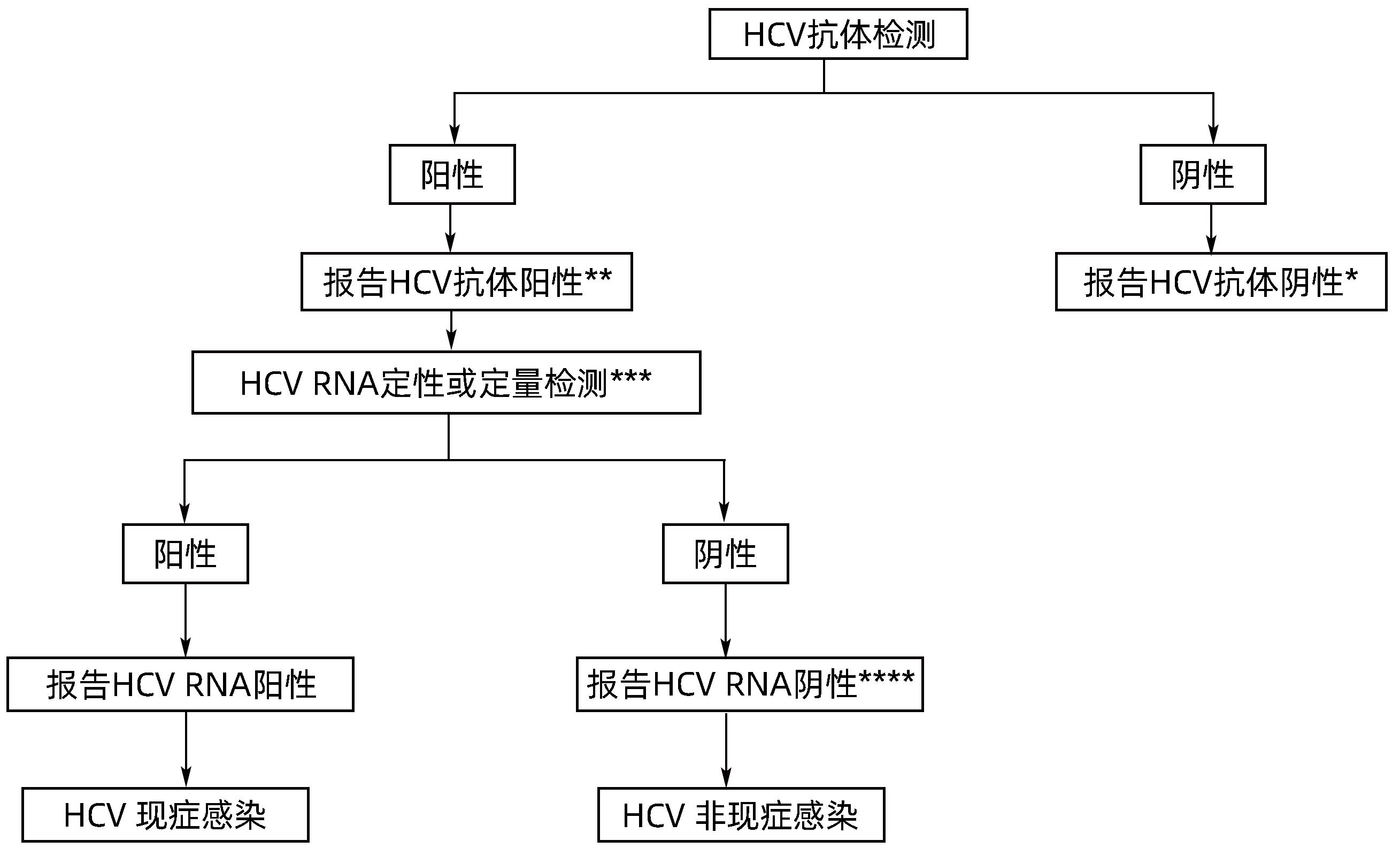
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
World Health Organization. Global Health Sector Strategy on Viral Hepatitis 2016-2021[M]. Geneva: WHO, 2016.
|
| [4] |
World Health Organization. Guidelines on Hepatitis B and C Testing[M]. Geneva: WHO, 2017.
|
| [5] |
Chinese Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Technical Specification for Laboratory Testing of Hepatitis C Virus(2023 Revised Edition)[Z]. 2023.
中国疾病预防控制中心. 丙型肝炎病毒实验室检测技术规范(2023年修订版)[Z]. 2023.
|
| [6] |
National Health and Family Planning Commission. Diagnosis for hepatitis C: WS 213—2018[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2018: 1- 9.
国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 丙型肝炎诊断: WS 213—2018[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018: 1- 9.
|
| [7] |
European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL recommendations on treatment of hepatitis C: Final update of the series[J]. J Hepatol, 2020, 73( 5): 1170- 1218. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.08.018. |
| [8] |
WARKAD SD, SONG KS, PAL D, et al. Developments in the HCV screening technologies based on the detection of antigens and antibodies[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19( 19): 4257. DOI: 10.3390/s19194257. |
| [9] |
GUPTA E, BAJPAI M, CHOUDHARY A. Hepatitis C virus: Screening, diagnosis, and interpretation of laboratory assays[J]. Asian J Transfus Sci, 2014, 8( 1): 19- 25. DOI: 10.4103/0973-6247.126683. |
| [10] |
DUFOUR DR, TALASTAS M, FERNANDEZ MDA, et al. Chemiluminescence assay improves specificity of hepatitis C antibody detection[J]. Clin Chem, 2003, 49( 6 Pt 1): 940- 944. DOI: 10.1373/49.6.940. |
| [11] |
SMITH BD, JEWETT A, DROBENIUC J, et al. Rapid diagnostic HCV antibody assays[J]. Antivir Ther, 2012, 17( 7 Pt B): 1409- 1413. DOI: 10.3851/IMP2470. |
| [12] |
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention(CDC). Testing for HCV infection: An update of guidance for clinicians and laboratorians[J]. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep, 2013, 62( 18): 362- 365.
|
| [13] |
WARKAD SD, NIMSE SB, SONG KS, et al. HCV detection, discrimination, and genotyping technologies[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18( 10): 3423. DOI: 10.3390/s18103423. |
| [14] |
SCHALASTA G, SPEICHER A, BÖRNER A, et al. Performance of the new aptima HCV quant dx assay in comparison to the cobas TaqMan HCV2 test for use with the high pure system in detection and quantification of hepatitis C virus RNA in plasma or serum[J]. J Clin Microbiol, 2016, 54( 4): 1101- 1107. DOI: 10.1128/JCM.03236-15. |
| [15] |
HENDRICKS DA, FRIESENHAHN M, TANIMOTO L, et al. Multicenter evaluation of the versant hcv RNA qualitative assay for detection of hepatitis c virus RNA[J]. J Clin Microbiol, 2003, 41( 2): 651- 656. DOI: 10.1128/JCM.41.2.651-656.2003. |
| [16] |
SCOTT JD, GRETCH DR. Molecular diagnostics of hepatitis C virus infection: A systematic review[J]. JAMA, 2007, 297( 7): 724- 732. DOI: 10.1001/jama.297.7.724. |
| [17] |
CATLETT B, CARRERA A, STARR M, et al. Performance evaluation of the Hologic Aptima HCV Quant Dx assay for detection of HCV RNA from dried blood spots[J]. J Clin Virol, 2019, 112: 40- 44. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcv.2019.01.010. |
| [18] |
WEBER J, SAHOO MK, TAYLOR N, et al. Evaluation of the aptima HCV quant dx assay using serum and dried blood spots[J]. J Clin Microbiol, 2019, 57( 4): e00030-19. DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00030-19. |
| [19] |
ROSS RS, VIAZOV S, SALLOUM S, et al. Analytical performance characteristics and clinical utility of a novel assay for total hepatitis C virus core antigen quantification[J]. J Clin Microbiol, 2010, 48( 4): 1161- 1168. DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01640-09. |
| [20] |
FREIMAN JM, TRAN TM, SCHUMACHER SG, et al. Hepatitis C core antigen testing for diagnosis of hepatitis C virus infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Ann Intern Med, 2016, 165( 5): 345- 355. DOI: 10.7326/M16-0065. |
| [21] |
LAMOURY FMJ, SOKER A, MARTINEZ D, et al. Hepatitis C virus core antigen: A simplified treatment monitoring tool, including for post-treatment relapse[J]. J Clin Virol, 2017, 92: 32- 38. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcv.2017.05.007. |
| [22] |
CHEVALIEZ S, FELD J, CHENG K, et al. Clinical utility of HCV core antigen detection and quantification in the diagnosis and management of patients with chronic hepatitis C receiving an all-oral, interferon-free regimen[J]. Antivir Ther, 2018, 23( 3): 211- 217. DOI: 10.3851/IMP3042. |
| [23] |
VAN TILBORG M, MARZOOQI SH AL, WONG WWL, et al. HCV core antigen as an alternative to HCV RNA testing in the era of direct-acting antivirals: Retrospective screening and diagnostic cohort studies[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 3( 12): 856- 864. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(18)30271-1. |
| [24] |
KUMAR R, CHAN KP, EKSTROM VSM, et al. Hepatitis C virus antigen detection is an appropriate test for screening and early diagnosis of hepatitis C virus infection in at-risk populations and immunocompromised hosts[J]. J Med Virol, 2021, 93( 6): 3738- 3743. DOI: 10.1002/jmv.26433. |
| [25] |
HONGJAISEE S, DOUNGJINDA N, KHAMDUANG W, et al. Rapid visual detection of hepatitis C virus using a reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay[J]. Int J Infect Dis, 2021, 102: 440- 445. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.10.082. |
| [26] |
CHIA CT, BENDER AT, LILLIS L, et al. Rapid detection of hepatitis C virus using recombinase polymerase amplification[J]. PLoS One, 2022, 17( 10): e0276582. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0276582. |
| [27] |
VIDIMLISKI PD, NIKOLOV I, GESHKOVSKA NM, et al. Review: Occult hepatitis C virus infection: Still remains a controversy[J]. J Med Virol, 2014, 86( 9): 1491- 1498. DOI: 10.1002/jmv.23979. |
| [28] |
KHATTAB MA, ZAKARIA Y, SADEK E, et al. Detection of hepatitis C virus(HCV) RNA in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells of HCV-infected patients following sustained virologic response[J]. Clin Exp Med, 2023, 23( 1): 131- 140. DOI: 10.1007/s10238-022-00791-7. |
| [29] |
FRÍAS M, RIVERO-JUÁREZ A, TÉLLEZ F, et al. Evaluation of hepatitis C viral RNA persistence in HIV-infected patients with long-term sustained virological response by droplet digital PCR[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9( 1): 12507. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-48966-9. |
| [30] |
World Health Organization. Guidelines for the screening, care and treatment of persons with chronic hepatitis C infection[M]. Geneva: WHO, 2016.
|
| [31] |
WORKOWSKI KA, BACHMANN LH, CHAN PA, et al. Sexually transmitted infections treatment guidelines, 2021[J]. MMWR Recomm Rep, 2021, 70( 4): 1- 187. DOI: 10.15585/mmwr.rr7004a1. |
| [32] |
CHEVALIEZ S, PAWLOTSKY JM. New virological tools for screening, diagnosis and monitoring of hepatitis B and C in resource-limited settings[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 69( 4): 916- 926. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.05.017. |
| [33] |
World Health Organization. Updated recommendations on simplified service delivery and diagnostics for hepatitis C infection[M]. Geneva: WHO, 2022.
|
| [34] |
GREBELY J, LAMOURY FMJ, HAJARIZADEH B, et al. Evaluation of the Xpert HCV Viral Load point-of-care assay from venepuncture-collected and finger-stick capillary whole-blood samples: A cohort study[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2017, 2( 7): 514- 520. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(17)30075-4. |
| [35] |
TRICKEY A, FAJARDO E, ALEMU D, et al. Impact of hepatitis C virus point-of-care RNA viral load testing compared with laboratory-based testing on uptake of RNA testing and treatment, and turnaround times: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 8( 3): 253- 270. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00346-6. |
| [36] |
ORU E, TRICKEY A, SHIRALI R, et al. Decentralisation, integration, and task-shifting in hepatitis C virus infection testing and treatment: A global systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Lancet Glob Health, 2021, 9( 4): e431- e445. DOI: 10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30505-2. |
| [37] |
TAO YS, TANG WM, FAJARDO E, et al. Reflex hepatitis C virus viral load testing following an initial positive hepatitis C virus antibody test: A global systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Clin Infect Dis, 2023, 77( 8): 1137- 1156. DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciad126. |
| [38] |
THOMPSON LA, FENTON J, CHARLTON CL. HCV reflex testing: A single-sample, low-contamination method that improves the diagnostic efficiency of HCV testing among patients in Alberta, Canada[J]. J Assoc Med Microbiol Infect Dis Can, 2022, 7( 2): 97- 107. DOI: 10.3138/jammi-2021-0028. |
| [39] |
MANTEUFFEL JJ, LEE MS, BUSSA RM, et al. Hepatitis C virus reflex testing protocol in an emergency department[J]. West J Emerg Med, 2022, 23( 2): 108- 114. DOI: 10.5811/westjem.2021.10.52468. |
| [40] |
DE LA PAZ CASAS M, GARCÍA F, FREYRE-CARRILLO C, et al. Towards the elimination of hepatitis C: Implementation of reflex testing in Andalusia[J]. Rev Esp Enferm Dig, 2020, 112( 7): 515- 519. DOI: 10.17235/reed.2020.6370/2019. |
| [41] |
JOHNSON LN, GAYNOR AM, WROBLEWSKI K, et al. Maximizing reflexive HCV RNA testing of HCV antibody-reactive samples within United States public health laboratories[J]. J Infect Dis, 2023: jiad191. DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiad191. |
| [42] |
World Health Organization. Recommendations and guidance on hepatitis C virus self-testing[M]. Geneva: WHO, 2021.
|



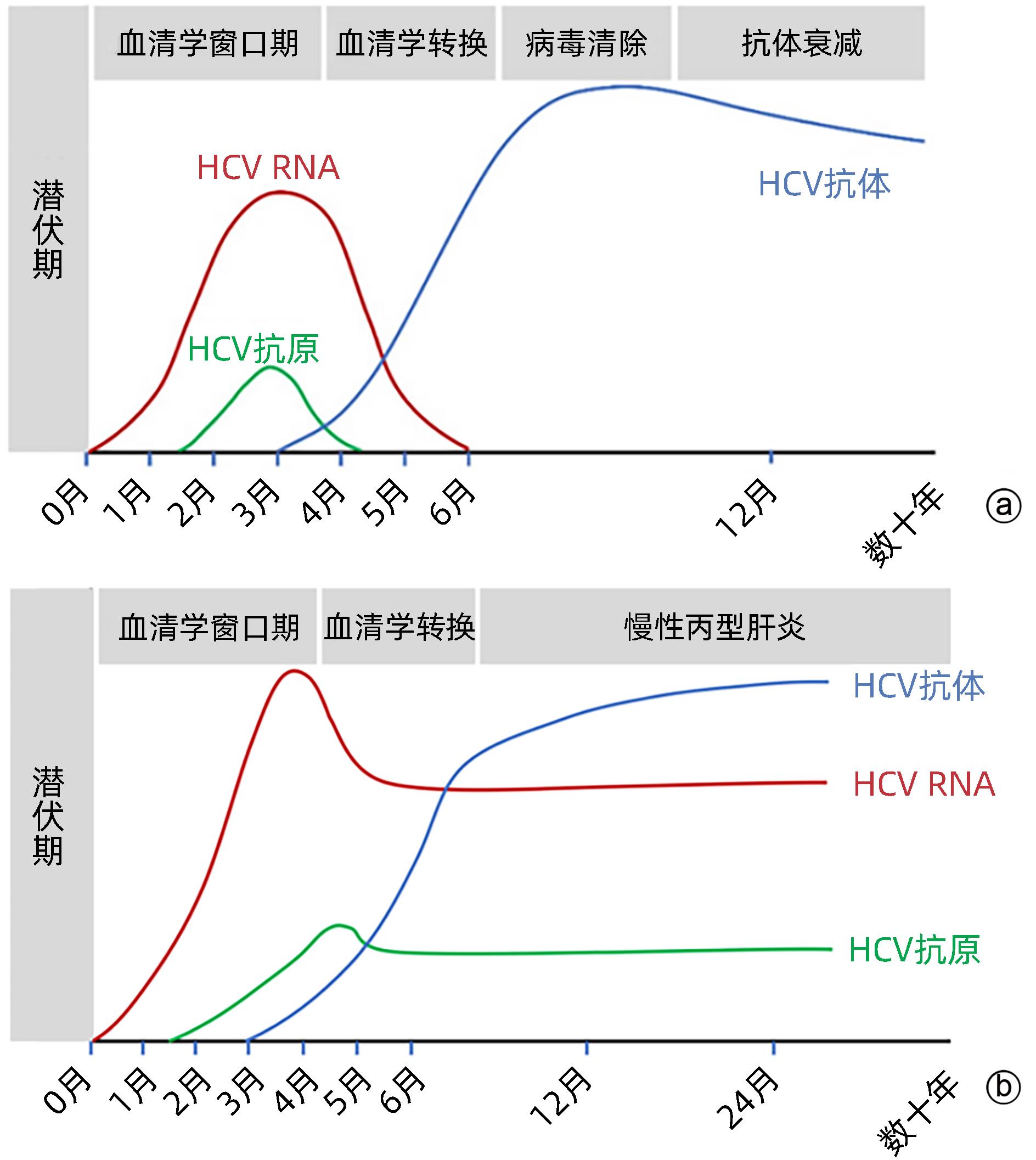




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: