv Med Oncol, 2021, 13: 17588359211036544. DOI: 10.1177/17588359211036544. [45] LEE CK, CHON HJ, CHEON J, et al. Trastuzumab plus FOLFOX for HER2-positive biliary tract cancer refractory to gemcitabine and cisplatin: A multi-institutional phase 2 trial of the Korean Cancer Study Group(KCSG-HB19-14)[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 8( 1): 56- 65. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00335-1. [46] SHI GM, HUANG XY, WU D, et al. Toripalimab combined with lenvatinib and GEMOX is a promising regimen as first-line treatment for advanced intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a single-center, single-arm, phase 2 study[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2023, 8( 1): 106. DOI: 10.1038/s41392-023-01317-7. -



 PDF下载 ( 868 KB)
PDF下载 ( 868 KB)

 下载:
下载:


