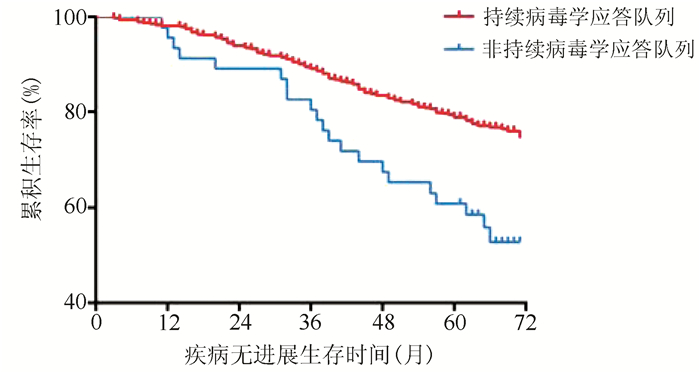
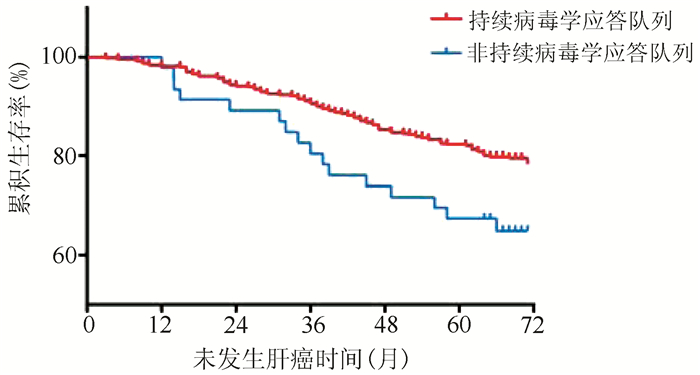
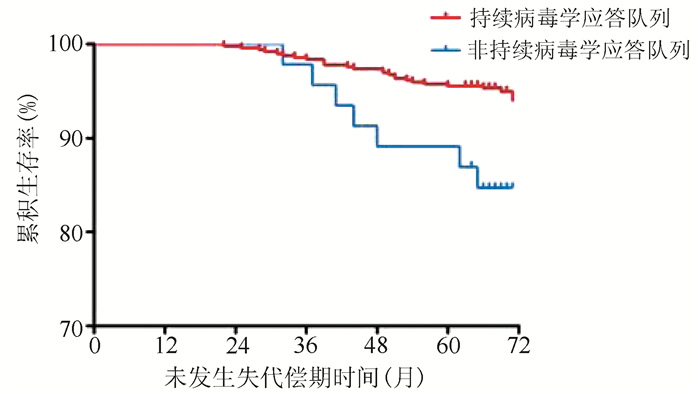
| [1] |
Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases and Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. The guideline of prevention and treatment for chronic hepatitis B: A 2019 update[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(12): 2648-2669. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.007. |
| [2] |
FATTOVICH G, BORTOLOTTI F, DONATO F. Natural history of chronic hepatitis B: Special emphasis on disease progression and prognostic factors[J]. J Hepatol, 2008, 48(2): 335-352. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2007.11.011. |
| [3] |
HOU JL, ZHAO W, LEE C, et al. Outcomes of long-term treatment of chronic HBV infection with entecavir or other agents from a randomized trial in 24 countries[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 18(2): 457-467.e21. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.07.010. |
| [4] |
Chinese Society of Hepatology and Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association. The guideline of prevention and treatment for chronic hepatitis B: A 2010 update[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2011, 27(1): 113-128. http://lcgdbzz.org/article/id/LCGD201101035 |
| [5] |
Ministry of Health of the People's Republic of China. Diagnosis, management, and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (V2011)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2011, 27(11): 1141-1159. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2011.11.004. |
| [6] |
WANG FS, FAN JG, ZHANG Z, et al. The global burden of liver disease: The major impact of China[J]. Hepatology, 2014, 60(6): 2099-2108. DOI: 10.1002/hep.27406. |
| [7] |
CHEN YC, CHU CM, YEH CT, et al. Natural course following the onset of cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B: A long-term follow-up study[J]. Hepatol Int, 2007, 1(1): 267-273. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-007-5001-0. |
| [8] |
ZHANG Y. The analysis of the risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with hepatitis B virus cirrhosis receiving antiviral treatment[D]. Shenyang: China Medical University, 2018.
张瑶. 接受抗病毒治疗的乙肝肝硬化患者进展为肝癌的危险因素分析[D]. 沈阳: 中国医科大学, 2018.
|
| [9] |
CHEN CJ, YANG HI, SU J, et al. Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma across a biological gradient of serum hepatitis B virus DNA level[J]. JAMA, 2006, 295(1): 65-73. DOI: 10.1001/jama.295.1.65. |
| [10] |
ZHANG MJ. Analysis and discussion on the effect of antiviral therapy for patients with decompensated cirrhosis of hepatitis B[J]. China Prac Med, 2018, 13(25): 5-7. DOI: 10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2018.25.003. |
| [11] |
NAM JY, CHANG Y, CHO H, et al. Delayed viral suppression during antiviral therapy is associated with increased hepatocellular carcinoma rates in HBeAg-positive high viral load chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2018, 25(5): 552-560. DOI: 10.1111/jvh.12838. |
| [12] |
TERRAULT NA, LOK A, MCMAHON BJ, et al. Update on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B: AASLD 2018 hepatitis B guidance[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 67(4): 1560-1599. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29800. |



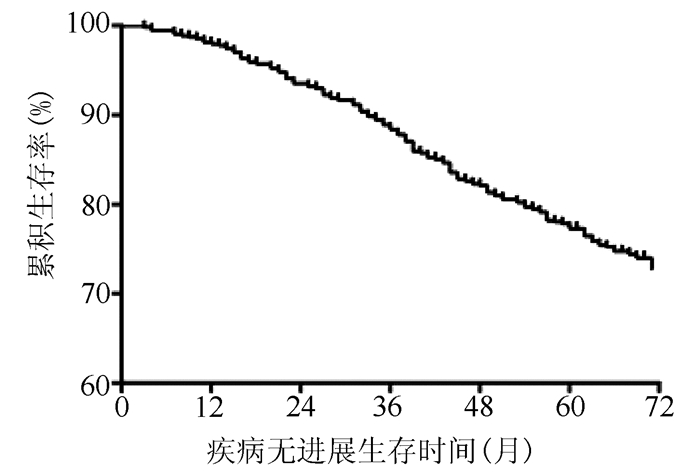




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: