| [1] |
REGA D, AIKO M, PEÑARANDA N, et al. Patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy show altered thermal sensitivity and autonomic function[J]. J Clin Med, 2021, 10(2): 239. DOI: 10.3390/jcm10020239. |
| [2] |
MONTAGNESE S, BAJAJ JS. Impact of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis on quality-of-life issues[J]. Drugs, 2019, 79(Suppl 1): 11-16. DOI: 10.1007/s40265-018-1019-y. |
| [3] |
YANG X, LIU W, DANG P, et al. Decreased brain noradrenaline in minimal hepatic encephalopathy is associated with cognitive impairment in rats[J]. Brain Res, 2022, 1793: 148041. DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2022.148041. |
| [4] |
CÓRDOBA J, MÍNGUEZ B. Hepatic encephalopathy[J]. Semin Liver Dis, 2008, 28(1): 70-80. DOI: 10.1055/s-2008-1040322. |
| [5] |
GU TM, ZHANG Y, JJIANG YP, et al. Efficacy of acarbose-linked ornithine aspartate in hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients[J]. Chin J Mod Appl Pharm, 2018, 35(10): 1538-1542. DOI: 10.13748/j.cnki.issn1007-7693.2018.10.023. |
| [6] |
FICHET J, MERCIER E, GENÉE O, et al. Prognosis and 1-year mortality of intensive care unit patients with severe hepatic encephalopathy[J]. J Crit Care, 2009, 24(3): 364-370. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2009.01.008. |
| [7] |
PESSIDJO DJOMATCHO L, KOWO MP, NDAM AN, et al. Normalisation of the psychometric encephalopathy score within the Cameroonian population[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2021, 21(1): 287. DOI: 10.1186/s12876-021-01858-7. |
| [8] |
HA ZY, MATHEW S, YEONG KY. Butyrylcholinesterase: a multifaceted pharmacological target and tool[J]. Curr Protein Pept Sci, 2020, 21(1): 99-109. DOI: 10.2174/1389203720666191107094949. |
| [9] |
TURECKY L, KUPCOVA V, DURFINOVA M, et al. Serum butyrylcholinesterase activities in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Comparison with liver proteosynthetic function and liver fibrosis[J]. Bratisl Lek Listy, 2021, 122(10): 689-694. DOI: 10.4149/BLL_2021_110. |
| [10] |
PAREKH PJ, BALART LA. Ammonia and its role in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy[J]. Clin Liver Dis, 2015, 19(3): 529-537. DOI: 10.1016/j.cld.2015.05.002. |
| [11] |
ZIMMERMANN M, REICHERT AS. Rapid metabolic and bioenergetic adaptations of astrocytes under hyperammonemia-a novel perspective on hepatic encephalopathy[J]. Biol Chem, 2021, 402(9): 1103-1113. DOI: 10.1515/hsz-2021-0172. |
| [12] |
PALOMERO-GALLAGHER N, ZILLES K. Neurotransmitter receptor alterations in hepatic encephalopathy: a review[J]. Arch Biochem Biophys, 2013, 536(2): 109-121. DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2013.02.010. |
| [13] |
FIATI KENSTON SS, SONG X, LI Z, et al. Mechanistic insight, diagnosis, and treatment of ammonia-induced hepatic encephalopathy[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 34(1): 31-39. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.14408. |
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Medical Association, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Consensus on diagnosis and treatment of hepatic encephalopathy in China (Chongqing, 2013)[J/CD]. Chin J Front Med Sci (Electronic Version), 2014, 6(2): 81-93.
中华医学会消化病学分会, 中华医学会肝病学分会. 中国肝性脑病诊治共识意见(2013年, 重庆)[J/CD]. 中国医学前沿杂志(电子版), 2014, 6(2): 81-93.
|
| [16] |
WANG JY, ZHANG NP, CHI BR, et al. Prevalence of minimal hepatic encephalopathy and quality of life evaluations in hospitalized cirrhotic patients in China[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2013, 19(30): 4984-4991. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i30.4984. |
| [17] |
HANSEN M, KJÆRGAARD K, ERIKSEN LL, et al. Psychometric methods for diagnosing and monitoring minimal hepatic encephalopathy -current validation level and practical use[J]. Metab Brain Dis, 2022, 37(3): 589-605. DOI: 10.1007/s11011-022-00913-w. |
| [18] |
BAJAJ JS, WADE JB, SANYAL AJ. Spectrum of neurocognitive impairment in cirrhosis: Implications for the assessment of hepatic encephalopathy[J]. Hepatology, 2009, 50(6): 2014-2021. DOI: 10.1002/hep.23216. |
| [19] |
HADJIHAMBI A, ARIAS N, SHEIKH M, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy: a critical current review[J]. Hepatol Int, 2018, 12(Suppl 1): 135-147. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-017-9812-3. |
| [20] |
SORIANO G, BAJAJ JS. Grading the range of hepatic encephalopathy from overt to covert: Animals to the rescue![J]. Hepatology, 2017, 66(1): 10-12. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29186. |
| [21] |
ELSAID MI, RUSTGI VK, LOO N, et al. The burden associated with thrombocytopenia and platelet transfusions among patients with chronic liver disease[J]. J Med Econ, 2020, 23(4): 378-385. DOI: 10.1080/13696998.2019.1699563. |
| [22] |
TAN L, MENG Y, ZENG T, et al. Clinical diagnostic significance of prealbumin, cholinesterase and retinol binding protein in liver cirrhosis combined with encephalopathy[J]. Br J Biomed Sci, 2019, 76(1): 24-28. DOI: 10.1080/09674845.2018.1523673. |
| [23] |
AMPUERO J, MONTOLIÚ C, SIMÓN-TALERO M, et al. Minimal hepatic encephalopathy identifies patients at risk of faster cirrhosis progression[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 33(3): 718-725. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.13917. |
| [24] |
RIGGIO O, AMODIO P, FARCOMENI A, et al. A model for predicting development of overt hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015, 13(7): 1346-1352. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2014.12.025. |
| [25] |
MONTAGNESE S, RUSSO FP, AMODIO P, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy 2018: A clinical practice guideline by the Italian Association for the Study of the Liver (AISF)[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2019, 51(2): 190-205. DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2018.11.035. |
| [26] |
GAO YY, ZHANG X, LI FH, et al. Measurement of glycosylated albumin and its application value in liver cirrhosis patients with different Child-Pugh classes[J]. Clin Hepatal, 2022, 38(2): 347-351. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.02.018. |
| [27] |
DJIAMBOU-NGANJEU H. Hepatic encephalopathy in liver cirrhosis[J]. J Transl Int Med, 2017, 5(1): 64-67. DOI: 10.1515/jtim-2017-0013. |



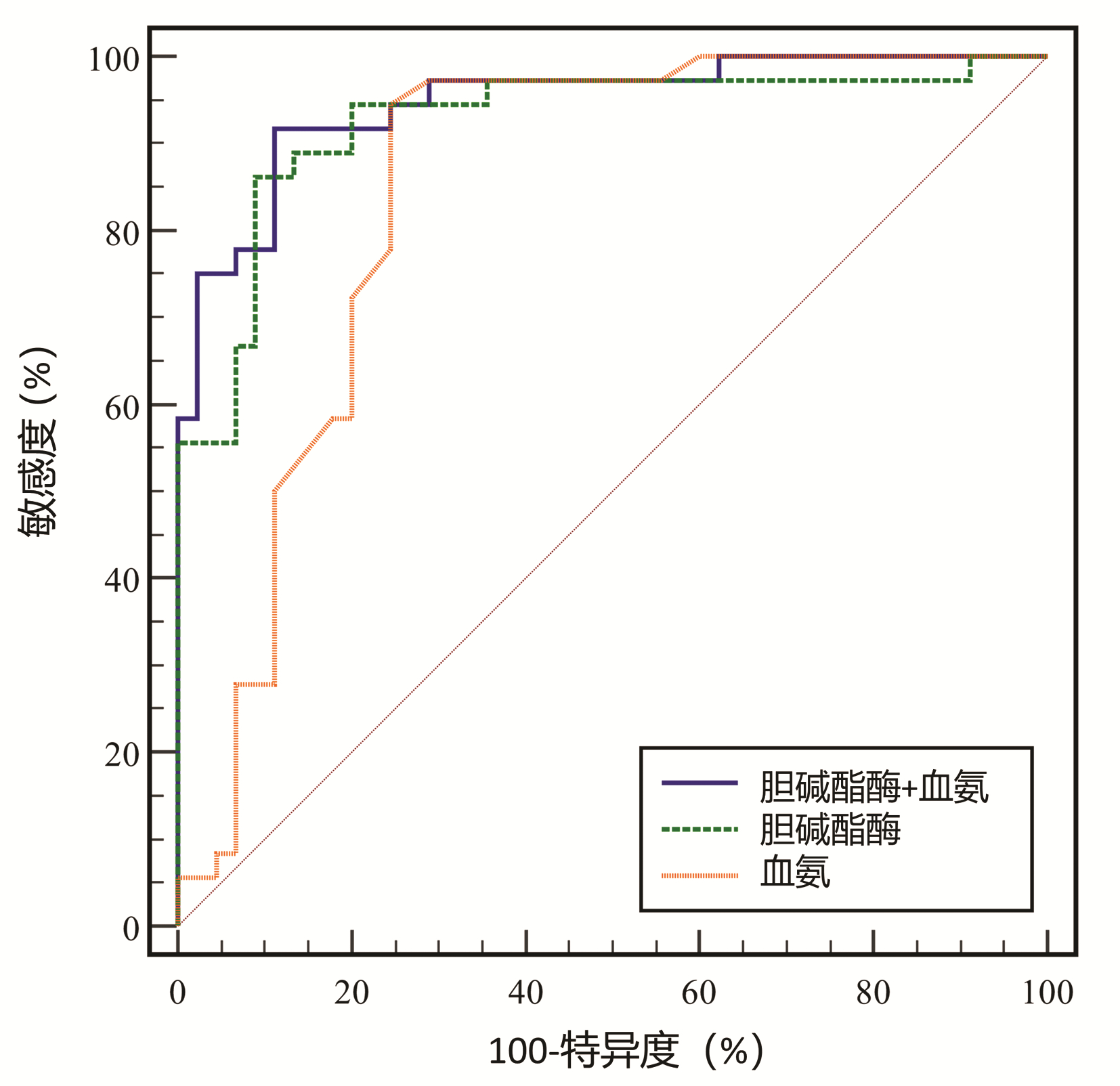




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: