| [1] |
|
| [2] |
Liver Failure and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association; Severe Liver Disease and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guideline for diagnosis and treatment of liver failure[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(1): 38-44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.01.007. |
| [3] |
SARIN SK, CHOUDHURY A. Acute-on-chronic liver failure: Terminology, mechanisms and management[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2016, 13(3): 131-149. DOI: 10.1038/nrgastro.2015.219. |
| [4] |
REEVES HM, WINTERS JL. The mechanisms of action of plasma exchange[J]. Br J Haematol, 2014, 164(3): 342-351. DOI: 10.1111/bjh.12629. |
| [5] |
YAO J, LI S, ZHOU L, et al. Therapeutic effect of double plasma molecular adsorption system and sequential half-dose plasma exchange in patients with HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. J Clin Apher, 2019, 34(4): 392-398. DOI: 10.1002/jca.21690. |
| [6] |
KAMATH PS, WIESNER RH, MALINCHOC M, et al. A model to predict survival in patients with end-stage liver disease[J]. Hepatology, 2001, 33(2): 464-470. DOI: 10.1053/jhep.2001.22172. |
| [7] |
BIGGINS SW, KIM WR, TERRAULT NA, et al. Evidence-based incorporation of serum sodium concentration into MELD[J]. Gastroenterology, 2006, 130(6): 1652-1660. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.02.010. |
| [8] |
ZOULIM F, LOCAMINI S. Hepatitis B virus resistance to nucleos(t)ide analogues[J]. Gastroenterology, 2009, 137: 1593-1608. e1-2. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.08.063. |
| [9] |
LING Q, XU X, WEI Q, et al. Downgrading MELD improves the outcomes after liver transplantation in patients with acute-on-chronic hepatitis B liver failure[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(1): e30322. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030322. |
| [10] |
YU JW, SUN LJ, ZHAO YH, et al. Prediction value of model for end-stage liver disease scoring system on prognosis in patients with acute-on-chronic hepatitis B liver failure after plasma exchange and lamivudine treatment[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2008, 23(8 Pt 1): 1242-1249. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2008.05484.x. |
| [11] |
CHEN JJ, HUANG JR, YANG Q, et al. Plasma exchange-centered artificial liver support system in hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure: A nationwide prospective multicenter study in China[J]. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int, 2016, 15(3): 275-281. DOI: 10.1016/s1499-3872(16)60084-x. |
| [12] |
XU X, LIU X, LING Q, et al. Artificial liver support system combined with liver transplantation in the treatment of patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(3): e58738. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058738. |
| [13] |
WIESNER R, EDWARDS E, FREEMAN R, et al. Model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) and allocation of donor livers[J]. Gastroenterology, 2003, 124(1): 91-96. DOI: 10.1053/gast.2003.50016. |
| [14] |
ROUILLARD SS, BASS NM, ROBERTS JP, et al. Severe hyperbilirubinemia after creation of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts: Natural history and predictors of outcome[J]. Ann Intern Med, 1998, 128(5): 374-377. DOI: 10.7326/0003-4819-128-5-199803010-00006. |
| [15] |
INTAGLIATA NM, DAVIS J, CALDWELL SH. Coagulation pathways, hemostasis, and thrombosis in liver failure[J]. Semin Respir Crit Care Med, 2018, 39(5): 598-608. DOI: 10.1055/s-0038-1673658. |
| [16] |
HARUKI K, SHIBA H, SAITO N, et al. Risk stratification using a novel liver functional reserve score of combination prothrombin time-international normalized ratio to albumin ratio and albumin in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Surgery, 2018, 164(3): 404-410. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2018.02.022. |
| [17] |
HU XP, GAO J. International normalized ratio and Model for End-stage Liver Disease score predict short-term outcome in cirrhotic patients after the resolution of hepatic encephalopathy[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2019, 25(26): 3426-3437. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i26.3426. |
| [18] |
O'LEARY JG, GREENBERG CS, PATTON HM, et al. AGA clinical practice update: Coagulation in cirrhosis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2019, 157(1): 34-43. e1. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.03.070. |
| [19] |
XIA Q, DAI X, ZHANG Y, et al. A modified MELD model for Chinese pre-ACLF and ACLF patients and it reveals poor prognosis in pre-ACLF patients[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(6): e64379. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064379. |
| [20] |
LU XC, LU D, PAN Y. Clinical significance of platelet parameters in diagnosis and treatment of acute leukemia[J]. Int J Lab Med, 2006, 27(10): 870-871, 873. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4130.2006.10.003. |
| [21] |
PECK-RADOSAVLJEVIC M, WICHLAS M, ZACHERL J, et al. Thrombopoietin induces rapid resolution of thrombocytopenia after orthotopic liver transplantation through increased platelet production[J]. Blood, 2000, 95(3): 795-801. DOI: 10.1182/blood.V95.3.795.003k25_795_801 |
| [22] |
HITCHCOCK IS, KAUSHANSKY K. Thrombopoietin from beginning to end[J]. Br J Haematol, 2014, 165(2): 259-268. DOI: 10.1111/bjh.12772. |
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
SAKAI K, IWAO T, OHO K, et al. Propranolol ameliorates thrombocytopenia in patients with cirrhosis[J]. J Gastroenterol, 2002, 37(2): 112-118. DOI: 10.1007/s005350200005. |
| [25] |
MA Z, WU Y. Current status of liver failure treatment[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2016, 32(9) : 1668-1672. DOI: 10.3969/ j.issn.1001- 5256.2016.09.007.
马臻, 乌云. 肝衰竭的治疗现状[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2016, 32(9): 1668- 1672. DOI: 10.3969/ j.issn.1001- 5256.2016.09.007.
|
| [26] |
XU SS, WEI XH, LIN W, et al. Clinical significance of platelet count and its dynamic change in patients with acute- on-chronic liver failure[J]. J CIin Hepatol, 2018, 34(4): 810-813. DOI: 10. 3969/ j. issn. 1001- 5256. 2018. 04. 023.
|
| [27] |
SHI XX, ZHANG YQ, ZHU P, et al. Prognostic risk factors in patients with acute- on- chronic hepatitis B liver failure[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2016, 32(4): 700-705. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256. 2016. 04. 018.
|
| [28] |
LI WY, ZHANG MX, QI TT, et al. The potential factors contributing to thrombocytopenia in acute-on-chronic liver failure patients[J]. Chin Hepatol, 2015, 20(6): 457-461. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1704.2015.06.009 |
| [29] |
LESURTEL M, GRAF R, ALEIL B, et al. Platelet-derived serotonin mediates liver regeneration[J]. Science, 2006, 312(5770): 104-107. DOI: 10.1126/science.1123842. |



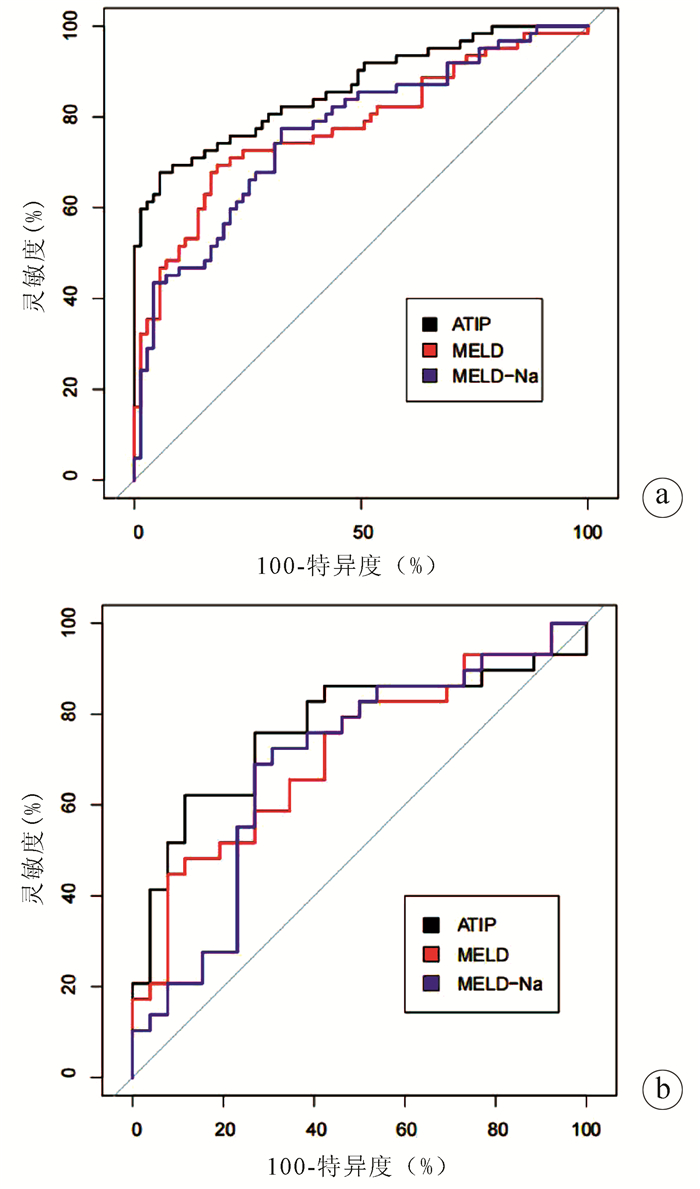




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: