| [1] |
BRAY F, FERLAY J, SOERJOMATARAM I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68(6): 394-424. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21492. |
| [2] |
FERLAY J, SOERJOMATARAM I, DIKSHIT R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012[J]. Int J Cancer, 2015, 136(5): E359-386. DOI: 10.1002/ijc.29210. |
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
XU D, YUAN WD. Clinical efficacy of hepatic artery chemoembolization in the treatment of patients with primary liver cancer[J]. J Prac Hepatol, 2015, 18(2): 195-196. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2015.02.024. |
| [5] |
Bureau of Medical Administration, National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China. Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer in China (2019 edition)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(2): 277-292. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.02.007. |
| [6] |
LLOVET JM, BRÚ C, BRUIX J. Prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: The BCLC staging classification[J]. Semin Liver Dis, 1999, 19(3): 329-338. DOI: 10.1055/s-2007-1007122. |
| [7] |
WIESNER R, EDWARDS E, FREEMAN R, et al. Model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) and allocation of donor livers[J]. Gastroenterology, 2003, 124(1): 91-96. DOI: 10.1053/gast.2003.50016. |
| [8] |
JOHNSON PJ, BERHANE S, KAGEBAYASHI C, et al. Assessment of liver function in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A new evidence-based approach-the ALBI grade[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2015, 33(6): 550-558. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2014.57.9151. |
| [9] |
XU Q, YAN Y, GU S, et al. A Novel inflammation-based prognostic score: The fibrinogen/albumin ratio predicts prognoses of patients after curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Immunol Res, 2018, 2018: 4925498. DOI: 10.1155/2018/4925498. |
| [10] |
GKIKA E, BETTINGER D, KRAFFT L, et al. The role of albumin-bilirubin grade and inflammation-based index in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy[J]. Strahlenther Onkol, 2018, 194(5): 403-413. DOI: 10.1007/s00066-017-1256-0. |
| [11] |
SAMAWI HH, SIM HW, CHAN KK, et al. Prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with sorafenib: A comparison of five models in a large Canadian database[J]. Cancer Med, 2018, 7(7): 2816-2825. DOI: 10.1002/cam4.1493. |
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
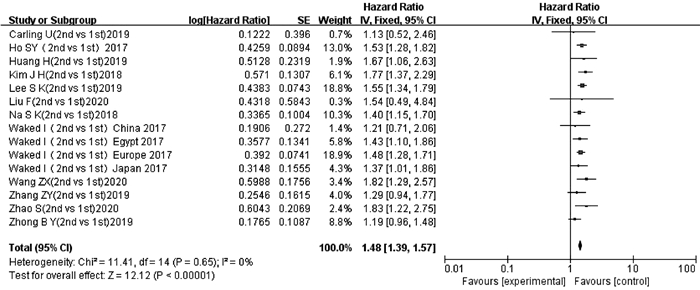
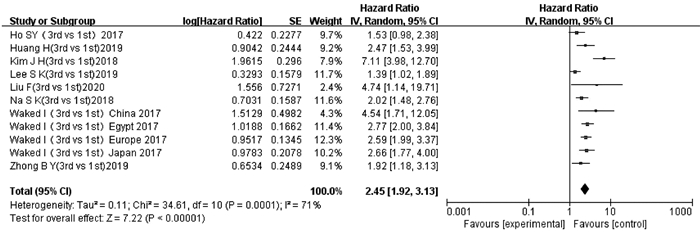
HO SY, LIU PH, HSU CY, et al. Prognostic role of noninvasive liver reserve markers in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing transarterial chemoembolization[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(7): e0180408. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0180408. |
| [14] |
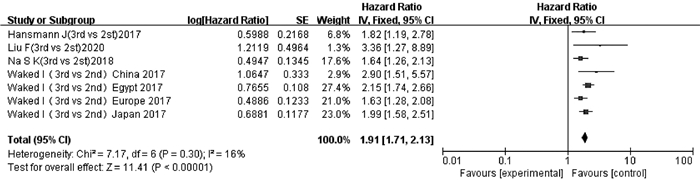
WAKED I, BERHANE S, TOYODA H, et al. Transarterial chemo-embolisation of hepatocellular carcinoma: Impact of liver function and vascular invasion[J]. Br J Cancer, 2017, 116(4): 448-454. DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2016.423. |
| [15] |
ZHAO S, ZHANG T, LI H, et al. Comparison of albumin-bilirubin grade versus Child-Pugh score in predicting the outcome of transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma using time-dependent ROC[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2020, 8(8): 538. DOI: 10.21037/atm.2020.02.124. |
| [16] |
KIM JH, SINN DH, LEE JH, et al. Novel albumin-bilirubin grade-based risk prediction model for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing chemoembolization[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2018, 63(4): 1062-1071. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-018-4934-6. |
| [17] |
NA SK, YIM SY, SUH SJ, et al. ALBI versus Child-Pugh grading systems for liver function in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Surg Oncol, 2018, 117(5): 912-921. DOI: 10.1002/jso.24992. |
| [18] |
ZHONG BY, NI CF, JI JS, et al. Nomogram and artificial neural network for prognostic performance on the albumin-bilirubin grade for hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing transarterial chemoembolization[J]. J Vasc Interv Radiol, 2019, 30(3): 330-338. DOI: 10.1016/j.jvir.2018.08.026. |
| [19] |
CARLING U, RØSOK B, LINE PD, et al. ALBI and P-ALBI grade in Child-Pugh A patients treated with drug eluting embolic chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Acta Radiol, 2019, 60(6): 702-709. DOI: 10.1177/0284185118799519. |
| [20] |
WANG ZX, WANG EX, XIA DD, et al. Value of Child-Pugh score versus albumin-bilirubin grade in predicting the prognosis of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma treated by transarterial chemoembolization[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(1): 113-117. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.01.025. |
| [21] |
LIU F, ZHOU YF. Child-Pugh score and albumin-bilirubin classification in prognostic value of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing arterial chemoembolization[J]. Sma Healt, 2020, 6(11): 135-136. DOI: 10.19335/j.cnki.2096-1219.2020.11.052. |
| [22] |
HUANG H, ZHU Y, BAO ZJ. Prognostic factors of elderly patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing transcatheter arte-rial chemoembolization[J]. Prac Geri, 2019, 33(6): 577-581. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9198.2019.06.015. |
| [23] |
ZHANG ZY, ZHANG GL, WAN L, et al. Prognostic value of ALBI grading in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with repeated TACE[J]. Tumor, 2019, 39(9): 722-729. DOI: 10.3781/j.issn.1000-7431.2019.33.203. |
| [24] |
LEE SK, SONG MJ, KIM SH, et al. Comparing various scoring system for predicting overall survival according to treatment modalities in hepatocellular carcinoma focused on Platelet-albumin-bilirubin (PALBI) and albumin-bilirubin (ALBI) grade: A nationwide cohort study[J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(5): e0216173. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0216173. |
| [25] |
HANSMANN J, EVERS MJ, BUI JT, et al. Albumin-bilirubin and platelet-albumin-bilirubin grades accurately predict overall survival in high-risk patients undergoing conventional transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Vasc Interv Radiol, 2017, 28(9): 1224-1231. e2. DOI: 10.1016/j.jvir.2017.05.020. |
| [26] |
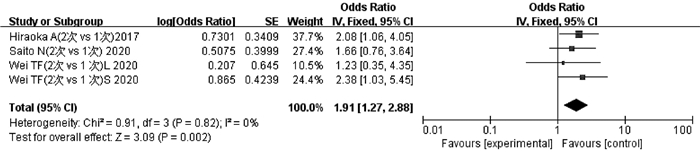
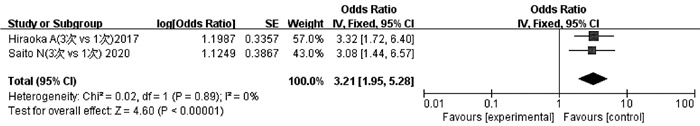
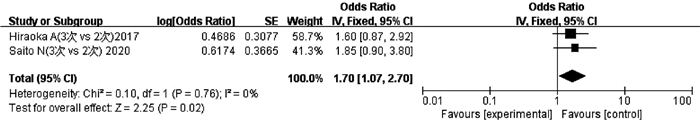
HIRAOKA A, KUMADA T, KUDO M, et al. Hepatic function during repeated TACE procedures and prognosis after introducing sorafenib in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Multicenter analysis[J]. Dig Dis, 2017, 35(6): 602-610. DOI: 10.1159/000480256. |
| [27] |
SAITO N, TANAKA T, NISHIOHUKU H, et al. Transarterial- chemoembolization remains an effective therapy for intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma with preserved liver function[J]. Hepatol Res, 2020, 50(10): 1176-1185. DOI: 10.1111/hepr.13550. |
| [28] |
WEI TF, HE SC, ZHU HD, et al. The impact of different intervals between two TACE procedures on the short-term liver functions in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Interv Radiol, 2020, 29(11): 1126-1130. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-794X.2020.11.014. 魏庭丰, 何仕诚, 朱海东, 等. 原发性肝癌肝动脉化疗栓塞治疗间隔长短对近期肝功能影响的比较[J]. 介入放射学杂志, 2020, 29(11): 1126-1130. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-794X. 2020.11.014.
|
| [29] |
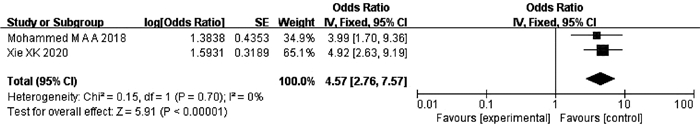
XIE XK, WANG ZY, CHEN XX, et al. Value of four scoring systems in predicting liver failure after transcatheter arterial che-moembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Chin J Clin Oncol, 2020, 47(12): 614-620. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8179. 2020.12.347.
|
| [30] |
MOHAMMED M, KHALAF MH, LIANG T, et al. Albumin-bilirubin score: An accurate predictor of hepatic decompensation in high-risk patients undergoing transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Vasc Interv Radiol, 2018, 29(11): 1527-1534. e1. DOI: 10.1016/j.jvir.2018.06.016. |
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
BRUIX J, SHERMAN M. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: An update[J]. Hepatology, 2011, 53(3): 1020-1022. DOI: 10.1002/hep.24199. |
| [33] |
CHILD CG, TURCOTTE JG. Surgery and portal hypertension[J]. Major Probl Clin Surg, 1964, 1: 1-85.
|
| [34] |
PUGH RN, MURRAY-LYON IM, DAWSON JL, et al. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices[J]. Br J Surg, 1973, 60(8): 646-649. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.1800600817. |
| [35] |
JOHNSON PJ, WILLIAMS R. Cirrhosis and the aetiology of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Hepatol, 1987, 4(1): 140-147. DOI: 10.1016/s0168-8278(87)80021-1. |
| [36] |
DURAND F, VALLA D. Assessment of prognosis of cirrhosis[J]. Semin Liver Dis, 2008, 28(1): 110-122. DOI: 10.1055/s-2008-1040325. |
| [37] |
BAǦ IRSAKÇ I E, ŞAHIN E, ATABEY N, et al. Role of albumin in growth inhibition in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Oncology, 2017, 93(2): 136-142. DOI: 10.1159/000471807. |
| [38] |
CHAN AW, CHONG CC, MO FK, et al. Incorporating albumin-bilirubin grade into the cancer of the liver Italian program system for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2017, 32(1): 221-228. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.13457. |
| [39] |
CHAN AW, CHONG CC, MO FK, et al. Applicability of albumin-bilirubin-based Japan integrated staging score in hepatitis B-associated hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2016, 31(10): 1766-1772. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.13339. |
| [40] |
CHAN AW, KUMADA T, TOYODA H, et al. Integration of albumin-bilirubin (ALBI) score into Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) system for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2016, 31(7): 1300-1306. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.13291. |
| [41] |
SHAO YY, LIU TH, LEE YH, et al. Modified CLIP with objective liver reserve assessment retains prognosis prediction for patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2016, 31(7): 1336-1341. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.13312. |
| [42] |
LAU WY, LAI ECH. Loco-regional intervention for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Intervent Med, 2019, 2(2): 43-46. DOI: 10.1016/jJimed.2019.07.001. |
| [43] |
WANG JC, LAO XM. Research progress on HBV DNA and liver function changes after TACE of HBV-induced hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. New Chin Med, 2016, 47(5): 290-294. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9802.2016.05.003. |
| [44] |
LENCIONI R, de BAERE T, SOULEN MC, et al. Lipiodol transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review of efficacy and safety data[J]. Hepatology, 2016, 64(1): 106-116. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28453. |
| [45] |
ZHANG CJ, HE SC, TENG GJ, et al. Analysis of related factors affecting liver function for hepatocellular carcinoma after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization[J]. J Southe Univ (Med Sci Edi), 2013, 32(1): 18-22. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6264.2013.01.005. |
| [46] |
ARIZUMI T, MINAMI T, CHISHINA H, et al. Time to transcatheter arterial chemoembolization refractoriness in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in Kinki Criteria Stages B1 and B2[J]. Dig Dis, 2017, 35(6): 589-597. DOI: 10.1159/000480208. |
| [47] |
PECK-RADOSAVLJEVIC M, RAOUL JL, LEE HC, et al. OPTIMIS: An international observational study to assess the use of sorafenib after transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) [J]. J Clin Oncol, 2014, 32(15): TPS4155. DOI: 10.1200/jco.2014.32.15_suppl.tps4155. |
| [48] |
Liver Failure and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association; Severe Liver Disease and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guideline for diagnosis and treatment of liver failure(2018)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(1): 38-44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.01.007. |
| [49] |
HERNAEZ R, SOLÀ E, MOREAU R, et al. Acute-on-chronic liver failure: An update[J]. Gut, 2017, 66(3): 541-553. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-312670. |
| [50] |
HSIN IF, HSU CY, HUANG HC, et al. Liver failure after transarterial chemoembolization for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and ascites: Incidence, risk factors, and prognostic prediction[J]. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2011, 45(6): 556-562. DOI: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e318210ff17. |
| [51] |
CHAN AW, CHAN RC, WONG GL, et al. New simple prognostic score for primary biliary cirrhosis: Albumin-bilirubin score[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015, 30(9): 1391-1396. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.12938. |
| [52] |
LIU PH, HSU CY, HSIA CY, et al. ALBI and PALBI grade predict survival for HCC across treatment modalities and BCLC stages in the MELD Era[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2017, 32(4): 879-886. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.13608. |



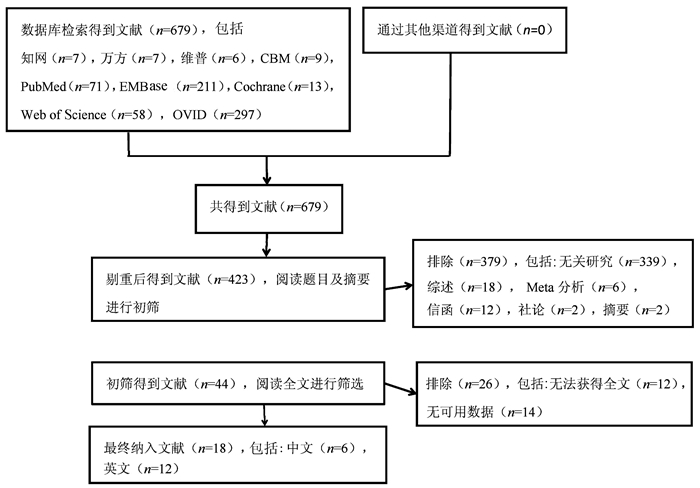




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: