| [1] |
SIEGEL RL, MILLER KD, JEMAL A. Cancer statistics, 2020[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2020, 70(1): 7-30. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21590. |
| [2] |
National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China. Diagnosis, management, and treatment of pancreatic adenocarcinoma (V2018)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(2): 281-293. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.02.009. |
| [3] |
MURAKAMI M, KAMIMURA D, HIRANO T. Pleiotropy and specificity: Insights from the interleukin 6 family of cytokines[J]. Immunity, 2019, 50(4): 812-831. DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.03.027. |
| [4] |
JONES SA, JENKINS BJ. Recent insights into targeting the IL-6 cytokine family in inflammatory diseases and cancer[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2018, 18(12): 773-789. DOI: 10.1038/s41577-018-0066-7. |
| [5] |
GULLUOGLU S, SAHIN M, TUYSUZ EC, et al. Leukemia inhibitory factor promotes aggressiveness of chordoma[J]. Oncol Res, 2017, 25(7): 1177-1188. DOI: 10.3727/096504017X14874349473815. |
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
XIA Y, ZHANG YL, YU C, et al. YAP/TEAD co-activator regulated pluripotency and chemoresistance in ovarian cancer initiated cells[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(11): e109575. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109575. |
| [8] |
MCLEAN K, TAN L, BOLLAND DE, et al. Leukemia inhibitory factor functions in parallel with interleukin-6 to promote ovarian cancer growth[J]. Oncogene, 2019, 38(9): 1576-1584. DOI: 10.1038/s41388-018-0523-6. |
| [9] |
PICCINNI MP, SCALETTI C, VULTAGGIO A, et al. Defective production of LIF, M-CSF and Th2-type cytokines by T cells at fetomaternal interface is associated with pregnancy loss[J]. J Reprod Immunol, 2001, 52(1-2): 35-43. DOI: 10.1016/s0165-0378(01)00111-5. |
| [10] |
METCALFE SM, WATSON TJ, SHUREY S, et al. Leukemia inhibitory factor is linked to regulatory transplantation tolerance[J]. Transplantation, 2005, 79(6): 726-730. DOI: 10.1097/01.tp.0000149324.42994.38. |
| [11] |
SILVER JS, HUNTER CA. gp130 at the nexus of inflammation, autoimmunity, and cancer[J]. J Leukoc Biol, 2010, 88(6): 1145-1156. DOI: 10.1189/jlb.0410217. |
| [12] |
LIGORIO M, SIL S, MALAGON-LOPEZ J, et al. Stromal microenvironment shapes the intratumoral architecture of pancreatic cancer[J]. Cell, 2019, 178(1): 160-175. e27. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.05.012. |
| [13] |
PASCUAL-GARCíA M, BONFILL-TEIXIDOR E, PLANAS-RIGOL E, et al. LIF regulates CXCL9 in tumor-associated macrophages and prevents CD8 + T cell tumor-infiltration impairing anti-PD1 therapy[J]. Nat Commun, 2019, 10(1): 2416. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-10369-9. |
| [14] |
GAO W, THOMPSON L, ZHOU Q, et al. Treg versus Th17 lymphocyte lineages are cross-regulated by LIF versus IL-6[J]. Cell Cycle, 2009, 8(9): 1444-1450. DOI: 10.4161/cc.8.9.8348. |
| [15] |
MOHAN V, DAS A, SAGI I. Emerging roles of ECM remodeling processes in cancer[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2020, 62: 192-200. DOI: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.09.004. |
| [16] |
GIUSSANI M, TRIULZI T, SOZZI G, et al. Tumor extracellular matrix remodeling: New perspectives as a circulating tool in the diagnosis and prognosis of solid tumors[J]. Cells, 2019, 8(2): 81. DOI: 10.3390/cells8020081. |
| [17] |
ALBRENGUES J, BOURGET I, PONS C, et al. LIF mediates proinvasive activation of stromal fibroblasts in cancer[J]. Cell Rep, 2014, 7(5): 1664-1678. DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.04.036. |
| [18] |
SHI Y, GAO W, LYTLE NK, et al. Targeting LIF-mediated paracrine interaction for pancreatic cancer therapy and monitoring[J]. Nature, 2019, 569(7754): 131-135. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-1130-6. |
| [19] |
AIELLO NM, KANG Y. Context-dependent EMT programs in cancer metastasis[J]. J Exp Med, 2019, 216(5): 1016-1026. DOI: 10.1084/jem.20181827. |
| [20] |
THOMAS SK, LEE J, BEATTY GL. Paracrine and cell autonomous signalling in pancreatic cancer progression and metastasis[J]. EBioMedicine, 2020, 53: 102662. DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102662. |
| [21] |
XING SN, CHEN W, YU HY. Research status of mesenchymal stem cells on tumorigenesis and development[J]. Clin J Med Offic, 2020, 48(8): 980-982. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2020.08.45. |
| [22] |
BAPAT AA, HOSTETTER G, von HOFF DD, et al. Perineural invasion and associated pain in pancreatic cancer[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2011, 11(10): 695-707. DOI: 10.1038/nrc3131. |
| [23] |
LI X, WANG Z, MA Q, et al. Sonic hedgehog paracrine signaling activates stromal cells to promote perineural invasion in pancreatic cancer[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2014, 20(16): 4326-4338. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-3426. |
| [24] |
BRESSY C, LAC S, NIGRI J, et al. LIF drives neural remodeling in pancreatic cancer and offers a new candidate biomarker[J]. Cancer Res, 2018, 78(4): 909-921. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-2790. |
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
WANG MT, FER N, GALEAS J, et al. Blockade of leukemia inhibitory factor as a therapeutic approach to KRAS driven pancreatic cancer[J]. Nat Commun, 2019, 10(1): 3055. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-11044-9. |
| [27] |
CHANG JH, JIANG Y, PILLARISETTY VG. Role of immune cells in pancreatic cancer from bench to clinical application: An updated review[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2016, 95(49): e5541. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000005541. |
| [28] |
BLANDO J, SHARMA A, HIGA MG, et al. Comparison of immune infiltrates in melanoma and pancreatic cancer highlights VISTA as a potential target in pancreatic cancer[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2019, 116(5): 1692-1697. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1811067116. |
| [29] |
YU H, YUE X, ZHAO Y, et al. LIF negatively regulates tumour-suppressor p53 through Stat3/ID1/MDM2 in colorectal cancers[J]. Nat Commun, 2014, 5: 5218. DOI: 10.1038/ncomms6218. |
| [30] |
LIU SC, TSANG NM, CHIANG WC, et al. Leukemia inhibitory factor promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression and radioresistance[J]. J Clin Invest, 2013, 123(12): 5269-5283. DOI: 10.1172/JCI63428. |
| [31] |
ARORA GK, GUPTA A, NARAYANAN S, et al. Cachexia-associated adipose loss induced by tumor-secreted leukemia inhibitory factor is counterbalanced by decreased leptin[J]. JCI Insight, 2018, 3(14): e121221. DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.121221. |
| [32] |
SETO DN, KANDARIAN SC, JACKMAN RW. A key role for leukemia inhibitory factor in C26 cancer cachexia[J]. J Biol Chem, 2015, 290(32): 19976-19986. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.638411. |
| [33] |
KANDARIAN SC, NOSACKA RL, DELITTO AE, et al. Tumour-derived leukaemia inhibitory factor is a major driver of cancer cachexia and morbidity in C26 tumour-bearing mice[J]. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle, 2018, 9(6): 1109-1120. DOI: 10.1002/jcsm.12346. |
| [34] |
HUNTER SA, MCINTOSH BJ, SHI Y, et al. An engineered ligand trap inhibits leukemia inhibitory factor as pancreatic cancer treatment strategy[J]. Commun Biol, 2021, 4(1): 452. DOI: 10.1038/s42003-021-01928-2. |
| [35] |
HURWITZ H, van CUTSEM E, BENDELL J, et al. Ruxolitinib+ capecitabine in advanced/metastatic pancreatic cancer after disease progression/intolerance to first-line therapy: JANUS 1 and 2 randomized phase Ⅲ studies[J]. Invest New Drugs, 2018, 36(4): 683-695. DOI: 10.1007/s10637-018-0580-2. |



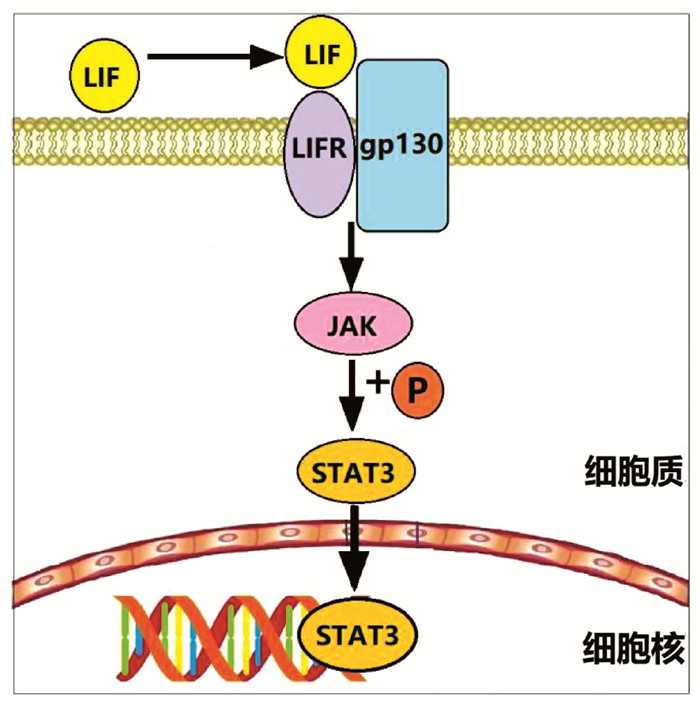




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: