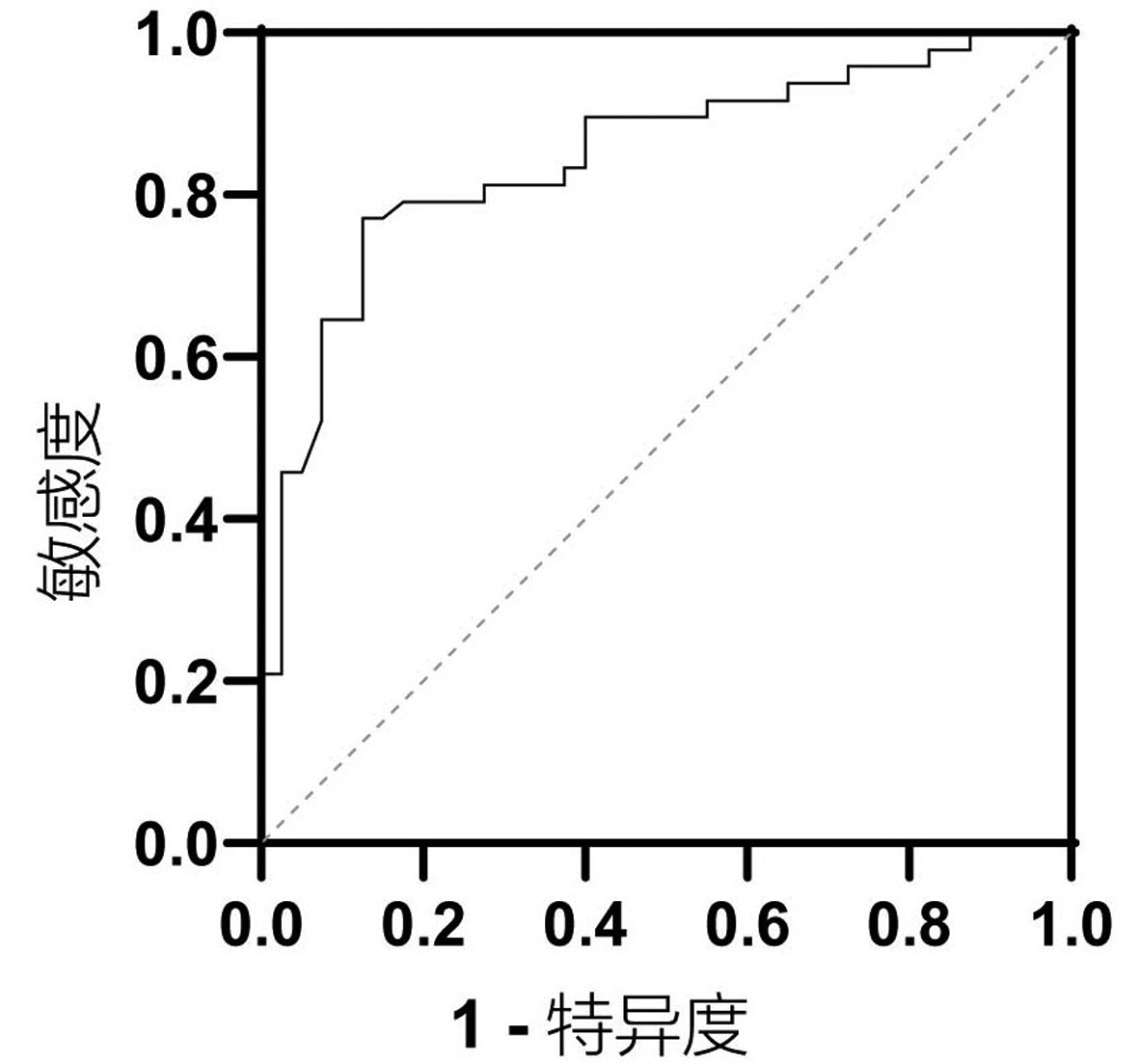
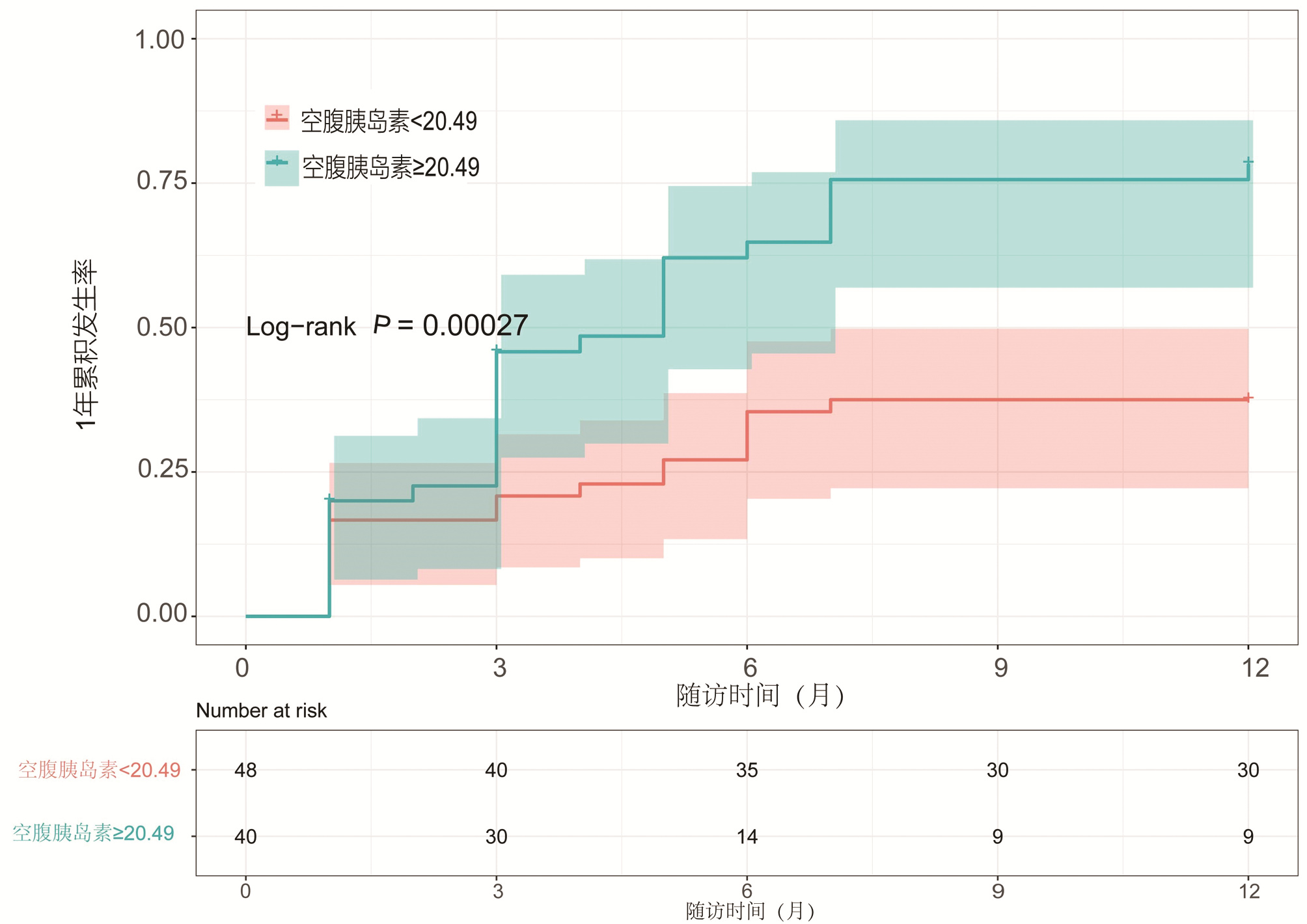
| [1] |
Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines on the management of ascites and complications in cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2017, 33(10): 1847-1863. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2017.10.003. |
| [2] |
PIANO S, TONON M, ANGELI P. Changes in the epidemiology and management of bacterial infections in cirrhosis[J]. Clin Mol Hepatol, 2021, 27(3): 437-445. DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2020.0329. |
| [3] |
PIANO S, ANGELI P. Bacterial infections in cirrhosis as a cause or consequence of decompensation?[J]. Clin Liver Dis, 2021, 25(2): 357-372. DOI: 10.1016/j.cld.2021.01.006. |
| [4] |
SCHULTALBERS M, TERGAST TL, SIMON N, et al. Frequency, characteristics and impact of multiple consecutive nosocomial infections in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis and ascites[J]. United European Gastroenterol J, 2020, 8(5): 567-576. DOI: 10.1177/2050640620913732. |
| [5] |
CRISMALE JF, FRIEDMAN SL. Acute liver injury and decompensated cirrhosis[J]. Med Clin North Am, 2020, 104(4): 647-662. DOI: 10.1016/j.mcna.2020.02.010. |
| [6] |
FERNÁNDEZ J, PRADO V, TREBICKA J, et al. Multidrug-resistant bacterial infections in patients with decompensated cirrhosis and with acute-on-chronic liver failure in Europe[J]. J Hepatol, 2019, 70(3): 398-411. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.10.027. |
| [7] |
ELKRIEF L, RAUTOU PE, SARIN S, et al. Diabetes mellitus in patients with cirrhosis: clinical implications and management[J]. Liver Int, 2016, 36(7): 936-948. DOI: 10.1111/liv.13115. |
| [8] |
TANASE DM, GOSAV EM, COSTEA CF, et al. The intricate relationship between type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), insulin resistance (IR), and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)[J]. J Diabetes Res, 2020, 2020: 3920196. DOI: 10.1155/2020/3920196. |
| [9] |
ZUWALA-JAGIELLO J, PAZGAN-SIMON M, SIMON K, et al. Serum endocan level in diabetes mellitus of patients with cirrhosis and risk of subsequent development of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis[J]. J Physiol Pharmacol, 2019, 70(3): 399-405. DOI: 10.26402/jpp.2019.3.06. |
| [10] |
COMAN LI, COMAN OA, BǍDǍRǍU IA, et al. Association between liver cirrhosis and diabetes mellitus: A review on hepatic outcomes[J]. J Clin Med, 2021, 10(2): 262. DOI: 10.3390/jcm10020262. |
| [11] |
LABENZ C, NAGEL M, KREMER WM, et al. Association between diabetes mellitus and hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2020, 52(3): 527-536. DOI: 10.1111/apt.15915. |
| [12] |
TAN ZJ, ZHAO J, LIU WX, et al. Analysis of pathogenic bacteris and factors affecting spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in patients with cirrhosis ascites[J]. Chin J Nosocomiol, 2019, 29(19): 2953-2956. DOI: 10.11816/cn.ci.2019-183023. |
| [13] |
LI YT, HUANG JR, PENG ML. Current status and prospects of spontaneous peritonitis in patients with cirrhosis[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2020, 2020: 3743962. DOI: 10.1155/2020/3743962. |
| [14] |
LEE WG, WELLS CI, MCCALL JL, et al. Prevalence of diabetes in liver cirrhosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Diabetes Metab Res Rev, 2019, 35(6): e3157. DOI: 10.1002/dmrr.3157. |
| [15] |
TERGAST TL, LASER H, GERBEL S, et al. Association between type 2 diabetes mellitus, HbA1c and the risk for spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis and ascites[J]. Clin Transl Gastroenterol, 2018, 9(9): 189. DOI: 10.1038/s41424-018-0053-0. |
| [16] |
ABU-FREHA N, MICHAEL T, POUPKO L, et al. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis among cirrhotic patients: Prevalence, clinical characteristics, and outcomes[J]. J Clin Med, 2021, 11(1): 227. DOI: 10.3390/jcm11010227. |
| [17] |
JIANG P, DOU RC, CUI ZJ, et al. Value of albumin-bilirubin score combined with neutrophil count and procalcitonin in ascites in predicting spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in patients with cirrhotic ascites[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37(9): 2097-2101. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.09.019. |
| [18] |
LIU H, ZHU P, NIE C, et al. The value of ascitic neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in decompensated liver cirrhosis with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis[J]. J Clin Lab Anal, 2020, 34(6): e23247. DOI: 10.1002/jcla.23247. |
| [19] |
ROSENBLATT R, ATTEBERRY P, TAFESH Z, et al. Uncontrolled diabetes mellitus increases risk of infection in patients with advanced cirrhosis[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2021, 53(4): 445-451. DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2020.10.022. |
| [20] |
TIAN CY, HU H, ZHANG GY, et al. Influence of glucose metabolism disorder on complications associated with liver cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37(5): 1197-1200. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.05.046. |



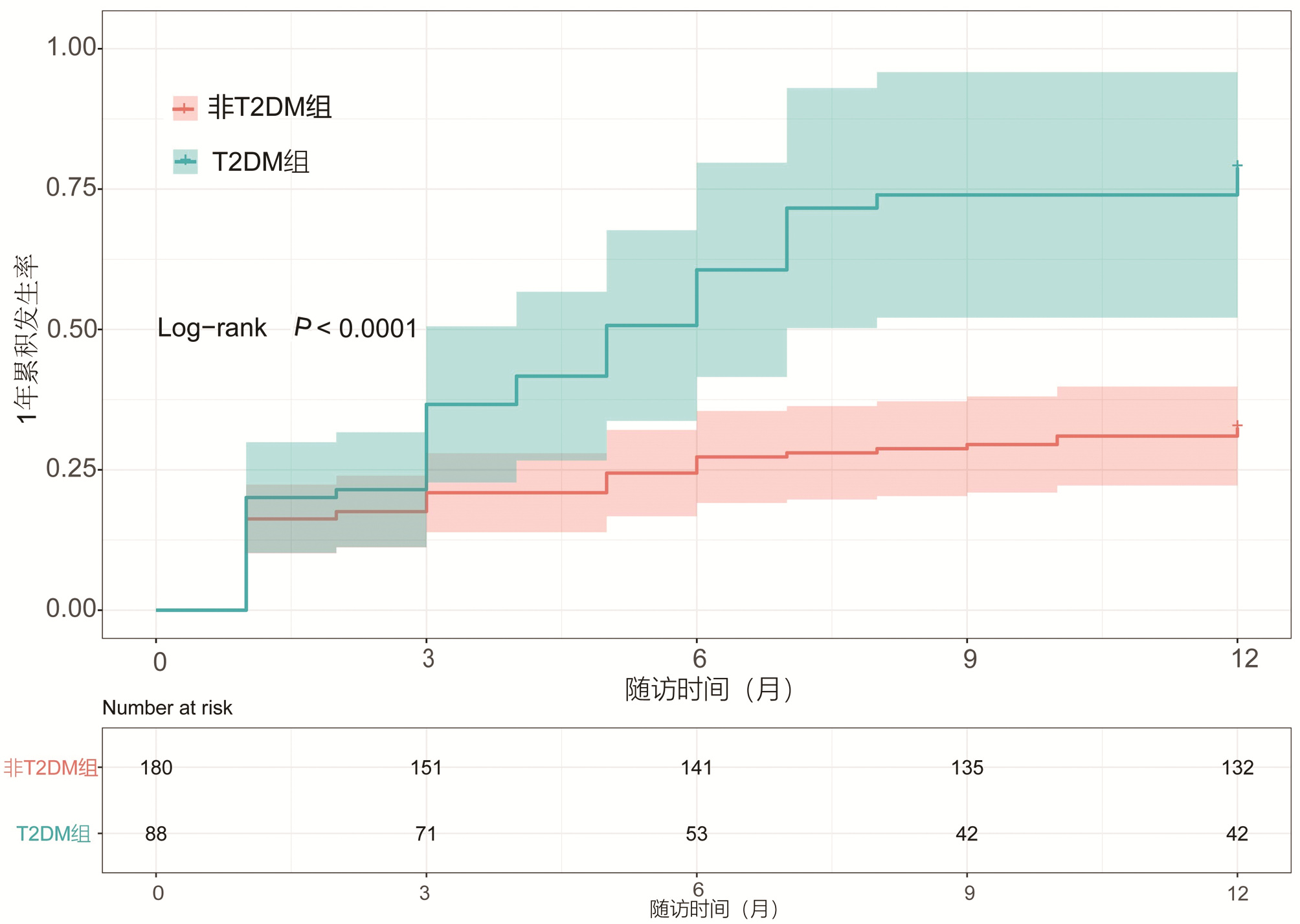




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: